This article mainly introduces the relevant information about the incomplete adjustment and update of Vue v2.5. Friends who need it can refer to it. I hope it can help everyone.
Vue 2.5 Level E released: List of new features
Recently, Vue v2.5 was released. In addition to better support for TypeScript, there are also some functional and syntax adjustments. You need to understand. This article does not talk about TypeScript, but only explains some major adjustments.
Originally, I was not very sensitive to Vue version upgrades, so I didn’t pay much attention to the recent v2.5 release. Today, when I re-downloaded the Vue build project, I found several warnings.

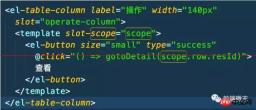
Looking at the warning message, I found out that it was because v2.5 of Vue was used, and the syntax of scoped slot was adjusted. Then I went to GitHub to check the release of v2.5. As you know, the scope attribute is no longer recommended in v2.5. It is recommended to use the slot-scope attribute to set the context.
Change scope="scope" in the code to slot-scope="scope". As shown below.
Let’s get to the point. Let’s list the main updates and adjustments in Vue v2.5.
Use errorCaptured hook to handle exceptions in components
Before v2.5, you can use a global config.errorHandler setting to provide a function for handling unknown exceptions for the application, or you can set renderError Component to handle exceptions within the render function. However, none of these provide a complete mechanism for handling exceptions within a single component.
In v2.5, a new hook function errorCaptured is provided in the component, which can capture all exceptions generated in all sub-component trees (excluding itself) in the component (including exceptions in asynchronous calls) , this hook function receives the same parameters as errorHandler, allowing developers to handle exceptions within components more friendly.
If you know React, you will find that this feature is very similar to the concept of "Error Boundary" introduced in React v16. They are both designed to better handle and display the rendering process of a single component. Medium exception. Previous articles on this official account and Zhihu column have specifically introduced the concept of exception boundaries in React. Click on the portal to view it.
To use errorCaputerd, you can encapsulate a general component to include other business components to capture exceptions within the business components and perform corresponding display processing. Below is a simple official example that encapsulates a common component (ErrorBoundary) to contain and handle exceptions from other business components (another component).
Vue.component('ErrorBoundary', {
data: () => ({ error: null }),
errorCaptured (err, vm, info) {
this.error = `${err.stack}\n\nfound in ${info} of component`
return false
},
render (h) {
if (this.error) {
return h('pre', { style: { color: 'red' }}, this.error)
}
// ignoring edge cases for the sake of demonstration
return this.$slots.default[0]
}
})
<error-boundary>
<another-component></another-component>
</error-boundary>
Transmission behavior characteristics of errorCaputed
If the global errorHandler is defined, all exceptions will still be passed to errorHadnler. If errorHandler is not defined, these exceptions can still be reported. Give a separate analysis service.
If multiple errorCapured hook functions are defined on a component through inheritance or parent components, these hook functions will all receive the same exception information.
You can return false in the errorCapured hook to prevent exception propagation, which means: the exception has been handled and can be ignored. Moreover, other errorCapured hook functions and global errorHandler functions will also be prevented from triggering this exception.
Single file components support "functional components"
Through vue-loader v13.3.0 or above, it is supported to define a " Functional Components" and supports features such as template compilation, scoped CSS, and hot deployment.
The definition of functional components needs to be declared by defining the functional attribute on the template tag. And the execution context of the expression in the template is the functional declaration context, so to access the properties of the component, you need to use props.xxx to obtain them. See a simple example below:
<template>
<p>{{ props.msg }}</p>
</template>
SSR environment
When using vue-server-renderer to build an SSR application, a Node.js environment is required by default, making some like php-v8js or Nashorn JavaScript cannot run in such a running environment. This has been improved in v2.5, so that SSR applications can run normally in the above environments.
In php-v8js and Nashorn, the global and process global objects need to be simulated during the preparation phase of the environment, and the environment variables of process need to be set separately. You need to set process.env.VUE_ENV to "server" and process.env.NODE_ENV to "development" or "production".
In addition, in Nashorn, you need to use Java's native timers to provide a polyfill for Promise and settimeout.
The official gives an example of use in php-v8js, as follows:
<?php $vue_source = file_get_contents('/path/to/vue.js');
$renderer_source = file_get_contents('/path/to/vue-server-renderer/basic.js');
$app_source = file_get_contents('/path/to/app.js');
$v8 = new V8Js();
$v8->executeString('var process = { env: { VUE_ENV: "server", NODE_ENV: "production" }}; this.global = { process: process };');
$v8->executeString($vue_source);
$v8->executeString($renderer_source);
$v8->executeString($app_source);
?>
// app.js
var vm = new Vue({
template: `<p>{{ msg }}</p>`,
data: {
msg: 'hello'
}
})
// exposed by vue-server-renderer/basic.js
renderVueComponentToString(vm, (err, res) => {
print(res)
})
v-on modifier
Key value key automatic modifier
In versions before Vue v2.5, if you want to use keyboard keys without built-in aliases in v-on, you must either use keyCode directly as a modifier (@keyup.13="foo"), or you need to use config .keyCodes to register aliases for key values.
