Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >Detailed example of JavaScript form script
Detailed example of JavaScript form script
- 黄舟Original
- 2017-10-18 10:27:391553browse
The following editor will bring you a JavaScript-based form script (detailed explanation). The editor thinks it’s pretty good, so I’ll share it with you now and give it as a reference. Let’s follow the editor and take a look.
What is a form?
A form has three basic components: Form tag: This contains the URL of the CGI program used to process the form data and the method for submitting the data to the server. Form fields: include text boxes, password boxes, hidden fields, multi-line text boxes, check boxes, radio button boxes, drop-down selection boxes and file upload boxes, etc. Form buttons: include submit buttons, reset buttons and general buttons; used to transfer data to CGI scripts on the server or cancel input. Form buttons can also be used to control other processing tasks with defined processing scripts.
The relationship between JavaScript and forms: The initial application of JS was to share the responsibility of the server for processing forms and break the dependence on the server. Although the web and JavaScript have made great progress, web forms still have not been used for this purpose. Many developers provide ready-made solutions for many common tasks, and many developers use JavaScript not only when validating forms, but also to enhance the default behavior of some standard form controls.
1. Basic knowledge of forms
In HTML, the form consists of the form tag. In JavaScript, the form corresponds to the HTMLFormElement type, HTMLFormElement type Inheriting the HTMLElement type, it has the same default attributes as other Element elements, and it also has its own attributes and methods:
acceptCharset: the character set that the server can handle; equivalent to accept-charset in HTML characteristic.
action: Accepts the requested URL; equivalent to the action attribute in HTML.
elements: A collection of all controls in the form (HTMLCollection).
enctype: Requested encoding type; equivalent to the enctype attribute in HTML.
length: The number of controls in the form.
method: The type of HTTP request to be sent, usually "get" or "post"; equivalent to the method attribute of HTML.
name: The name of the form; equivalent to the name attribute of HTML.
reset(): Resets all form fields to default values.
submit(): Submit the form.
target: The name of the window used to send requests and receive responses; equivalent to the target attribute of HTML.
The methods to obtain form form elements are: var form=document.getElementById('form1'); //Get form elements through id
var firstForm=document.forms[0] ; //Get all the form elements in the page through document.forms, and get the first form element through the index value '0'
var form2=document.forms['form2']; //Pass document.forms to get all the form elements in the page, and get the specific form element through the name value
Submit the form:
<!-- 通用提交按钮 --> <input type="submit" value="Submit Form"> <!-- 自定义提交按钮 --> <button type="submit">Submit Form</button> <!-- 图像按钮 --> <input type="image" src="graphic.gif">
Submit in this way form, the browser fires the submit event before sending the request to the server. This gives us the opportunity to validate the form data and use it to decide whether to allow the form submission. Blocking the default behavior of this event can cancel the form submission
In JS we can also programmatically call the submit() method to submit the form:
var form = document.getElementById("myForm");
//提交表单
form.submit();Prevent form submission (prevent default event):
var form = document.getElementById("myForm");
EventUtil.addHandler(form, "submit", function(event){
//取得事件对象
event = EventUtil.getEvent(event);
//阻止默认事件
EventUtil.preventDefault(event);
});This technique can be used when the form data is invalid and cannot be sent to the server
Re- Reset form:
<!-- 通用重置按钮 --> <input type="reset" value="Reset Form"> <!-- 自定义重置按钮 --> <button type="reset">Reset Form</button>
When resetting the form, all form fields will be restored to their initial values when the page is just loaded
Use JS method to reset Reset the form:
var form = document.getElementById("myForm");
//重置表单
form.reset();Prevent the default action of resetting the form:
var form = document.getElementById("myForm");
EventUtil.addHandler(form, "reset", function(event){
//取得事件对象
event = EventUtil.getEvent(event);
//阻止表单重置
EventUtil.preventDefault(event);
});Form fields:
Each form has an Element property, which is a collection of all form elements (fields) in the form. This collection is an ordered list. The order in which each form field appears in the element collection is the same as the order in which it appears in the tag. They can be accessed by position and name value. Common form fields include input, select, and fieldset. To obtain the form fields in the form:
var form = document.getElementById("form1");
//取得表单中的第一个字段
var field1 = form.elements[0];
//取得名为"textbox1"的字段
var field2 = form.elements["textbox1"];
//取得表单中包含的字段的数量
var fieldCount = form.elements.length;Common form field attributes:
disabled: Boolean Value indicating whether the current field is disabled.
form: Pointer to the form to which the current field belongs; read-only.
name: The name of the current field.
readOnly: Boolean value, indicating whether the current field is read-only.
tabIndex: Indicates the switching (tab) sequence number of the current field.
type: The type of the current field, such as "checkbox", "radio", etc.
value: The value of the current field that will be submitted to the server. For file fields, this attribute is read-only and contains the path of the file on the computer.
