Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >Detailed explanation of how Vue-cli implements cross-domain requests
Detailed explanation of how Vue-cli implements cross-domain requests
- Y2JOriginal
- 2017-05-24 11:32:132552browse
This article mainly introduces the detailed explanation of how to make cross-domain requests for projects created by Vue-cli. The editor thinks it is quite good, so I will share it with you now and give it as a reference. Let’s follow the editor and take a look.
Problem description:
For projects created using Vue-cli, the development address is localhost:8023 and needs to be accessed on localhost:9000 Interface
Analysis reason:
Access between different domain names requires cross-domain to request correctly. There are many cross-domain methods, which usually require background configuration
However, projects created by Vue-cli can directly use theNode.js proxy server to implement cross-domain requests
Solution:
The interface address was originally /form/save, but in order to match the proxy address, add a /api
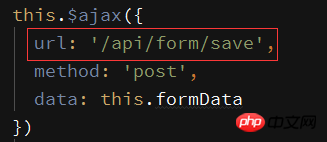
##
axios.defaults.baseURL = '/api'
Add the configuration item proxyTable in the dev of config>index.js:
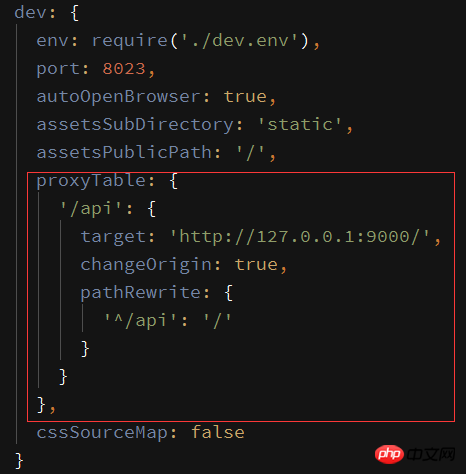
proxyTable: {
'/api': {
target: 'http://127.0.0.1:9000/',
changeOrigin: true,
pathRewrite: {
'^/api': '/'
}
}
},where '/api' is the matching item, and target is the requested address
Because in ajax The prefix '/api' is added to the url, but the original interface does not have this prefix
So you need to use pathRewrite to rewrite the address and convert the prefix '/api' to '/'
If your own interface address has a common prefix like '/api', you can delete pathRewrite
[Related recommendations]
1.
Javacript Free Video TutorialDetailed example of easyUI drop-down list click event Example tutorial of cross-domain webpack development environmentIntroduction to the method of deleting elements in an array using JSTutorial on using the koa2 framework in nodejs6The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of how Vue-cli implements cross-domain requests. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- An in-depth analysis of the Bootstrap list group component
- Detailed explanation of JavaScript function currying
- Complete example of JS password generation and strength detection (with demo source code download)
- Angularjs integrates WeChat UI (weui)
- How to quickly switch between Traditional Chinese and Simplified Chinese with JavaScript and the trick for websites to support switching between Simplified and Traditional Chinese_javascript skills

