Home >Java >javaTutorial >Summary of JAVA collection classes
Summary of JAVA collection classes
- 巴扎黑Original
- 2017-07-20 13:17:111529browse
1. Sets and Arrays
Array (can store basic data types) is a container used to store objects, but the length of the array is fixed and is not suitable for the number of objects. Used when unknown.
The collection (which can only store objects, and the object types can be different) has variable length and can be used in most cases.
2. Hierarchical relationship
As shown in the figure: In the figure, the solid line border is the implementation class, the polyline border is the abstract class, and the dotted line border is It is the interface
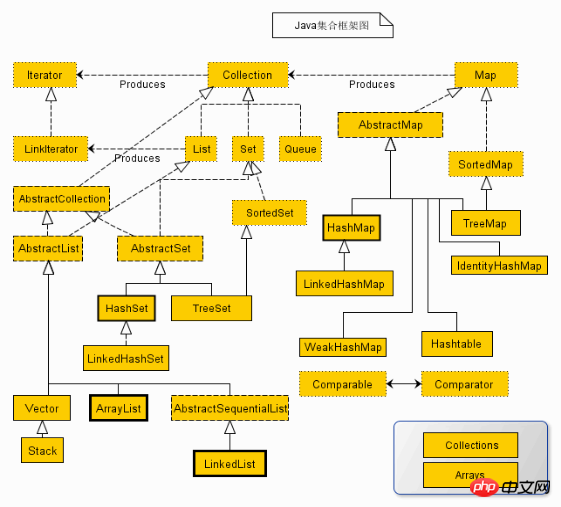
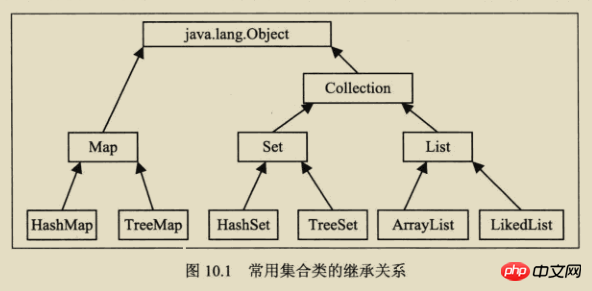
Collection interface is the root interface of the collection class. There is no direct interface for this interface in Java. Implementation class. But it was inherited to produce two interfaces, namely Set and List. Set cannot contain duplicate elements. List is an ordered collection that can contain repeated elements and provides access by index.
Map is another interface in the Java.util package. It has nothing to do with the Collection interface and is independent of each other, but they are both part of the collection class. Map contains key-value pairs. Map cannot contain duplicate keys, but it can contain the same value.
Iterator, all collection classes, implement the Iterator interface. This is an interface used to traverse elements in a collection. It mainly includes the following three methods:
1. Is there any next method in hasNext() an element.
2.next() returns the next element.
3.remove() deletes the current element.
3. Introduction to several important interfaces and classes
1. List (ordered, repeatable)
The objects stored in the List are ordered , and it is also repeatable. List focuses on indexes, has a series of methods related to indexes, and has fast query speed. Because when inserting or deleting data into the list collection, it will be accompanied by the movement of subsequent data, and all insertion and deletion of data are slow.
2. Set (unordered, cannot be repeated)
The objects stored in Set are unordered and cannot be repeated. The objects in the set are not sorted in a specific way, but the objects are simply added to the set. middle.
3. Map (key-value pairs, unique keys, non-unique values)
The Map collection stores key-value pairs. Keys cannot be repeated, but values can be repeated. Obtain the value according to the key. When traversing the map collection, first obtain the set collection of the key, traverse the set collection, and obtain the corresponding value.
The comparison is as follows:
|
|
Whether it is in order |
Whether elements are allowed to be repeated |
Collection |
No |
##Yes | |
| List | Yes
|
is | |
| AbstractSet | No | No | |
| HashSet | |||
| TreeSet | Yes (using a binary sorted tree) | ||
| AbstractMap | No | Use key-value to map and store data. The key must be unique and the value can be repeated. | |
| HashMap | ## | ||
TreeMap |
is ( Use binary sorting tree) |
#
4. Traversal The following four common output methods are provided in the class set: 1) Iterator: iterative output, It is the most commonly used output method. 2) ListIterator: It is a sub-interface of Iterator, specially used to output the contents of List. 3) foreach output: a new function provided after JDK1.5, which can output arrays or collections. 4) for loop The code example is as follows: The form of for: for (int i=0;i The form of foreach: for (int i: arr) {...} The form of iterator: 5. ArrayList and LinkedList Usage of ArrayList and LinkedList There is no difference, but there is still a functional difference. LinkedList is often used in situations where there are many additions and deletions but few query operations, while ArrayList is the opposite. 6. Map collection Implementation classes: HashMap, Hashtable, LinkedHashMap and TreeMap HashMap HashMap is the most commonly used Map, which stores data according to the HashCode value of the key, can directly obtain its value according to the key, and has a very fast access speed. When traversing, the order in which the data is obtained is completely random. Because the key object cannot be repeated, HashMap only allows the key of one record to be Null, and allows the value of multiple records to be Null, which is asynchronous Hashtable Hashtable is similar to HashMap, and is The thread-safe version of HashMap supports thread synchronization, that is, only one thread can write to Hashtable at any time, which also causes Hashtale to be slower when writing. It inherits from the Dictionary class, but the difference is that it does not allow recording. The key or value is null and the efficiency is low. ConcurrentHashMap Thread-safe and lock-separated. ConcurrentHashMap uses segments internally to represent these different parts. Each segment is actually a small hash table, and they have their own locks. Multiple modification operations can occur concurrently as long as they occur on different segments. LinkedHashMap LinkedHashMap saves the insertion order of records. When traversing LinkedHashMap with Iteraor, the record obtained first must be inserted first. It will be slower than HashMap during traversal. There is HashMap All features. TreeMap TreeMap implements the SortMap interface, which can sort the records it saves according to keys. The default is to sort by key values in ascending order (natural order). You can also specify a sorting comparator. When using When the Iterator traverses the TreeMap, the records obtained are sorted. The key value is not allowed to be empty and non-synchronous; Traversal of map First type: KeySet() Second type: entrySet() 7. Summary of the differences between main implementation classes Vector and ArrayList arraylist and linkedlist HashMap and TreeMap HashTable and HashMap |
|
The above is the detailed content of Summary of JAVA collection classes. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