Except the form attribute, any other attribute can be dynamically modified through JavaScript.
Being able to dynamically modify form field attributes means that we can dynamically operate the form at any time and in any way.
用户可能会重复单击表单的提交按钮。在涉及信用卡消费时,这就是个问题:因为会导致费用翻番。
为此,最常见的解决方案,就是在第一次单击后就禁用提交按钮。只要侦听 submit 事件,并在该事件发生时禁用提交按钮即可 :
//避免多次提交表单
EventUtil.addHandler(form, "submit", function(event){
event = EventUtil.getEvent(event);
var target = EventUtil.getTarget(event);
//取得提交按钮
var btn = target.elements["submit-btn"];
//禁用它
btn.disabled = true;
});除了2b5469ab79cf842344327415c3b3bb95之外,所有表单字段都有 type 属性。对于d5fd7aea971a85678ba271703566ebfd元素,这个值等于 HTML 特性 type 的值。对于其他元素,这个 type 属性的值如下表所列。
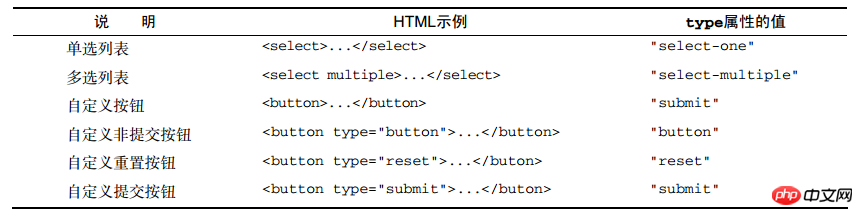
共有的表单字段方法 :
每个表单字段都有两个方法: focus()和 blur()。使用 focus()方法,可以将用户的注意力吸引到页面中的某个部位。例如,在页面加载完毕后,将焦点转移到表单中的第一个字段。
EventUtil.addHandler(window, "load", function(event){ /*给window绑定一个监听事件,放页面加载完成,光标自动对准在指定的表单字段*/
document.forms[0].elements[0].focus();
});HTML5 为表单字段新增了一个 autofocus 属性。在支持这个属性的浏览器中,只要设置这个属性,不用 JavaScript 就能自动把焦点移动到相应字段。
例如:
dc00ec850078be1b8515e2d33d7a435a
与 focus()方法相对的是 blur()方法,它的作用是从元素中移走焦点:
document.forms[0].elements[0].blur();
change事件:对于d5fd7aea971a85678ba271703566ebfd和4750256ae76b6b9d804861d8f69e79d3元素,在它们失去焦点且 value 值改变时触发;对于
221f08282418e2996498697df914ce4e元素,在其选项改变时触发。
二,文本框脚本
在 HTML 中,有两种方式来表现文本框:一种是使用d5fd7aea971a85678ba271703566ebfd元素的单行文本框,另一种是使用4750256ae76b6b9d804861d8f69e79d3的多行文本框。
选择文本:
在文本框获得焦点时选择其所有文本,这是一种非常常见的做法 ,实现代码如下:
EventUtil.addHandler(textbox, "focus", function(event){
event = EventUtil.getEvent(event);
var target = EventUtil.getTarget(event);
target.select();
});取得选择的文本 :
虽然通过 select 事件我们可以知道用户什么时候选择了文本,但仍然不知道用户选择了什么文本。HTML5 通过一些扩展方案解决了这个问题,以便更顺利地取得选择的文本。该规范采取的办法是添加两个属性: selectionStart 和 selectionEnd。
function getSelectedText(textbox){
return textbox.value.substring(textbox.selectionStart, textbox.selectionEnd);
}IE9+、 Firefox、 Safari、 Chrome 和 Opera 都支持这两个属性。 IE8 及之前版本不支持这两个属性,而是提供了另一种方案。 IE8 及更早的版本中有一个 document.selection 对象,其中保存着用户在整个文档范围内选择的文本信息
function getSelectedText(textbox){
if (typeof textbox.selectionStart == "number"){
return textbox.value.substring(textbox.selectionStart,
textbox.selectionEnd);
} else if (document.selection){
return document.selection.createRange().text;
}
}过滤输入:
我们经常会要求用户在文本框中输入特定的数据,或者输入特定格式的数据。
EventUtil.addHandler(textbox, "keypress", function(event){
event = EventUtil.getEvent(event);
var target = EventUtil.getTarget(event);//取得输入键的字符编码
var charCode = EventUtil.getCharCode(event);
if (!/\d/.test(String.fromCharCode(charCode))){ //将字符编码转换到字符,并用正则表达式检测是否符合匹配
EventUtil.preventDefault(event);
}
