This article mainly introduces the CSS position attribute and application examples, absolute (absolute positioning), relative (relative positioning), the combination of relative and absolute, and fixed (fixed positioning). Friends in need can refer to it
At present, almost all mainstream browsers support the position attribute (except "inherit", "inherit" does not support all browsers including IE8 and previous versions of IE, and IE9 and IE10 have not been tested). The following is w3school's explanation of position Explanation of the five values:

Among them, absolute and relative are the most commonly used, and fixed is also used more frequently (IE6 does not support fixed).
1. Absolute (absolute positioning)
Absolute is an element that generates visual positioning and is separated from the text flow (that is, it is already in the document) does not occupy the position), refer to the upper left corner of the browser through top, right, bottom, left (referred to as TRBL) positioning. You can select a positioned parent object (the combination of relative and absolute will be discussed below) or the body coordinate origin for positioning, or you can perform hierarchical classification through z-index. When the TRBL value is not set, absolute uses the coordinates of the parent object as the starting point. When the TRBL value is set, the upper left corner of the browser is used as the original point. The specific case is as follows:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>position:absolute定位</title>
<style type="text/css">
html,body,p{
margin:0;
padding:0;
list-style:none;
}
.center{
margin:30px;
border:#999999 solid 10px;
width:400px;
height:300px;
}
.p1{
width:200px;
height:200px;
background:#0099FF;
/*设定TRBL*/
position:absolute;
left:0px;
top:0px;
}
.p2{
width:400px;
height:300px;
font-size:30px;
font-weight:bold;
color:#fff;
background:#FF0000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="center">
<p class="p1"></p>
<p class="p2">position:absolute定位测试</p>
</p>
</body>
</html>The effect of this code is as follows:
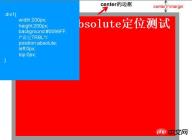
This is the setting The effect after TRBL (setting TRBL to the upper left corner of the browser as the origin), when TRBL is not set (TRBL is not set, using the coordinates of the parent object as the origin), that is, when p1 is changed to the following code
.p1{
width:200px;
height:200px;
background:#0099FF;
/*没有设定TRBL*/
position:absolute;
}
The effect is as follows:

## 2. relative (relative positioning)
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>position:relative定位</title>
<style type="text/css">
html,body,p{
margin:0;
padding:0;
list-style:none;
}
.center{
margin:30px;
border:#999999 solid 10px;
width:400px;
height:300px;
background:#FFFF00;
}
.p1{
width:200px;
height:150px;
background:#0099FF;
position:relative;
top:-20px;
left:0px;
}
.p2{
width:400px;
height:150px;
font-size:30px;
font-weight:bold;
color:#fff;
background:#FF0000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="center">
<p class="p1"></p>
<p class="p2">position:relative定位测试</p>
</p>
</body>
</html>The effect produced by the code is as follows:

3. The combination of relative and absolute
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<style type="text/css">
html,body,p,ul,li,a{
margin:0;
padding:0;
list-style:none;
}
a, a:hover{
color:#000;
border:0;
text-decoration:none;
}
#warp,#head,#main,#foot
{
width: 962px;
}
/*设置居中*/
#warp{
margin: 0 auto;
}
#head{
height:132px;
position:relative;
}
.logo{
position:absolute;
top:17px;
}
.head_pic{
position:absolute;
top:17px;
left:420px;
}
.sc{
position:absolute;
right:5px;
top:12px;
}
.sc a{
padding-left:20px;
color:#666;
}
.nav{
width:960px;
height:42px;
line-height:42px;
position:absolute;
bottom:0px;
background:url(img/nav_bj.jpg) no-repeat center;
}
.nav ul{
float:left;
padding:0 10px;
}
.nav li{
float:left;
background:url(img/li_bj.jpg) no-repeat right center;
padding-right:40px;
padding-left:20px;
text-align:center;
display:inline;
}
.nav li a{
font-size:14px;
font-family:Microsoft YaHei !important;
white-space:nowrap;
}
.nav li a:hover{
color:#FBECB7;
}
</style>
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<p id="warp">
<p id="head">
<p class="logo"><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="img/logo.jpg" class="lazy" / alt="Detailed explanation of CSS position property examples" ></p>
<p class="head_pic"><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="img/head_pic.jpg" class="lazy" / alt="Detailed explanation of CSS position property examples" ></p>
<p class="sc">
<a href=""><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="img/sc_btn.jpg" class="lazy" / alt="Detailed explanation of CSS position property examples" ></a>
<a href=""><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="img/sy_btn.jpg" class="lazy" / alt="Detailed explanation of CSS position property examples" ></a>
<a href=""><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="img/kf_btn.jpg" class="lazy" / alt="Detailed explanation of CSS position property examples" ></a>
</p>
<p class="nav">
<ul>
<li><a href="">首页</a></li>
<li><a href="">关于我们</a></li>
<li><a href="">团队文化</a></li>
<li><a href="">公司动态</a></li>
<li><a href="">资讯参考</a></li>
<li><a href="">业务中心</a></li>
<li><a href="">合作银行</a></li>
<li><a href="">联系我们</a></li>
</ul>
</p>
</p>
<p id="main"></p>
<p id="foot"></p>
</p>
</body>
</html>The effect is as shown below:

In the above code, the first thing is to set the relative positioning for the head. , then you can see that all child elements inside will be positioned relative to the head instead of relative to the body after setting absolute. This is much simpler and more convenient than using floating, and there is no need to worry about compatibility issues.
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of CSS position property examples. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 The Lost CSS Tricks of Cohost.orgApr 25, 2025 am 09:51 AM
The Lost CSS Tricks of Cohost.orgApr 25, 2025 am 09:51 AMIn this post, Blackle Mori shows you a few of the hacks found while trying to push the limits of Cohost’s HTML support. Use these if you dare, lest you too get labelled a CSS criminal.
 Next Level CSS Styling for CursorsApr 23, 2025 am 11:04 AM
Next Level CSS Styling for CursorsApr 23, 2025 am 11:04 AMCustom cursors with CSS are great, but we can take things to the next level with JavaScript. Using JavaScript, we can transition between cursor states, place dynamic text within the cursor, apply complex animations, and apply filters.
 Worlds Collide: Keyframe Collision Detection Using Style QueriesApr 23, 2025 am 10:42 AM
Worlds Collide: Keyframe Collision Detection Using Style QueriesApr 23, 2025 am 10:42 AMInteractive CSS animations with elements ricocheting off each other seem more plausible in 2025. While it’s unnecessary to implement Pong in CSS, the increasing flexibility and power of CSS reinforce Lee's suspicion that one day it will be a
 Using CSS backdrop-filter for UI EffectsApr 23, 2025 am 10:20 AM
Using CSS backdrop-filter for UI EffectsApr 23, 2025 am 10:20 AMTips and tricks on utilizing the CSS backdrop-filter property to style user interfaces. You’ll learn how to layer backdrop filters among multiple elements, and integrate them with other CSS graphical effects to create elaborate designs.
 SMIL on?Apr 23, 2025 am 09:57 AM
SMIL on?Apr 23, 2025 am 09:57 AMWell, it turns out that SVG's built-in animation features were never deprecated as planned. Sure, CSS and JavaScript are more than capable of carrying the load, but it's good to know that SMIL is not dead in the water as previously
 'Pretty' is in the eye of the beholderApr 23, 2025 am 09:40 AM
'Pretty' is in the eye of the beholderApr 23, 2025 am 09:40 AMYay, let's jump for text-wrap: pretty landing in Safari Technology Preview! But beware that it's different from how it works in Chromium browsers.
 CSS-Tricks Chronicles XLIIIApr 23, 2025 am 09:35 AM
CSS-Tricks Chronicles XLIIIApr 23, 2025 am 09:35 AMThis CSS-Tricks update highlights significant progress in the Almanac, recent podcast appearances, a new CSS counters guide, and the addition of several new authors contributing valuable content.
 Tailwind's @apply Feature is Better Than it SoundsApr 23, 2025 am 09:23 AM
Tailwind's @apply Feature is Better Than it SoundsApr 23, 2025 am 09:23 AMMost of the time, people showcase Tailwind's @apply feature with one of Tailwind's single-property utilities (which changes a single CSS declaration). When showcased this way, @apply doesn't sound promising at all. So obvio


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version






