Introduction
Recently, I suddenly saw the problem of lazy loading of pictures. The general meaning is that in the initial state, the page only loads pictures in the visible area of the browser, and the remaining pictures are in Loading starts when the browser's viewable area is scrolled to its position. It seems that many large websites now implement lazy loading, so I thought about this issue. First of all, the first problem is that the browser does not have the relevant API method to detect whether an element is in the visible area, so we can only calculate it manually, so this involves the knowledge of the element length, width, and scroll bar position. The knowledge involved in this article includes the difference between element length and width clientWidth/offsetWidth/scrollWidth, and the difference between clientTop/offsetTop/scrollTop, and the source code for obtaining element coordinates is given.
1. The difference between clientWidth, offsetWidth and scrollWidth
Usually when everyone gets the length and width of an element, they use some frame-encapsulated methods. , such as jQuery.prototype.width(), these frameworks are convenient and quick to use, but they still involve a lot of knowledge. There are many ways to obtain the length and width of elements, and their actual meanings are also different.
Simply put, you can use the following formula:
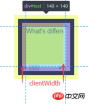
clientWidth = width (visual area) + padding
offsetWidth = width (visual area) + padding + border
ScrollWidth = width(content area)
Suppose we have the following element:
1 #test {2 width: 100px;3 height: 100px;4 margin: 10px;5 border: 10px solid #293482;6 padding: 10px;7 background-color: yellow;8 overflow: auto;9 }| clientWidth | ##offsetWidth | scrollWidth |

|  |  |
 | ||
| ##offsetWidth | scrollWidth | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
 This is actually equivalent to the width of the content This is actually equivalent to the width of the content |

|
|||||||||||||||||||
二、clientTop、offsetTop、scrollTop 的区别我们使用以下公式: clientTop = border offsetTop = 元素边框外围至父元素边框内围 scrollTop = 元素可视区域顶部至实际内容区域的顶部 给定以下两个元素 container 和 test 1 #container { 2 background-color: #F08D8D; 3 padding: 10px; 4 } 5 #test { 6 position: relative; 7 top: 10px; 8 width: 100px; 9 height: 100px;10 margin: 20px;11 border: 15px solid #293482;12 padding: 10px;13 background-color: yellow;14 }
三、获取页面元素绝对定位坐标有了以上知识基础之后,我们现在需要考虑的问题是,如何获取页面元素的绝对位置,也就是在文档流内容区的位置。我们知道,元素的 offsetTop 属性可以获取当前元素边框外围至父元素边框内围的的距离,clientTop 可以获取元素边框的宽度。那么现在用一个递归的公式就可以求得当前元素在页面中的绝对位置: Element.absoluteTop = Element.parent.absoluteTop + Element.offsetTop + Element.clientTop; 同理,我们用参照元素的长宽减去 left 和 top 和定位,即可得到 right 和 bottom 的定位; 所以我们可以编写以下工具来获取元素的绝对位置,也就是在内容区的定位(参照元素必须是目标元素的祖先元素): 1 var Position = {}; 2 (function () { 3 Position.getAbsolute = function (reference, target) { 4 //因为我们会将目标元素的边框纳入递归公式中,这里先减去对应的值 5 var result = { 6 left: -target.clientLeft, 7 top: -target.clientTop 8 } 9 var node = target;10 while(node != reference && node != document){11 result.left = result.left + node.offsetLeft + node.clientLeft;12 result.top = result.top + node.offsetTop + node.clientTop;13 node = node.parentNode;14 }15 if(isNaN(reference.scrollLeft)){16 result.right = document.documentElement.scrollWidth - result.left;17 result.bottom = document.documentElement.scrollHeight - result.top;18 }else {19 result.right = reference.scrollWidth - result.left;20 result.bottom = reference.scrollHeight - result.top;21 }22 return result;23 }24 })();此方法可以获取一个元素相对于一个父元素的定位,如果要获取元素在整张页面,直接传入 document 即可: 1 Position.getAbsolute(document, targetNode); //{left: left, right: right, top: top, bottom: bottom}四、获取元素的可视区定位坐标在上一小节中,我们封装了一个函数,这个函数可以用来获取一个元素的相对于一个祖先元素的绝对定位坐标,在这一小节中,我们来获取元素相对于浏览器窗口可视区域的定位坐标。