});以上代码实现对表单字段中输入的数据的控制,只允许输入数字
有时我们想要屏蔽哪些非数字的键,而不像屏蔽哪些基本键和按下ctrl键的操作。
自动切换焦点:
使用 JavaScript 可以从多个方面增强表单字段的易用性。其中,最常见的一种方式就是在用户填写完当前字段时,自动将焦点切换到下一个字段。为增强易用性,同时加快数据输入,可以在前一个文本框中的字符达到最大数量后,自动将焦点切换到下一个文本框。
比如对于下面的表单字段而言:
<input type="text" name="tel1" id="txtTel1" maxlength="3"> <input type="text" name="tel2" id="txtTel2" maxlength="3"> <input type="text" name="tel3" id="txtTel3" maxlength="4">
想要达到自动切换焦点的效果,可以这样做:
(function(){
function tabForward(event){
event = EventUtil.getEvent(event);
var target = EventUtil.getTarget(event); //取得事件源
if (target.value.length == target.maxLength){ //检测输入的字符是否达到最大的字符要求
var form = target.form;//取得该字段所在的表单
for (var i=0, len=form.elements.length; i < len; i++) { //遍历表单的字段
if (form.elements[i] == target) {//当遍历到当前所在的目标字段时,将焦点对准下一个表单字段
if (form.elements[i+1]){
form.elements[i+1].focus();
}
return;
}
}
}
}
var textbox1 = document.getElementById("txtTel1"); //取得目标
var textbox2 = document.getElementById("txtTel2");
var textbox3 = document.getElementById("txtTel3");
EventUtil.addHandler(textbox1, "keyup", tabForward); //绑定事件
EventUtil.addHandler(textbox2, "keyup", tabForward);
EventUtil.addHandler(textbox3, "keyup", tabForward);
})();HTML5约束验证API
为了在将表单提交到服务器之前验证数据,HTML5 新增了一些功能。
必填字段:required,例子比如:4c63fe08691f6a2f2ebc676ed196c69c
type属性:"email"类型要求输入的文本必须符合电子邮件地址的模式,而"url"类型要求输入的文本必须符合 URL 的模式。
pattern属性:这个属性的值是一个正则表达式,用于匹配文本框中的值。例子如:5364a03e92c84c9cd54c9d5f4abeb134
禁用验证:通过设置 novalidate 属性,可以告诉表单不进行验证。 例子如:
<form method="post" action="signup.php" novalidate> <!--这里插入表单元素--> </form>
三,选择框脚本
选择框是通过221f08282418e2996498697df914ce4e和5a07473c87748fb1bf73f23d45547ab8元素创建的。 该类型还提供下列属性和方法:
add(newOption, relOption):向控件中插入新5a07473c87748fb1bf73f23d45547ab8元素,其位置在相关项(relOption)之前。
multiple:布尔值,表示是否允许多项选择;等价于 HTML 中的 multiple 特性。
options:控件中所有5a07473c87748fb1bf73f23d45547ab8元素的 HTMLCollection。
remove(index):移除给定位置的选项。
selectedIndex:基于 0 的选中项的索引,如果没有选中项,则值为-1。对于支持多选的控件,只保存选中项中第一项的索引。
size:选择框中可见的行数;等价于 HTML 中的 size 特性。
选择框的 type 属性不是"select-one",就是"select-multiple",这取决于 HTML 代码中有没有 multiple 特性。选择框的 value 属性由当前选中项决定,相应规则如下。
如果没有选中的项,则选择框的 value 属性保存空字符串。
如果有一个选中项,而且该项的 value 特性已经在 HTML 中指定,则选择框的 value 属性等于选中项的 value 特性。即使 value 特性的值是空字符串,也同样遵循此条规则。
如果有一个选中项,但该项的 value 特性在 HTML 中未指定,则选择框的 value 属性等于该项的文本。
如果有多个选中项,则选择框的 value 属性将依据前两条规则取得第一个选中项的值。
选择选项:
对于只允许选择一项的选择框,访问选中项的最简单方式,就是使用选择框的 selectedIndex 属性。例子如:
var selectedOption = selectbox.options[selectbox.selectedIndex];
添加选项:
可以使用 JavaScript 动态创建选项,并将它们添加到选择框中。
第一种方式就是使用如下所示的 DOM 方法:
var newOption = document.createElement("option");
newOption.appendChild(document.createTextNode("Option text"));
newOption.setAttribute("value", "Option value");