In v2.5, you can directly use the legal key value key value (refer to KeyboardEvent.key in MDN) as a modifier to use it in series. as follows:
<input>
上述例子中,事件处理函数只会在 $event.key === ‘PageDown' 时被调用。
注意:现有键值修饰符仍然可用。在IE9中,一些键值(.esc 和 方向键的 key)不是一致的值,如果要兼容 IE9,需要按 IE9 中内置的别名来处理。
.exact 修饰符
新增了一个 .exact 修饰符,该修饰符应该和其他系统修饰符(.ctrl, .alt, .shift and .meta)结合使用,可用用来区分一些强制多个修饰符结合按下才会触发事件处理函数。如下:
<!-- 当 Alt 或 Shift 被按下也会触发处理函数 --> <button>A</button> <!-- 只有当 Ctrl 被按下,才会触发处理函数 --> <button>A</button>
简化 Scoped Slots 的使用
之前,如果要在 template 标签上使用 scope 属性定义一个 scoped slot,可以像下面这样定义:
<comp>
<template>
<p>{{ props.msg }}</p>
</template>
</comp>
在 v2.5 中,scope 属性已被弃用(仍然可用,但是会爆出一个警告,就像本文文首的那样),我们使用 slot-scope 属性替代 scope 属性来表示一个 scoped slot,且 slot-scope 属性除了可以被用在 template 上,还可以用在标签元素和组件上。如下:
<comp>
<p>
{{ props.msg }}
</p>
</comp>
注意:这次的调整,表示 slot-scope 已经是一个保留属性了,不能再被单独用在组件属性上了。
Inject 新增了默认值选项
本次调整中,Injections 可以作为可选配置,并且可以声明默认值。也可以用 from 来表示原属性。
export default {
inject: {
foo: {
from: 'bar',
default: 'foo'
}
}
}
与属性类似,数组和对象的默认值需要使用一个工厂函数返回。
export default {
inject: {
foo: {
from: 'bar',
default: () => [1, 2, 3]
}
}
}
相关推荐:
vue、vuecli、webpack中使用mockjs模拟后端数据
The above is the detailed content of Regarding the incomplete adjustment and update of Vue v2.5. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Javascript Data Types : Is there any difference between Browser and NodeJs?May 14, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Javascript Data Types : Is there any difference between Browser and NodeJs?May 14, 2025 am 12:15 AMJavaScript core data types are consistent in browsers and Node.js, but are handled differently from the extra types. 1) The global object is window in the browser and global in Node.js. 2) Node.js' unique Buffer object, used to process binary data. 3) There are also differences in performance and time processing, and the code needs to be adjusted according to the environment.
 JavaScript Comments: A Guide to Using // and /* */May 13, 2025 pm 03:49 PM
JavaScript Comments: A Guide to Using // and /* */May 13, 2025 pm 03:49 PMJavaScriptusestwotypesofcomments:single-line(//)andmulti-line(//).1)Use//forquicknotesorsingle-lineexplanations.2)Use//forlongerexplanationsorcommentingoutblocksofcode.Commentsshouldexplainthe'why',notthe'what',andbeplacedabovetherelevantcodeforclari
 Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AMThe main difference between Python and JavaScript is the type system and application scenarios. 1. Python uses dynamic types, suitable for scientific computing and data analysis. 2. JavaScript adopts weak types and is widely used in front-end and full-stack development. The two have their own advantages in asynchronous programming and performance optimization, and should be decided according to project requirements when choosing.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AMWhether to choose Python or JavaScript depends on the project type: 1) Choose Python for data science and automation tasks; 2) Choose JavaScript for front-end and full-stack development. Python is favored for its powerful library in data processing and automation, while JavaScript is indispensable for its advantages in web interaction and full-stack development.
 Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMPython and JavaScript each have their own advantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1. Python is easy to learn, with concise syntax, suitable for data science and back-end development, but has a slow execution speed. 2. JavaScript is everywhere in front-end development and has strong asynchronous programming capabilities. Node.js makes it suitable for full-stack development, but the syntax may be complex and error-prone.
 JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AMJavaScriptisnotbuiltonCorC ;it'saninterpretedlanguagethatrunsonenginesoftenwritteninC .1)JavaScriptwasdesignedasalightweight,interpretedlanguageforwebbrowsers.2)EnginesevolvedfromsimpleinterpreterstoJITcompilers,typicallyinC ,improvingperformance.
 JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript can be used for front-end and back-end development. The front-end enhances the user experience through DOM operations, and the back-end handles server tasks through Node.js. 1. Front-end example: Change the content of the web page text. 2. Backend example: Create a Node.js server.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AMChoosing Python or JavaScript should be based on career development, learning curve and ecosystem: 1) Career development: Python is suitable for data science and back-end development, while JavaScript is suitable for front-end and full-stack development. 2) Learning curve: Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners; JavaScript syntax is flexible. 3) Ecosystem: Python has rich scientific computing libraries, and JavaScript has a powerful front-end framework.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.






