1) Use path to draw :
beginPath()——Start a new path;
closePath()——Try to close the existing path by drawing a line connecting the end point of the last line and the initial coordinate;
fill()——Fill with sub The shape described by the path;
isPointInPath(x,y) - Returns true if the specified point is within the shape described by the current path;
lineTo(x,y)——Draw a subpath to the specified coordinates;
moveTo(x,y)——Move to the specified coordinates without drawing a subpath ;
rect(x,y,w,h)——Draw a rectangle with its upper left corner at (x,y), width w, and height h;
stroke()——Draw an outline for the shape described by the sub-path;
<style type="text/css">
canvas{
border:thin solid black;
margin: 4px;
}
body > *{
float: left;
}
</style><canvas id="canvas1" width="500" height="140">
您的浏览器不支持<code>canvas</code>!
</canvas> <script>
//由直线创建路径
var ctx=document.getElementById("canvas1").getContext("2d");
ctx.fillStyle="#136455";
ctx.strokeStyle="blue";
ctx.lineWidth=4;
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(10,10);
ctx.lineTo(110,10);
ctx.lineTo(110,120);
ctx.closePath();
ctx.fill();
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(150,10);
ctx.lineTo(200,10);
ctx.lineTo(200,120);
ctx.lineTo(190,120);
ctx.fill();
ctx.stroke();
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(250,10);
ctx.lineTo(250,120);
ctx.stroke();
</script>
lineCap——Set the style of the end of the line when drawing a line or closed shape;
<canvas id="canvas2" width="500" height="140">
您的浏览器不支持<code>canvas</code>!
</canvas> <script>
//设置lineCap属性
var ctx2=document.getElementById("canvas2").getContext("2d");
ctx2.strokeStyle="red";
ctx2.lineWidth=2;
ctx2.beginPath();
ctx2.moveTo(0,50);
ctx2.lineTo(200,50);
ctx2.stroke();
ctx2.strokeStyle="black";
ctx2.lineWidth=40;
var xpos=50;
var styles=["butt","round","square"];
for(var i=0;i<styles.length;i++){
ctx2.beginPath();
ctx2.lineCap=styles[i];
ctx2.moveTo(xpos,50);
ctx2.lineTo(xpos,150);
ctx2.stroke();
xpos+=50;
}
</script>
<canvas id="canvas3" width="500" style="max-width:90%">
您的浏览器不支持<code>canvas</code>!
</canvas> <script>
//用Rect方法绘制矩形
var ctx3=document.getElementById("canvas3").getContext("2d");
ctx3.fillStyle="yellow";
ctx3.strokeStyle="black";
ctx3.lineWidth=4;
ctx3.beginPath();
ctx3.moveTo(110,10);
ctx3.lineTo(110,100);
ctx3.lineTo(10,10);
ctx3.closePath();
ctx3.rect(110,10,100,90);
ctx3.rect(110,100,130,30);
ctx3.fill();
ctx3.stroke();
</script>
2) Draw an arc:
arc(x,y,rad,startAngle,end Angle,direction)——Draw an arc to (x, y), the radius is rad, the starting angle is startAngle, and the end angle is endAngle. The optional parameter direction specifies the direction of the arc;
arcTo(x1,y1,x2,y2,rad)——Drawing An arc with a radius of rad, passing through (x1, y1) and ending at (x2, y2);
<canvas id="canvas4" width="500" height="140">
您的浏览器不支持<code>canvas</code>!
</canvas> <script>
//使用arcTo方法
var ctx4=document.getElementById("canvas4").getContext("2d");
var point1=[100,10];
var point2=[200,10];
var point3=[200,110];
ctx4.fillStyle="yellow";
ctx4.strokeStyle="black";
ctx4.lineWidth=4;
ctx4.beginPath();
ctx4.moveTo(point1[0],point1[1]);
ctx4.arcTo(point2[0],point2[1],point3[0],point3[1],100);
ctx4.stroke();
drawPoint(point1[0],point1[1]);
drawPoint(point2[0],point2[1]);
drawPoint(point3[0],point3[1]);
ctx4.beginPath();
ctx4.moveTo(point1[0],point1[1]);
ctx4.lineTo(point2[0],point2[1]);
ctx4.lineTo(point3[0],point3[1]);
ctx4.stroke();
function drawPoint(x,y){
ctx4.lineWidth=1;
ctx4.strokeStyle="red";
ctx4.strokeRect(x-2,y-2,4,4);
}
</script>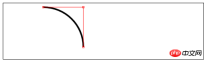
<canvas id="canvas5" width="500" style="max-width:90%">
您的浏览器不支持<code>canvas</code>!
