Home >Web Front-end >CSS Tutorial >Detailed explanation of the hight attribute in CSS
Detailed explanation of the hight attribute in CSS
- 迷茫Original
- 2017-03-25 14:12:142863browse
Directory structure:
contents structure [-]
hight attribute value type list
| value | description |
| ##auto | Default |
| Absolute length | |
| Relative length | |
| Inherit |
Usage of the % value of height
Definition:
This value is a percentage, which is based on the percentage of the block-level element that contains it.Example:
<!DOCTYPE html><html>
<head>
<title>height.html</title>
<meta name="content-type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"><style>p{
width:50%;
height:50%;
border:1px solid red;}body{
border:1px solid green;
display:block;
height:100px;}</style></head><body><p>I am box with width 50% and height 50%</p></body></html>Readers can press "F12" in the Chrome browser and select "element" to view. Readers can easily Quickly find that the height of e388a4556c0f65e1904146cc1a846bee is exactly 50% of the parent element 6c04bd5ca3fcae76e30b72ad730ca86d.
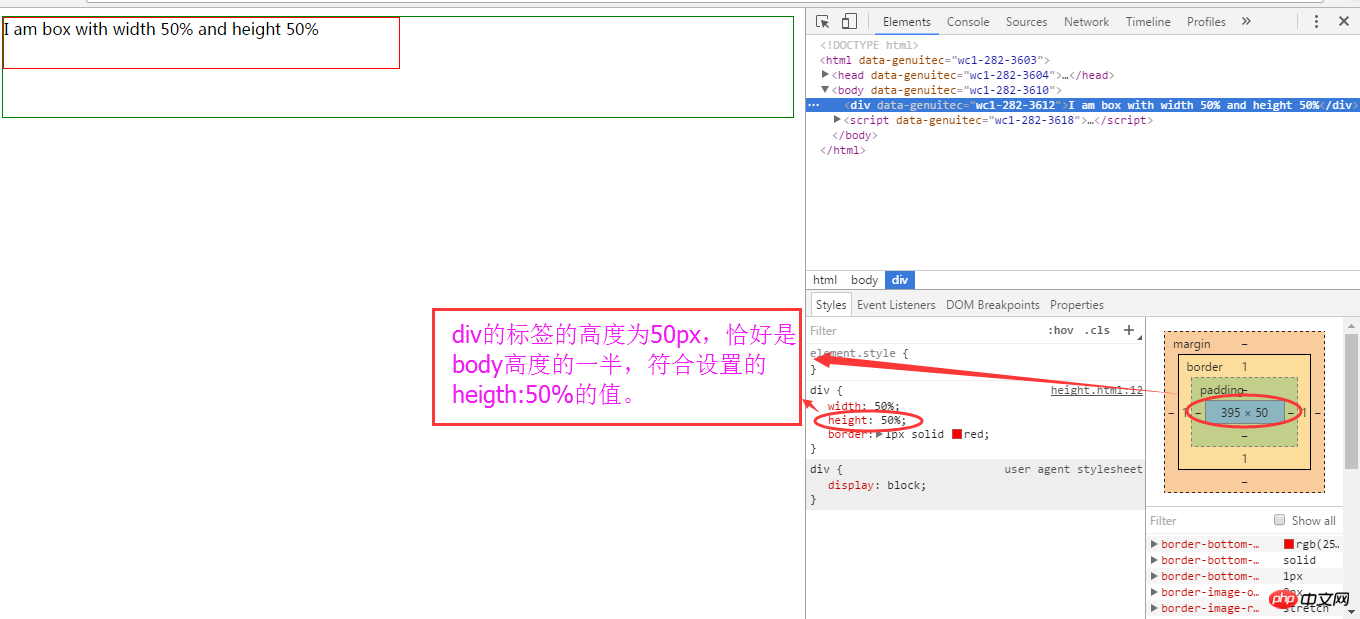
Things to note
In the above example, we verify Understand the usage of the relative value of height. However, readers need to note that if the parent element does not define hight, the height of the child element using percentage will not work. At this time, the height value is equivalent to the auto value, unless it is changed by an absolute value. Here, hight is not defined, which means that height is not written at all, which is different from defining height as 0px. Readers can try the following code:<body id="b" style="width:0px;height:0px;">
<br>
<p id="er" style="width:50%;height:50%;border:1px solid red;"></p>
Then remove the style attribute of the body and try again.
<body id="b">
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the hight attribute in CSS. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Statement:
The content of this article is voluntarily contributed by netizens, and the copyright belongs to the original author. This site does not assume corresponding legal responsibility. If you find any content suspected of plagiarism or infringement, please contact admin@php.cn
Previous article:How to implement dividers using CSSNext article:How to implement dividers using CSS

