 Backend Development
Backend Development C#.Net Tutorial
C#.Net Tutorial Share WebApi2 file and image upload and download function examples
Share WebApi2 file and image upload and download function examplesThis article mainly introduces the WebApi2 file and image upload and download functions. Friends in need can refer to
Asp.Net Framework webapi2 File upload and download The front-end interface is executed using Ajax
1. Project structure
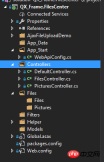
1.App_Start is configured with cross- Domain access to avoid requests that cannot be submitted due to cross-domain issues. The specific cross-domain configuration method is as follows, if you know it, please skip it by yourself.
Cross-domain configuration: NewGet installs dll Microsofg.AspNet.Cors

Then write the cross-domain configuration code in WebApiConfig.cs under the App_Start folder .
public static class WebApiConfig
{
public static void Register(HttpConfiguration config)
{
// Web API configuration and services
// Web API routes
config.MapHttpAttributeRoutes();
// Web API configuration and services
//跨域配置 //need reference from nuget
config.EnableCors(new EnableCorsAttribute("*", "*", "*"));
config.Routes.MapHttpRoute(
name: "DefaultApi",
routeTemplate: "api/{controller}/{id}",
defaults: new { id = RouteParameter.Optional }
);
//if config the global filter input there need not write the attributes
//config.Filters.Add(new App.WebApi.Filters.ExceptionAttribute_DG());
}
}Even if the cross-domain is completed, please test it yourself.
2. Create two new controllers, one PicturesController.cs and one FilesController.cs. Of course, pictures are also files. Here pictures and files are processed in different ways. Because the file upload of the picture method was not successful, the other Find another way. If anyone here has a better way, please feel free to enlighten me!
2. Project code
1. Let’s first talk about the image upload and download controller interface. There is actually nothing to say here, just Get Get the file, the parameter is the full name of the file; Post upload the file; directly upload the code.
using QX_Frame.App.WebApi;
using QX_Frame.FilesCenter.Helper;
using QX_Frame.Helper_DG;
using QX_Frame.Helper_DG.Extends;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Net.Http.Headers;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Web.Http;
/**
* author:qixiao
* create:2017-5-26 16:54:46
* */
namespace QX_Frame.FilesCenter.Controllers
{
public class PicturesController : WebApiControllerBase
{
//Get : api/Pictures
public HttpResponseMessage Get(string fileName)
{
HttpResponseMessage result = null;
DirectoryInfo directoryInfo = new DirectoryInfo(IO_Helper_DG.RootPath_MVC + @"Files/Pictures");
FileInfo foundFileInfo = directoryInfo.GetFiles().Where(x => x.Name == fileName).FirstOrDefault();
if (foundFileInfo != null)
{
FileStream fs = new FileStream(foundFileInfo.FullName, FileMode.Open);
result = new HttpResponseMessage(HttpStatusCode.OK);
result.Content = new StreamContent(fs);
result.Content.Headers.ContentType = new System.Net.Http.Headers.MediaTypeHeaderValue("application/octet-stream");
result.Content.Headers.ContentDisposition = new ContentDispositionHeaderValue("attachment");
result.Content.Headers.ContentDisposition.FileName = foundFileInfo.Name;
}
else
{
result = new HttpResponseMessage(HttpStatusCode.NotFound);
}
return result;
}
//POST : api/Pictures
public async Task<IHttpActionResult> Post()
{
if (!Request.Content.IsMimeMultipartContent())
{
throw new Exception_DG("unsupported media type", 2005);
}
string root = IO_Helper_DG.RootPath_MVC;
IO_Helper_DG.CreateDirectoryIfNotExist(root + "/temp");
var provider = new MultipartFormDataStreamProvider(root + "/temp");
// Read the form data.
await Request.Content.ReadAsMultipartAsync(provider);
List<string> fileNameList = new List<string>();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
long fileTotalSize = 0;
int fileIndex = 1;
// This illustrates how to get the file names.
foreach (MultipartFileData file in provider.FileData)
{
//new folder
string newRoot = root + @"Files/Pictures";
IO_Helper_DG.CreateDirectoryIfNotExist(newRoot);
if (File.Exists(file.LocalFileName))
{
//new fileName
string fileName = file.Headers.ContentDisposition.FileName.Substring(1, file.Headers.ContentDisposition.FileName.Length - 2);
string newFileName = Guid.NewGuid() + "." + fileName.Split('.')[1];
string newFullFileName = newRoot + "/" + newFileName;
fileNameList.Add($"Files/Pictures/{newFileName}");
FileInfo fileInfo = new FileInfo(file.LocalFileName);
fileTotalSize += fileInfo.Length;
sb.Append($" #{fileIndex} Uploaded file: {newFileName} ({ fileInfo.Length} bytes)");
fileIndex++;
File.Move(file.LocalFileName, newFullFileName);
Trace.WriteLine("1 file copied , filePath=" + newFullFileName);
}
}
return Json(Return_Helper.Success_Msg_Data_DCount_HttpCode($"{fileNameList.Count} file(s) /{fileTotalSize} bytes uploaded successfully! Details -> {sb.ToString()}", fileNameList, fileNameList.Count));
}
}
}There may be some code written in the Help class. In fact, it is just to obtain the server root path and create the directory if it is judged that the folder does not exist. The implementation of the code is as follows:
public static string RootPath_MVC
{
get { return System.Web.HttpContext.Current.Server.MapPath("~"); }
}
//create Directory
public static bool CreateDirectoryIfNotExist(string filePath)
{
if (!Directory.Exists(filePath))
{
Directory.CreateDirectory(filePath);
}
return true;
}2. The file upload and download interface is similar to that of pictures.
using QX_Frame.App.WebApi;
using QX_Frame.FilesCenter.Helper;
using QX_Frame.Helper_DG;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Net.Http.Headers;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Http;
/**
* author:qixiao
* create:2017-5-26 16:54:46
* */
namespace QX_Frame.FilesCenter.Controllers
{
public class FilesController : WebApiControllerBase
{
//Get : api/Files
public HttpResponseMessage Get(string fileName)
{
HttpResponseMessage result = null;
DirectoryInfo directoryInfo = new DirectoryInfo(IO_Helper_DG.RootPath_MVC + @"Files/Files");
FileInfo foundFileInfo = directoryInfo.GetFiles().Where(x => x.Name == fileName).FirstOrDefault();
if (foundFileInfo != null)
{
FileStream fs = new FileStream(foundFileInfo.FullName, FileMode.Open);
result = new HttpResponseMessage(HttpStatusCode.OK);
result.Content = new StreamContent(fs);
result.Content.Headers.ContentType = new System.Net.Http.Headers.MediaTypeHeaderValue("application/octet-stream");
result.Content.Headers.ContentDisposition = new ContentDispositionHeaderValue("attachment");
result.Content.Headers.ContentDisposition.FileName = foundFileInfo.Name;
}
else
{
result = new HttpResponseMessage(HttpStatusCode.NotFound);
}
return result;
}
//POST : api/Files
public async Task<IHttpActionResult> Post()
{
//get server root physical path
string root = IO_Helper_DG.RootPath_MVC;
//new folder
string newRoot = root + @"Files/Files/";
//check path is exist if not create it
IO_Helper_DG.CreateDirectoryIfNotExist(newRoot);
List<string> fileNameList = new List<string>();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
long fileTotalSize = 0;
int fileIndex = 1;
//get files from request
HttpFileCollection files = HttpContext.Current.Request.Files;
await Task.Run(() =>
{
foreach (var f in files.AllKeys)
{
HttpPostedFile file = files[f];
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(file.FileName))
{
string fileLocalFullName = newRoot + file.FileName;
file.SaveAs(fileLocalFullName);
fileNameList.Add($"Files/Files/{file.FileName}");
FileInfo fileInfo = new FileInfo(fileLocalFullName);
fileTotalSize += fileInfo.Length;
sb.Append($" #{fileIndex} Uploaded file: {file.FileName} ({ fileInfo.Length} bytes)");
fileIndex++;
Trace.WriteLine("1 file copied , filePath=" + fileLocalFullName);
}
}
});
return Json(Return_Helper.Success_Msg_Data_DCount_HttpCode($"{fileNameList.Count} file(s) /{fileTotalSize} bytes uploaded successfully! Details -> {sb.ToString()}", fileNameList, fileNameList.Count));
}
}
}After implementing the above two controller codes, we need front-end code to debug the docking, the code is as follows.
<!doctype>
<head>
<script src="jquery-3.2.0.min.js"></script>
<!--<script src="jquery-1.11.1.js"></script>-->
<!--<script src="ajaxfileupload.js"></script>-->
<script>
$(document).ready(function () {
var appDomain = "http://localhost:3997/";
$("#btn_fileUpload").click(function () {
/**
* 用ajax方式上传文件 -----------
* */
//-------asp.net webapi fileUpload
//
var formData = new FormData($("#uploadForm")[0]);
$.ajax({
url: appDomain + 'api/Files',
type: 'POST',
data: formData,
async: false,
cache: false,
contentType: false,
processData: false,
success: function (data) {
console.log(JSON.stringify(data));
},
error: function (data) {
console.log(JSON.stringify(data));
}
});
//----end asp.net webapi fileUpload
//----.net core webapi fileUpload
// var fileUpload = $("#files").get(0);
// var files = fileUpload.files;
// var data = new FormData();
// for (var i = 0; i < files.length; i++) {
// data.append(files[i].name, files[i]);
// }
// $.ajax({
// type: "POST",
// url: appDomain+'api/Files',
// contentType: false,
// processData: false,
// data: data,
// success: function (data) {
// console.log(JSON.stringify(data));
// },
// error: function () {
// console.log(JSON.stringify(data));
// }
// });
//--------end net core webapi fileUpload
/**
* ajaxfileupload.js 方式上传文件
* */
// $.ajaxFileUpload({
// type: 'post',
// url: appDomain + 'api/Files',
// secureuri: false,
// fileElementId: 'files',
// success: function (data) {
// console.log(JSON.stringify(data));
// },
// error: function () {
// console.log(JSON.stringify(data));
// }
// });
});
//end click
})
</script>
</head>
<title></title>
<body>
<article>
<header>
<h2 id="article-form">article-form</h2>
</header>
<p>
<form action="/" method="post" id="uploadForm" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" id="files" name="files" placeholder="file" multiple>file-multiple属性可以选择多项<br><br>
<input type="button" id="btn_fileUpload" value="fileUpload">
</form>
</p>
</article>
</body>At this point, all our functions have been implemented, let’s test it:

Visible, file upload Success, returned in the expected format!
Next we test single image upload ->

Then we press the returned address to access the image address.

I found that there is no pressure at all!
Test multi-image upload below ->

Perfect~
At this point, we have implemented WebApi2 file and image upload and download all functions.
Here you need to pay attention to the total size supported by the Web.config configuration upload file. What I configured here is that the maximum supported file size is 1MB
<requestFiltering>
<requestLimits maxAllowedContentLength="1048576" />
</requestFiltering>
<system.webServer>
<handlers>
<remove name="ExtensionlessUrlHandler-Integrated-4.0" />
<remove name="OPTIONSVerbHandler" />
<remove name="TRACEVerbHandler" />
<add name="ExtensionlessUrlHandler-Integrated-4.0" path="*." verb="*" type="System.Web.Handlers.TransferRequestHandler" preCondition="integratedMode,runtimeVersionv4.0" />
</handlers>
<security>
<requestFiltering>
<requestLimits maxAllowedContentLength="1048576" /><!--1MB-->
</requestFiltering>
</security>
</system.webServer>[Related recommendations]
1. ASP.NET Free Video Tutorial
2. Detailed introduction to ASP.NET MVC--routing
3. Detailed Introducing ASP.NET MVC--controller
4. Introducing ASP.NET MVC--View in detail
The above is the detailed content of Share WebApi2 file and image upload and download function examples. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 C# .NET Framework vs. .NET Core/5/6: What's the Difference?May 07, 2025 am 12:06 AM
C# .NET Framework vs. .NET Core/5/6: What's the Difference?May 07, 2025 am 12:06 AM.NETFrameworkisWindows-centric,while.NETCore/5/6supportscross-platformdevelopment.1).NETFramework,since2002,isidealforWindowsapplicationsbutlimitedincross-platformcapabilities.2).NETCore,from2016,anditsevolutions(.NET5/6)offerbetterperformance,cross-
 The Community of C# .NET Developers: Resources and SupportMay 06, 2025 am 12:11 AM
The Community of C# .NET Developers: Resources and SupportMay 06, 2025 am 12:11 AMThe C#.NET developer community provides rich resources and support, including: 1. Microsoft's official documents, 2. Community forums such as StackOverflow and Reddit, and 3. Open source projects on GitHub. These resources help developers improve their programming skills from basic learning to advanced applications.
 The C# .NET Advantage: Features, Benefits, and Use CasesMay 05, 2025 am 12:01 AM
The C# .NET Advantage: Features, Benefits, and Use CasesMay 05, 2025 am 12:01 AMThe advantages of C#.NET include: 1) Language features, such as asynchronous programming simplifies development; 2) Performance and reliability, improving efficiency through JIT compilation and garbage collection mechanisms; 3) Cross-platform support, .NETCore expands application scenarios; 4) A wide range of practical applications, with outstanding performance from the Web to desktop and game development.
 Is C# Always Associated with .NET? Exploring AlternativesMay 04, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Is C# Always Associated with .NET? Exploring AlternativesMay 04, 2025 am 12:06 AMC# is not always tied to .NET. 1) C# can run in the Mono runtime environment and is suitable for Linux and macOS. 2) In the Unity game engine, C# is used for scripting and does not rely on the .NET framework. 3) C# can also be used for embedded system development, such as .NETMicroFramework.
 The .NET Ecosystem: C#'s Role and BeyondMay 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The .NET Ecosystem: C#'s Role and BeyondMay 03, 2025 am 12:04 AMC# plays a core role in the .NET ecosystem and is the preferred language for developers. 1) C# provides efficient and easy-to-use programming methods, combining the advantages of C, C and Java. 2) Execute through .NET runtime (CLR) to ensure efficient cross-platform operation. 3) C# supports basic to advanced usage, such as LINQ and asynchronous programming. 4) Optimization and best practices include using StringBuilder and asynchronous programming to improve performance and maintainability.
 C# as a .NET Language: The Foundation of the EcosystemMay 02, 2025 am 12:01 AM
C# as a .NET Language: The Foundation of the EcosystemMay 02, 2025 am 12:01 AMC# is a programming language released by Microsoft in 2000, aiming to combine the power of C and the simplicity of Java. 1.C# is a type-safe, object-oriented programming language that supports encapsulation, inheritance and polymorphism. 2. The compilation process of C# converts the code into an intermediate language (IL), and then compiles it into machine code execution in the .NET runtime environment (CLR). 3. The basic usage of C# includes variable declarations, control flows and function definitions, while advanced usages cover asynchronous programming, LINQ and delegates, etc. 4. Common errors include type mismatch and null reference exceptions, which can be debugged through debugger, exception handling and logging. 5. Performance optimization suggestions include the use of LINQ, asynchronous programming, and improving code readability.
 C# vs. .NET: Clarifying the Key Differences and SimilaritiesMay 01, 2025 am 12:12 AM
C# vs. .NET: Clarifying the Key Differences and SimilaritiesMay 01, 2025 am 12:12 AMC# is a programming language, while .NET is a software framework. 1.C# is developed by Microsoft and is suitable for multi-platform development. 2..NET provides class libraries and runtime environments, and supports multilingual. The two work together to build modern applications.
 Beyond the Hype: Assessing the Current Role of C# .NETApr 30, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Beyond the Hype: Assessing the Current Role of C# .NETApr 30, 2025 am 12:06 AMC#.NET is a powerful development platform that combines the advantages of the C# language and .NET framework. 1) It is widely used in enterprise applications, web development, game development and mobile application development. 2) C# code is compiled into an intermediate language and is executed by the .NET runtime environment, supporting garbage collection, type safety and LINQ queries. 3) Examples of usage include basic console output and advanced LINQ queries. 4) Common errors such as empty references and type conversion errors can be solved through debuggers and logging. 5) Performance optimization suggestions include asynchronous programming and optimization of LINQ queries. 6) Despite the competition, C#.NET maintains its important position through continuous innovation.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software