selectbox.appendChild(newOption);第二种方式是使用 Option 构造函数来创建新选项 :
var newOption = new Option("Option text", "Option value");
selectbox.appendChild(newOption);第三种添加新选项的方式是使用选择框的 add()方法,DOM 规定这个方法接受两个参数,要添加的新选项和将位于新选项之后的选项 :
var newOption = new Option("Option text", "Option value"); //
selectbox.add(newOption, undefined); //最佳方案 ,将新选项添加到列表最后移除选项:
DOM 的 removeChild()方法,为其传入要移除的选项,如下面的例子所示:
selectbox.removeChild(selectbox.options[0]); //移除第一个选项
其次,可以使用选择框的 remove()方法 :
selectbox.remove(0); //移除第一个选项
最后一种方式,就是将相应选项设置为 null:
selectbox.options[0] = null; //移除第一个选项
要清除选择框中所有的项,需要迭代所有选项并逐个移除它们 :
function clearSelectbox(selectbox){
for(var i=0, len=selectbox.options.length; i < len; i++){
selectbox.remove(0);
}
}这个函数每次只移除选择框中的第一个选项。由于移除第一个选项后,所有后续选项都会自动向上移动一个位置,因此重复移除第一个选项就可以移除所有选项了。
移动和重排选项:
如果为 appendChild()方法传入一个文档中已有的元素,那么就会先从该元素的父节点中移除它,再把它添加到指定的位置 :
var selectbox1 = document.getElementById("selLocations1"); //每个子节点只有一个父节点,所以会先删除以前位置的节点
var selectbox2 = document.getElementById("selLocations2");
selectbox2.appendChild(selectbox1.options[0]);重排选项次序的过程也十分类似,最好的方式仍然是使用 DOM 方法。要将选择框中的某一项移动到特定位置,最合适的 DOM 方法就是 insertBefore();
var optionToMove = selectbox.options[1]; selectbox.insertBefore(optionToMove, selectbox.options[optionToMove.index-1]); //要在选择框中向前移动一个选项的位置
表单序列化:
表单序列化简单说就是将,各表单字段按名值对的形式进行url编码。
表单序列化有以下规则:
对表单字段的名称和值进行 URL 编码,使用和号(&)分隔。
不发送禁用的表单字段。
只发送勾选的复选框和单选按钮。
不发送 type 为"reset"和"button"的按钮。
多选选择框中的每个选中的值单独一个条目。
在单击提交按钮提交表单的情况下,也会发送提交按钮;否则,不发送提交按钮。也包括 type为"image"的d5fd7aea971a85678ba271703566ebfd元素。
221f08282418e2996498697df914ce4e元素的值,就是选中的5a07473c87748fb1bf73f23d45547ab8元素的 value 特性的值。如果5a07473c87748fb1bf73f23d45547ab8元素没有value 特性,则是5a07473c87748fb1bf73f23d45547ab8元素的文本值。
四,富文本编辑
这一技术的本质,就是在页面中嵌入一个包含空 HTML 页面的 iframe。通过设置 designMode 属性,这个空白的 HTML 页可以被编辑,而编辑对象则是该页面6c04bd5ca3fcae76e30b72ad730ca86d元素的 HTML 代码。 designMode 属性有两个可能的值: "off"(默认值)和"on"。在设置为"on"时,整个文档都会变得可以编辑(显示插入符号),然后就可以像使用字处理软件一样,通过键盘将文本内容加粗、变成斜体,等等。另一种编辑富文本内容的方式是使用名为 contenteditable 的特殊属性,这个属性也是由 IE 最早实现的。可以把 contenteditable 属性应用给页面中的任何元素,然后用户立即就可以编辑该元素。
The above is the detailed content of Detailed example of JavaScript form script. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- An in-depth analysis of the Bootstrap list group component
- Detailed explanation of JavaScript function currying
- Complete example of JS password generation and strength detection (with demo source code download)
- Angularjs integrates WeChat UI (weui)
- How to quickly switch between Traditional Chinese and Simplified Chinese with JavaScript and the trick for websites to support switching between Simplified and Traditional Chinese_javascript skills