在上一个函数中,我们可以获取一个元素在 document 当中的定位,还记得我们在第二小节中的 scrollTop 属性吗?该属性可以获取滚动窗口可视区域顶端距离内容区顶端的距离,我们用元素的绝对定位坐标减去 document 的滚动定位就是我们想要的浏览器窗口定位啦(相对于浏览器左上角): ViewportTop = Element.absoluteTop - document.body.scrollTop; 这里需要注意一个兼容性的问题,在 Chrome 中可以用 document.body.scrollTop 和 window.pageYOffset,IE 7/8 只能通过 document.documentElement.scrollTop 获取, FireFox 和 IE9+ 可以用 document.documentElement.scrollTop 和 window.pageYOffset 获取,Safari 需要 window.pageYOffset 获取。所以这里我们需要做一下浏览器兼容: scrollTop = window.pageYOffset || document.documentElement.scrollTop || document.body.scrollTop; 注意这里的顺序,在 IE7/8 中 window.pageYOffset 是 undefined ,document.body.scrollTop 在任何浏览器中都有,只是不支持的值为 0,如果表达式返回 undefined ,会影响后面的计算操作。而 || 运算符是一个短路取真运算符,所以我们要所有浏览器都有的 document.body.scrollTop 方法放在最后,关于 || 运算符的问题,可以参考 《探寻 JavaScript 逻辑运算符(与、或)的真谛》。 我们在刚才的工具上添加一个方法: 1 var Position = {}; 2 (function () { 3 Position.getAbsolute = function (reference, target) { 4 var result = { 5 left: -target.clientLeft, 6 top: -target.clientTop 7 } 8 var node = target; 9 while(node != reference && node != document){10 result.left = result.left + node.offsetLeft + node.clientLeft;11 result.top = result.top + node.offsetTop + node.clientTop;12 node = node.parentNode;13 }14 if(isNaN(reference.scrollLeft)){15 result.right = document.documentElement.scrollWidth - result.left;16 result.bottom = document.documentElement.scrollHeight - result.top;17 }else {18 result.right = reference.scrollWidth - result.left;19 result.bottom = reference.scrollHeight - result.top;20 }21 return result;22 }23 Position.getViewport = function (target) {24 var scrollTop = window.pageYOffset || document.documentElement.scrollTop || document.body.scrollTop;25 var scrollLeft = window.pageXOffset || document.documentElement.scrollLeft || document.body.scrollLeft;26 var absolutePosi = this.getAbsolute(document, target);27 var Viewport = {28 left: absolutePosi.left - scrollLeft,29 top: absolutePosi.top - scrollTop,30 }31 return Viewport;32 }33 })();通过 Position.getViewport 方法可以获取元素相对于浏览器窗口的定位: 1 Postion.getViewport(targetNode); //{left: left, top: top}五、判断可视区域在上面的几个方法中,我们可以获取元素的文档流定位和视窗定位,不过这还是不能判断一个元素是否在可视区域内,因为视窗定位可以是非常大的数字,这样元素就在视窗的后面。这里我们需要使用浏览器视窗高度 window.innerHeight 属性,在 IE8 以下需要用 document.documentElement.clientHeight 来获取。 windowHeight = window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.clientHeight; 现在,我们用窗口的高度,减去相对于浏览器窗口的定位,即可获取相对于浏览器窗口右下角的定位; 1 var Position = {}; 2 (function () { 3 Position.getAbsolute = function (reference, target) { 4 var result = { 5 left: -target.clientLeft, 6 top: -target.clientTop 7 } 8 var node = target; 9 while(node != reference && node != document){10 result.left = result.left + node.offsetLeft + node.clientLeft;11 result.top = result.top + node.offsetTop + node.clientTop;12 node = node.parentNode;13 }14 if(isNaN(reference.scrollLeft)){15 result.right = document.documentElement.scrollWidth - result.left;16 result.bottom = document.documentElement.scrollHeight - result.top;17 }else {18 result.right = reference.scrollWidth - result.left;19 result.bottom = reference.scrollHeight - result.top;20 }21 return result;22 }23 Position.getViewport = function (target) {24 var scrollTop = window.pageYOffset || document.documentElement.scrollTop || document.body.scrollTop;25 var scrollLeft = window.pageXOffset || document.documentElement.scrollLeft || document.body.scrollLeft;26 var windowHeight = window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.offsetHeight;27 var windowWidth = window.innerWidth || document.documentElement.offsetWidth;28 var absolutePosi = this.getAbsolute(document, target);29 var Viewport = {30 left: absolutePosi.left - scrollLeft,31 top: absolutePosi.top - scrollTop,32 right: windowWidth - (absolutePosi.left - scrollLeft),33 bottom: windowHeight - (absolutePosi.top - scrollTop)34 }35 return Viewport;36 }37 })();现在我们使用 Position.getViewport(targetNode) 方法可以获取元素左上角相对于窗口4个方向的定位: 1 Position.getViewport(targetNode); //{left: left, top: top, right: right, bottom: bottom}有了这个方法,现在就可以真正的判断元素是否在可视区域内了: 1 var Position = {}; 2 (function () { 3 Position.getAbsolute = function (reference, target) { 4 //因为我们会将目标元素的边框纳入递归公式中,这里先减去对应的值 5 var result = { 6 left: -target.clientLeft, 7 top: -target.clientTop 8 } 9 var node = target;10 while(node != reference && node != document){11 result.left = result.left + node.offsetLeft + node.clientLeft;12 result.top = result.top + node.offsetTop + node.clientTop;13 node = node.parentNode;14 }15 if(isNaN(reference.scrollLeft)){16 result.right = document.documentElement.scrollWidth - result.left;17 result.bottom = document.documentElement.scrollHeight - result.top;18 }else {19 result.right = reference.scrollWidth - result.left;20 result.bottom = reference.scrollHeight - result.top;21 }22 return result;23 }24 Position.getViewport = function (target) {25 var scrollTop = window.pageYOffset || document.documentElement.scrollTop || document.body.scrollTop;26 var scrollLeft = window.pageXOffset || document.documentElement.scrollLeft || document.body.scrollLeft;27 var windowHeight = window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.offsetHeight;28 var windowWidth = window.innerWidth || document.documentElement.offsetWidth;29 var absolutePosi = this.getAbsolute(document, target);30 var Viewport = {31 left: absolutePosi.left - scrollLeft,32 top: absolutePosi.top - scrollTop,33 right: windowWidth - (absolutePosi.left - scrollLeft),34 bottom: windowHeight - (absolutePosi.top - scrollTop)35 }36 return Viewport;37 }38 Position.isViewport = function (target) {39 var position = this.getViewport(target);40 //这里需要加上元素自身的宽高,因为定位点是元素的左上角41 if(position.left + target.offsetWidth 判断理由很简单,如果有一边的定位是负值,那么元素就不在视窗内。 1 Position.getAbsolute(document, targetNode); //获取元素在文档流中的绝对坐标2 Position.getViewport(targetNode); //获取元素相对于浏览器视窗的坐标3 Position.isViewport(targetNode); //判断元素是否在浏览器视窗内
浏览器兼容性:
IE7 也可以使用,不过结果可能会有一点差异。 扩展:图片懒加载在文章的开始,我们提到过图片懒加载的问题,那么具体需要怎么实现呢?这里只是给出一个思路: 初始状态下不设置 img 的 src,将图片的真实 url 缓存在 Img 标签上,我们可以设置为 data-src ,这样图片就不会加载了,随后给鼠标添加 mousescroll 事情,每次鼠标滚动的时候将进入可视区域的图片的 src 还原,这样也就实现了图片懒加载效果。不过初始状态下需要将页面可视区域的图片先加载出来。 参考文献: 阮一峰 — 用 JavaScript 获取元素页面元素位置 张媛媛 — js实现一个图片懒加载插件 | |||||||||||||||||||||
The above is the detailed content of How to get the coordinates of an element in JavaScript. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 From Websites to Apps: The Diverse Applications of JavaScriptApr 22, 2025 am 12:02 AM
From Websites to Apps: The Diverse Applications of JavaScriptApr 22, 2025 am 12:02 AMJavaScript is widely used in websites, mobile applications, desktop applications and server-side programming. 1) In website development, JavaScript operates DOM together with HTML and CSS to achieve dynamic effects and supports frameworks such as jQuery and React. 2) Through ReactNative and Ionic, JavaScript is used to develop cross-platform mobile applications. 3) The Electron framework enables JavaScript to build desktop applications. 4) Node.js allows JavaScript to run on the server side and supports high concurrent requests.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Use Cases and Applications ComparedApr 21, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Use Cases and Applications ComparedApr 21, 2025 am 12:01 AMPython is more suitable for data science and automation, while JavaScript is more suitable for front-end and full-stack development. 1. Python performs well in data science and machine learning, using libraries such as NumPy and Pandas for data processing and modeling. 2. Python is concise and efficient in automation and scripting. 3. JavaScript is indispensable in front-end development and is used to build dynamic web pages and single-page applications. 4. JavaScript plays a role in back-end development through Node.js and supports full-stack development.
 The Role of C/C in JavaScript Interpreters and CompilersApr 20, 2025 am 12:01 AM
The Role of C/C in JavaScript Interpreters and CompilersApr 20, 2025 am 12:01 AMC and C play a vital role in the JavaScript engine, mainly used to implement interpreters and JIT compilers. 1) C is used to parse JavaScript source code and generate an abstract syntax tree. 2) C is responsible for generating and executing bytecode. 3) C implements the JIT compiler, optimizes and compiles hot-spot code at runtime, and significantly improves the execution efficiency of JavaScript.
 JavaScript in Action: Real-World Examples and ProjectsApr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AM
JavaScript in Action: Real-World Examples and ProjectsApr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AMJavaScript's application in the real world includes front-end and back-end development. 1) Display front-end applications by building a TODO list application, involving DOM operations and event processing. 2) Build RESTfulAPI through Node.js and Express to demonstrate back-end applications.
 JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use CasesApr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use CasesApr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AMThe main uses of JavaScript in web development include client interaction, form verification and asynchronous communication. 1) Dynamic content update and user interaction through DOM operations; 2) Client verification is carried out before the user submits data to improve the user experience; 3) Refreshless communication with the server is achieved through AJAX technology.
 Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation DetailsApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation DetailsApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AMUnderstanding how JavaScript engine works internally is important to developers because it helps write more efficient code and understand performance bottlenecks and optimization strategies. 1) The engine's workflow includes three stages: parsing, compiling and execution; 2) During the execution process, the engine will perform dynamic optimization, such as inline cache and hidden classes; 3) Best practices include avoiding global variables, optimizing loops, using const and lets, and avoiding excessive use of closures.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of UseApr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of UseApr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AMPython is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and ResourcesApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and ResourcesApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AMPython and JavaScript have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of community, libraries and resources. 1) The Python community is friendly and suitable for beginners, but the front-end development resources are not as rich as JavaScript. 2) Python is powerful in data science and machine learning libraries, while JavaScript is better in front-end development libraries and frameworks. 3) Both have rich learning resources, but Python is suitable for starting with official documents, while JavaScript is better with MDNWebDocs. The choice should be based on project needs and personal interests.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools











