This time I will bring you a detailed explanation of webpack style loading. What are the precautions for webpack style loading? . Here is a practical case, let’s take a look.
You need to use css-loader and style-loader to load css. css-loader processes @import and url into regular ES6 imports. If @import points to an external resource, css-loader will skip it. Only internal resources will be processed. After css-loader processing, style-loader will inject the output css into the packaging file. CSS defaults to inline mode and implements the HMR interface. But inline is not suitable for production environments (all output is on the page). You will also need to generate a separate css file using the extracttextplugin, but let’s do it step by step first.
1. Style packaging
1. Install css-loader, style-loader
npm install css-loader style-loader --save-dev
2. Modify webpack.config.js
Add a The regular expression of level sub-node
module:{
rules:[{
test:/\.css$/,
use: ['style-loader', 'css-loader'],
}]
},
test will match the .css file. The order of execution in use is from right to left. The execution of the loader is continuous, like a pipeline, first to css-loader and then to style-loader. loaders: ['style-loader', 'css-loader'] can be understood as: styleloader(cssloader(input)).
3. Add style
app/mian.css
body {
background: cornsilk;
}
Then introduce
import './main.css';
in index.js and then run npm start, at http: Open
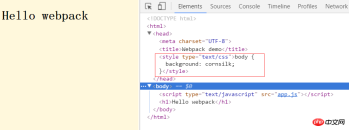

Update method.
2. Load less Let’s take a look at how to load less. First install less-loadernpm install less less-loader --save-devand then modify the
configuration file:
module:{
rules:[{
test: /\.less$/,
use: ['style-loader', 'css-loader', 'less-loader'], }]
}, Then create a less file. less.less
@base: #f938ab;
.box-shadow(@style, @c) when (iscolor(@c)) {
-webkit-box-shadow: @style @c;
box-shadow: @style @c;
}.box-shadow(@style, @alpha: 50%) when (isnumber(@alpha)) {
.box-shadow(@style, rgba(0, 0, 0, @alpha));}.box {
color: saturate(@base, 5%);
border-color: lighten(@base, 30%);
p { .box-shadow(0 0 5px, 30%) }}
body {
background: cornsilk;
}Modify index.js
import './less.less';
import component from './component';var ele=document.createElement("p");
ele.innerHTML="this is an box";
ele.className="box";
document.body.appendChild(ele);
let demoComponent=component();
document.body.appendChild(demoComponent); to get the effect:
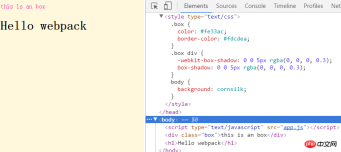
module:{
rules:[{
test:/\.css$/,
use: ['style-loader', {
loader: 'css-loader',
options: { modules: true,//让css-loader支持Css Modules。
},
},], Then define a new style (main.css):
body {
background: cornsilk;
}
.redButton { background: red;color:yellow;} Add a style to the component, first introduce main.css .
import styles from './main.css';export default function () { var element = document.createElement('h1');
element.className=styles.redButton;
element.innerHTML = 'Hello webpack'; return element;
}At this time we see that the interface has changed.

.redButton {
background:rebeccapurple;color:snow;
}It also has a .redbutton class (but the effect is Purple), then create a p element in index.js and add the redbutton style to it.
import './main.css';import styles from './other.css';import component from './component';var ele=document.createElement("p");
ele.innerHTML="this is an other button";ele.className=styles.redButton;document.body.appendChild(ele);
let demoComponent=component();
document.body.appendChild(demoComponent);Let’s see the effect again

上面这个图说明了两问题,一个是我们在index.js中引入了2个样式文件,在index页面就输出了两个style,这让人有点不爽,但我们后面再解决。另外一个就是虽然两个样式文件中都有redButton这个类,但是这两者还是保持独立的。这样就避免了命名空间的相互干扰。如果你这个时候直接赋值
element.className="redButton";
这样是获取不到样式的。直接对元素的样式默认是全局的。
全局样式
如果想让某个样式是全局的。可以通过:global来包住。
other.css
:global(.redButton) {
background:rebeccapurple;color:snow;
border: 1px solid red;
}
main.css
:global(.redButton) {
background: red;color:yellow;
}
这个时候redbutton这两个样式就会合并。需要直接通过样式名来获取。
element.className="redButton";

组合样式
我们再修改other.css,创建一个shadowButton 样式,内部通过composes组合redbutton类。
.redButton {
background:rebeccapurple;color:snow;
border: 1px solid red;
}
.shadowButton{
composes:redButton;
box-shadow: 0 0 15px black;
}
修改index.js:
var ele=document.createElement("p");
ele.innerHTML="this is an shadowButton button";console.log(styles);
ele.className=styles.shadowButton;
document.body.appendChild(ele);
看一下是什么效果:

日志打印出来的是styles对象,它包含了两个类名。可以看见shadowButton是由两个类名组合而成的。p的class和下面的对应。
四、输出样式文件
css嵌在页面里面不是我们想要的,我们希望能够分离,公共的部分能够分开。extracttextplugin 可以将多个css合成一个文件,但是它不支持HMR(直接注释掉hotOnly:true)。用在生产环境挺好的
npm install extract-text-webpack-plugin --save-dev
先安装extracttextplugin这个插件,然后再webpack.config.js中进行配置:
const ExtractTextPlugin = require('extract-text-webpack-plugin');
const extractTxtplugin = new ExtractTextPlugin({ filename: '[name].[contenthash:8].css',});
const commonConfig={
entry: {
app: PATHS.app,
},
output: {
path: PATHS.build,
filename: '[name].js',
},
module:{
rules:[{
test:/\.css$/, use:extractTxtplugin.extract({
use:'css-loader',
fallback: 'style-loader',
})
}]},
plugins: [ new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
title: 'Webpack demo',
}), extractTxtplugin
],
}
一开始看到这个配置,让人有点懵。首先看fileName,表示最后输出的文件按照这个格式'[name].[contenthash:8].css',name默认是对应的文件夹名称(这里是app),contenthash会返回特定内容的hash值,而:8表示取前8位。当然你也可以按照其他的格式写,比如直接命名:
new ExtractTextPlugin('style.css')
而ExtractTextPlugin.extract本身是一个loader。fallback:'style-loader'的意思但有css没有被提取(外部的css)的时候就用style-loader来处理。注意到现在我们的index.js如下:
import './main.css';
import styles from './other.css';
import component from './component';var ele=document.createElement("p");
ele.innerHTML="this is an box";
ele.className=styles.shadowButton;
document.body.appendChild(ele);
let demoComponent=component();
document.body.appendChild(demoComponent);//HMR 接口if(module.hot){
module.hot.accept('./component',()=>{
const nextComponent=component();
document.body.replaceChild(nextComponent,demoComponent);
demoComponent=nextComponent;
})
}
View Code
引入了两个css文件。
这个时候我们执行 npm run build

再看文件夹得到一个样式文件。(如果不想看到日志可以直接npm build)

但是我们在第三部分使用了CSS Modules,发现other.css的样式没有打包进来。所以,我们的webpack.config.js还要修改:
module:{
rules:[{
test:/\.css$/,
use:extractTxtplugin.extract({
use:[ { loader: 'css-loader',
options: {
modules: true,
},
}],
fallback: 'style-loader',
})
}]},
再次build。

相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
推荐阅读:
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of webpack style loading. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 From Websites to Apps: The Diverse Applications of JavaScriptApr 22, 2025 am 12:02 AM
From Websites to Apps: The Diverse Applications of JavaScriptApr 22, 2025 am 12:02 AMJavaScript is widely used in websites, mobile applications, desktop applications and server-side programming. 1) In website development, JavaScript operates DOM together with HTML and CSS to achieve dynamic effects and supports frameworks such as jQuery and React. 2) Through ReactNative and Ionic, JavaScript is used to develop cross-platform mobile applications. 3) The Electron framework enables JavaScript to build desktop applications. 4) Node.js allows JavaScript to run on the server side and supports high concurrent requests.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Use Cases and Applications ComparedApr 21, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Use Cases and Applications ComparedApr 21, 2025 am 12:01 AMPython is more suitable for data science and automation, while JavaScript is more suitable for front-end and full-stack development. 1. Python performs well in data science and machine learning, using libraries such as NumPy and Pandas for data processing and modeling. 2. Python is concise and efficient in automation and scripting. 3. JavaScript is indispensable in front-end development and is used to build dynamic web pages and single-page applications. 4. JavaScript plays a role in back-end development through Node.js and supports full-stack development.
 The Role of C/C in JavaScript Interpreters and CompilersApr 20, 2025 am 12:01 AM
The Role of C/C in JavaScript Interpreters and CompilersApr 20, 2025 am 12:01 AMC and C play a vital role in the JavaScript engine, mainly used to implement interpreters and JIT compilers. 1) C is used to parse JavaScript source code and generate an abstract syntax tree. 2) C is responsible for generating and executing bytecode. 3) C implements the JIT compiler, optimizes and compiles hot-spot code at runtime, and significantly improves the execution efficiency of JavaScript.
 JavaScript in Action: Real-World Examples and ProjectsApr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AM
JavaScript in Action: Real-World Examples and ProjectsApr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AMJavaScript's application in the real world includes front-end and back-end development. 1) Display front-end applications by building a TODO list application, involving DOM operations and event processing. 2) Build RESTfulAPI through Node.js and Express to demonstrate back-end applications.
 JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use CasesApr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use CasesApr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AMThe main uses of JavaScript in web development include client interaction, form verification and asynchronous communication. 1) Dynamic content update and user interaction through DOM operations; 2) Client verification is carried out before the user submits data to improve the user experience; 3) Refreshless communication with the server is achieved through AJAX technology.
 Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation DetailsApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation DetailsApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AMUnderstanding how JavaScript engine works internally is important to developers because it helps write more efficient code and understand performance bottlenecks and optimization strategies. 1) The engine's workflow includes three stages: parsing, compiling and execution; 2) During the execution process, the engine will perform dynamic optimization, such as inline cache and hidden classes; 3) Best practices include avoiding global variables, optimizing loops, using const and lets, and avoiding excessive use of closures.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of UseApr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of UseApr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AMPython is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and ResourcesApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and ResourcesApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AMPython and JavaScript have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of community, libraries and resources. 1) The Python community is friendly and suitable for beginners, but the front-end development resources are not as rich as JavaScript. 2) Python is powerful in data science and machine learning libraries, while JavaScript is better in front-end development libraries and frameworks. 3) Both have rich learning resources, but Python is suitable for starting with official documents, while JavaScript is better with MDNWebDocs. The choice should be based on project needs and personal interests.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software