</canvas> <script>
//响应鼠标移动绘制圆弧
var canvasElem = document.getElementById("canvas5");
var ctx5 = canvasElem.getContext("2d");
var point1 = [100, 10];
var point2 = [200, 10];
var point3 = [200, 110];
draw();
canvasElem.onmousemove = function (e) {
if (e.ctrlKey) {
point1 = [e.clientX, e.clientY];
} else if(e.shiftKey) {
point2 = [e.clientX, e.clientY];
} else {
point3 = [e.clientX, e.clientY];
}
ctx5.clearRect(0, 0, 540, 140);
draw();
}
function draw() {
ctx5.fillStyle = "yellow";
ctx5.strokeStyle = "black";
ctx5.lineWidth = 4;
ctx5.beginPath();
ctx5.moveTo(point1[0], point1[1]);
ctx5.arcTo(point2[0], point2[1], point3[0], point3[1], 50);
ctx5.stroke();
drawPoint(point1[0], point1[1]);
drawPoint(point2[0], point2[1]);
drawPoint(point3[0], point3[1]);
ctx5.beginPath();
ctx5.moveTo(point1[0], point1[1]);
ctx5.lineTo(point2[0], point2[1]);
ctx5.lineTo(point3[0], point3[1]);
ctx5.stroke();
}
function drawPoint(x, y) {
ctx5.lineWidth = 1;
ctx5.strokeStyle = "red";
ctx5.strokeRect(x -2, y-2, 4, 4);
}
</script>
<canvas id="canvas6" width="500" style="max-width:90%">
您的浏览器不支持<code>canvas</code>!
</canvas> <script>
//使用arc方法
var ctx6=document.getElementById("canvas6").getContext("2d");
ctx6.fillStyle="yellow";
ctx6.lineWidth=3;
ctx6.beginPath();
ctx6.arc(70,70,60,0,Math.PI,true);
ctx6.stroke();
ctx6.beginPath();
ctx6.arc(200,70,60,Math.PI/2,Math.PI/4,false);
ctx6.fill();
ctx6.stroke();
ctx6.beginPath();
var val=0;
for(var i=0;i<4;i++){
ctx6.arc(350,70,60,val,val+Math.PI/4,false);
val+=Math.PI/2;
}
ctx6.closePath();
ctx6.fill();
ctx6.stroke();
</script>
3) Draw Bezier curve
bezierCurveTo(cx1,cy1,cx2, cy2,x,y)——Draw a Bezier curve to point (x,y), the control points are (cx1,cy1) and (cx2,cy2);
quadraticCurveTo(cx,xy,x,y)——Draw a quadratic Bezier curve to point (x,y), the control point is (cx,cy);
<canvas id="canvas" width="500" height="140">
Your browser doesn't support the <code>canvas</code> element
</canvas> <script>
var canvasElem = document.getElementById("canvas");
var ctx = canvasElem.getContext("2d");
var startPoint = [50, 100];
var endPoint = [400, 100];
var cp1 = [250, 50];
var cp2 = [350, 50];
canvasElem.onmousemove = function(e) {
if (e.shiftKey) {
cp1 = [e.clientX, e.clientY];
} else if (e.ctrlKey) {
cp2 = [e.clientX, e.clientY];
}
ctx.clearRect(0, 0, 500, 140);
draw();
}
draw();
function draw() {
ctx.lineWidth = 3;
ctx.strokeStyle = "black";
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(startPoint[0], startPoint[1]);
ctx.bezierCurveTo(cp1[0], cp1[1], cp2[0], cp2[1],
endPoint[0], endPoint[1]);
ctx.stroke();
ctx.lineWidth = 1;
ctx.strokeStyle = "red";
var points = [startPoint, endPoint, cp1, cp2];
for (var i = 0; i < points.length; i++) {
drawPoint(points[i]);
}
drawLine(startPoint, cp1);
drawLine(endPoint, cp2);
}
function drawPoint(point) {
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.strokeRect(point[0] -2, point[1] -2, 4, 4);
}
function drawLine(from, to) {
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(from[0], from[1]);
ctx.lineTo(to[0], to[1]);
ctx.stroke();
}
</script>
<canvas id="canvas" width="500" style="max-width:90%">
Your browser doesn't support the <code>canvas</code> element
</canvas> <script>
//绘制二次贝塞尔曲线
var canvasElem = document.getElementById("canvas");
var ctx = canvasElem.getContext("2d");
var startPoint = [50, 100];
var endPoint = [400, 100];
var cp1 = [250, 50];
canvasElem.onmousemove = function(e) {
if (e.shiftKey) {
cp1 = [e.clientX, e.clientY];
}
ctx.clearRect(0, 0, 500, 140);
draw();
}
draw();
function draw() {
ctx.lineWidth = 3;
ctx.strokeStyle = "black";
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(startPoint[0], startPoint[1]);
ctx.quadraticCurveTo(cp1[0], cp1[1], endPoint[0], endPoint[1]);
ctx.stroke();
ctx.lineWidth = 1;
ctx.strokeStyle = "red";
var points = [startPoint, endPoint, cp1];
for (var i = 0; i < points.length; i++) {
drawPoint(points[i]);
}
drawLine(startPoint, cp1);
drawLine(endPoint, cp1);
}
function drawPoint(point) {
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.strokeRect(point[0] -2, point[1] -2, 4, 4);
}
function drawLine(from, to) {
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(from[0], from[1]);
ctx.lineTo(to[0], to[1]);
ctx.stroke();
}
</script>
4) Create a clipping area
clip()——Create a new clipping area;
##
<canvas id="canvas7" width="500" height="140">
您的浏览器不支持<code>canvas</code>!
</canvas>rrree
 5) Draw text:
5) Draw text:
fillText(
strokeText(
font——设置绘制文本时使用的字体;
textAlign——设置文本的对齐方式:start、end、left、right、center;
textBaseline——设置文本的基线:top、hanging、middle、alphabetic、ideographic、bottom;
6)使用特效和转换:
6.1)使用阴影:
shadowBlur——设置阴影的模糊程度;
shadowColor——设置阴影的颜色;
shadowOffsetX——设置阴影的水平偏移量;
shadowOffsetY——设置阴影的垂直偏移量;
<canvas id="canvas8" width="500" height="140">
您的浏览器不支持<code>canvas</code>!
</canvas> <script>
//给图形和文本应用阴影
var ctx8=document.getElementById("canvas8").getContext("2d");
ctx8.fillStyle="lightgrey";
ctx8.strokeStyle="black";
ctx8.lineWidth=3;
ctx8.shadowOffsetX=5;
ctx8.shadowOffsetY=5;
ctx8.shadowBlur=5;
ctx8.shadowColor="grey";
ctx8.beginPath();
ctx8.arc(420,70,50,0,Math.PI,true);
ctx8.stroke();
ctx8.beginPath();
ctx8.arc(420,80,40,0,Math.PI,false);
ctx8.fill();
ctx8.font="100px sans-serif";
ctx8.fillText("hello",50,100);
ctx8.strokeText("hello",50,100);
</script>
6.2)使用透明度:
globalAlpha——给文本和图形设置透明度(从0到1);
<canvas id="canvas9" width="300" height="120">
您的浏览器不支持<code>canvas</code>!
</canvas> <script>
//使用globalAlpha属性,设置透明度
var ctx9=document.getElementById("canvas9").getContext("2d");
ctx9.fillStyle="lightgrey";
ctx9.strokeStyle="black";
ctx9.lineWidth=3;
ctx9.font="100px sans-serif";
ctx9.fillText("hello",10,100);
ctx9.strokeText("hello",10,100);
ctx9.fillStyle="red";
ctx9.globalAlpha=0.5;
ctx9.fillRect(10,10,240,100);
</script>
6.3)使用合成:
globalCompositeOperation——与透明度属性结合使用,来控制图形和文本在画布上绘制的方式;
globalCompositeOperation允许的值:
=copy——将来源绘制于目标之上,忽略一切透明度设置;
=source-atop——在两个图像都不透明处显示来源图像,
目标图像不透明但来源图像透明处显示目标图像,其它位置显示为透明;
=source-in——来源图像和目标图像都不透明处显示来源图像。其它位置显示为透明;
=source-out——来源图像不透明但目标图像透明处显示来源图像。其它位置显示为透明;
=source-over——来源图像不透明处显示来源图像。其它位置显示目标图像;
=destination-atop——与source-atop相同,但用目标图像替代来源图像,反之亦然;
=destination-in——与source-in相同,但用目标图像替代来源图像,反之亦然;
=destination-over——与source-over相同,但用目标图像替代来源图像,反之亦然;
=destination-out——与source-out相同,但用目标图像替代来源图像,反之亦然;
=lighter——显示来源图像与目标图像的总和,颜色值限制最高255(100%);
=xor——对来源图像和目标图像执行异或运算;
<canvas id="canvas10" width="300" height="120">
您的浏览器不支持<code>canvas</code>!
</canvas>
<label>Comosition Value:</label>
<select id="list">
<option>copy</option>
<option>destination-atop</option>
<option>destination-in</option>
<option>destination-over</option>
<option>destination-out</option>
<option>lighter</option>
<option>source-atop</option>
<option>source-in</option>
<option>source-out</option>
<option>source-over</option>
<option>xor</option>
</select> <script>
//使用globalCompositeOperation属性
var ctx10=document.getElementById("canvas10").getContext("2d");
ctx10.fillStyle="lightgrey";
ctx10.strokeStyle="black";
ctx10.lineWidth=3;
var compVal="copy";
document.getElementById("list").onchange=function(e){
compVal= e.target.value;
draw();
}
draw();
function draw(){
ctx10.clearRect(0,0,300,120);
ctx10.globalAlpha=1.0;
ctx10.font="100px sans-serif";
ctx10.fillText("hello",10,100);
ctx10.strokeText("hello",10,100);
ctx10.globalCompositeOperation=compVal;
ctx10.fillStyle="red";
ctx10.globalAlpha=0.5;
ctx10.fillRect(100,10,150,100);
}
</script>
6.4)使用变换:
scale(
rotate(
translate(
transform(a,b,c,d,e,f)——合并现有的变换和a-f值所指定的矩阵;
setTansform(a,b,c,d,e,f)——用a-f值所指定的矩阵替换现有的变换;
<canvas id="canvas11" width="400" height="200">
您的浏览器不支持<code>canvas</code>!
</canvas> <script>
//使用变换
var ctx11=document.getElementById("canvas11").getContext("2d");
ctx11.fillStyle="lightgrey";
ctx11.strokeStyle="black";
ctx11.lineWidth=3;
ctx11.clearRect(0,0,300,120);
ctx11.globalAlpha=1.0;
ctx11.font="100px sans-serif";
ctx11.fillText("hello",10,100);
ctx11.strokeText("hello",10,100);
ctx11.scale(1.3,1.3);
ctx11.translate(100,-50);
ctx11.rotate(0.5);
ctx11.fillStyle="red";
ctx11.globalAlpha=0.5;
ctx11.fillRect(100,10,150,100);
ctx11.strokeRect(0,0,300,200);
</script>
The above is the detailed content of Detailed code explanation of HTML5 canvas advanced code (picture). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 HTML5 and H5: Understanding the Common UsageApr 22, 2025 am 12:01 AM
HTML5 and H5: Understanding the Common UsageApr 22, 2025 am 12:01 AMThere is no difference between HTML5 and H5, which is the abbreviation of HTML5. 1.HTML5 is the fifth version of HTML, which enhances the multimedia and interactive functions of web pages. 2.H5 is often used to refer to HTML5-based mobile web pages or applications, and is suitable for various mobile devices.
 HTML5: The Building Blocks of the Modern Web (H5)Apr 21, 2025 am 12:05 AM
HTML5: The Building Blocks of the Modern Web (H5)Apr 21, 2025 am 12:05 AMHTML5 is the latest version of the Hypertext Markup Language, standardized by W3C. HTML5 introduces new semantic tags, multimedia support and form enhancements, improving web structure, user experience and SEO effects. HTML5 introduces new semantic tags, such as, ,, etc., to make the web page structure clearer and the SEO effect better. HTML5 supports multimedia elements and no third-party plug-ins are required, improving user experience and loading speed. HTML5 enhances form functions and introduces new input types such as, etc., which improves user experience and form verification efficiency.
 H5 Code: Writing Clean and Efficient HTML5Apr 20, 2025 am 12:06 AM
H5 Code: Writing Clean and Efficient HTML5Apr 20, 2025 am 12:06 AMHow to write clean and efficient HTML5 code? The answer is to avoid common mistakes by semanticizing tags, structured code, performance optimization and avoiding common mistakes. 1. Use semantic tags such as, etc. to improve code readability and SEO effect. 2. Keep the code structured and readable, using appropriate indentation and comments. 3. Optimize performance by reducing unnecessary tags, using CDN and compressing code. 4. Avoid common mistakes, such as the tag not closed, and ensure the validity of the code.
 H5: How It Enhances User Experience on the WebApr 19, 2025 am 12:08 AM
H5: How It Enhances User Experience on the WebApr 19, 2025 am 12:08 AMH5 improves web user experience with multimedia support, offline storage and performance optimization. 1) Multimedia support: H5 and elements simplify development and improve user experience. 2) Offline storage: WebStorage and IndexedDB allow offline use to improve the experience. 3) Performance optimization: WebWorkers and elements optimize performance to reduce bandwidth consumption.
 Deconstructing H5 Code: Tags, Elements, and AttributesApr 18, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Deconstructing H5 Code: Tags, Elements, and AttributesApr 18, 2025 am 12:06 AMHTML5 code consists of tags, elements and attributes: 1. The tag defines the content type and is surrounded by angle brackets, such as. 2. Elements are composed of start tags, contents and end tags, such as contents. 3. Attributes define key-value pairs in the start tag, enhance functions, such as. These are the basic units for building web structure.
 Understanding H5 Code: The Fundamentals of HTML5Apr 17, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Understanding H5 Code: The Fundamentals of HTML5Apr 17, 2025 am 12:08 AMHTML5 is a key technology for building modern web pages, providing many new elements and features. 1. HTML5 introduces semantic elements such as, , etc., which enhances web page structure and SEO. 2. Support multimedia elements and embed media without plug-ins. 3. Forms enhance new input types and verification properties, simplifying the verification process. 4. Offer offline and local storage functions to improve web page performance and user experience.
 H5 Code: Best Practices for Web DevelopersApr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
H5 Code: Best Practices for Web DevelopersApr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AMBest practices for H5 code include: 1. Use correct DOCTYPE declarations and character encoding; 2. Use semantic tags; 3. Reduce HTTP requests; 4. Use asynchronous loading; 5. Optimize images. These practices can improve the efficiency, maintainability and user experience of web pages.
 H5: The Evolution of Web Standards and TechnologiesApr 15, 2025 am 12:12 AM
H5: The Evolution of Web Standards and TechnologiesApr 15, 2025 am 12:12 AMWeb standards and technologies have evolved from HTML4, CSS2 and simple JavaScript to date and have undergone significant developments. 1) HTML5 introduces APIs such as Canvas and WebStorage, which enhances the complexity and interactivity of web applications. 2) CSS3 adds animation and transition functions to make the page more effective. 3) JavaScript improves development efficiency and code readability through modern syntax of Node.js and ES6, such as arrow functions and classes. These changes have promoted the development of performance optimization and best practices of web applications.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor





