CSS practical tutorial on fixing the footer to the bottom of the page
This article mainly introduces the actual CSS practice of fixing the footer at the bottom of the page. Pay attention to the issue of CSS clearing floats. Friends in need can refer to
Footer position issues
The footer of a web page is where help links and copyright information are usually placed. The footer should naturally be located at the bottom of the page, but according to general practice, if the web page content before the footer is relatively small, or a monitor with a large vertical resolution is used, the footer may not appear to be on the page. The situation at the bottom is as shown below. 
Since the footer is basically a common part of all pages of a website, the amount of content on different pages varies, so it is indeed possible that some pages may not have enough content. Such a question. In addition, especially for footers that contain background colors, this problem will seriously affect the appearance.
So, we hope that the footer can be accurately located at the bottom regardless of the content of the web page.
How to fix the footer to the bottom
Is absolute positioning feasible?
Maybe someone has thought of setting the footer to position:fixed and then positioning it at the bottom. Regardless of IE6, which does not support this attribute value, in effect, if the content of the web page itself is sufficient, this way of writing will cause the footer to appear at the bottom of the browser from the beginning, and when scrolling the web page, the footer will appear at the bottom of the browser. will remain in its original position. This effect is obviously not suitable for most websites.
As you can imagine, the effect we need is:
When the web page has a lot of content, you can only see the bottom footer when you scroll to the bottom.
When the content of the web page is small, the footer is still located at the bottom of the entire page, and the rest is left blank.
Conventional, simple implementation method
CSS Sticky Footer provides a reasonable implementation method for fixing the footer at the bottom. However, on the one hand, this is an English site, and on the other hand, the writing method it provides can still be improved, so this article will refer to its content and give a reasonable implementation method.
First you need such an html structure:
<body>
<p class="wrapper">
<!--网页内容-->
<p class="footer_placeholder"></p>
</p>
<p class="footer">
<!--页脚-->
</p>
</body>
p.wrapper is the outer container for all content in the web page except the footer, and the footer p.footer It's on the same level as it. p.footer_placeholder must be placed at the end of all content on the web page, that is, as the last child element of p.wrapper. Its function will be explained later.
Next write the css and explain it in turn.
html, body{height:100%;}
When the content of the web page is insufficient, the actual height of the body and html may be smaller than the visible range of the browser, so write the height of 100% for the body and html. In addition, the following direct child elements will also use the percentage writing method. The percentage writing method must be effective only when the direct parent element has a certain height definition.
.wrapper{
min-height:100%;
_height:100%;
margin-bottom:-120px; /*假定页脚的高度为120px*/
}
All web content is in this p.wrapper, and the minimum height is defined (IE6 uses a hack). Since the parent element of this element is the body that defines 100% height, no matter Regardless of the content, the height of the p.wrapper element will occupy the entire visible range of the browser. Then, set equal negative values for the bottom margin according to the height of the footer, so that the footer will appear exactly at the end of the page content.
.footer, .footer_placeholder{height:120px;} /*假定页脚的高度为120px*/
p.footer_placeholder, as literally, the placeholder element of the footer, it is just an empty p, the definition height is the same as the footer, it exists to give the footer Leave a spot. Without it, something like this might happen ↓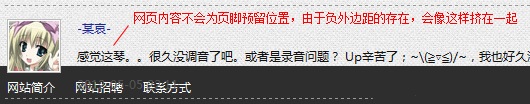
At this point, the footer fixed at the bottom has been implemented. The sum of the css parts is:
html, body{height:100%;}
.wrapper{
min-height:100%;
_height:100%;
margin-bottom:-120px; /*假定页脚的高度为120px*/
}
.footer, .footer_placeholder{height:120px;}
如果还需要考虑css初始化和清理浮动,可能你还需要添加下面这部分css:
body{margin:0;}
.footer_placeholder{clear:both;}The above is the detailed content of CSS practical tutorial on fixing the footer to the bottom of the page. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Iterating a React Design with Styled ComponentsApr 21, 2025 am 11:29 AM
Iterating a React Design with Styled ComponentsApr 21, 2025 am 11:29 AMIn a perfect world, our projects would have unlimited resources and time. Our teams would begin coding with well thought out and highly refined UX designs.
 Oh, the Many Ways to Make Triangular Breadcrumb Ribbons!Apr 21, 2025 am 11:26 AM
Oh, the Many Ways to Make Triangular Breadcrumb Ribbons!Apr 21, 2025 am 11:26 AMOh, the Many Ways to Make Triangular Breadcrumb Ribbons
 SVG Properties in CSS GuideApr 21, 2025 am 11:21 AM
SVG Properties in CSS GuideApr 21, 2025 am 11:21 AMSVG has its own set of elements, attributes and properties to the extent that inline SVG code can get long and complex. By leveraging CSS and some of the forthcoming features of the SVG 2 specification, we can reduce that code for cleaner markup.
 A Few Functional Uses for Intersection Observer to Know When an Element is in ViewApr 21, 2025 am 11:19 AM
A Few Functional Uses for Intersection Observer to Know When an Element is in ViewApr 21, 2025 am 11:19 AMYou might not know this, but JavaScript has stealthily accumulated quite a number of observers in recent times, and Intersection Observer is a part of that
 Revisting prefers-reduced-motionApr 21, 2025 am 11:18 AM
Revisting prefers-reduced-motionApr 21, 2025 am 11:18 AMWe may not need to throw out all CSS animations. Remember, it’s prefers-reduced-motion, not prefers-no-motion.
 How to Get a Progressive Web App into the Google Play StoreApr 21, 2025 am 11:10 AM
How to Get a Progressive Web App into the Google Play StoreApr 21, 2025 am 11:10 AMPWA (Progressive Web Apps) have been with us for some time now. Yet, each time I try explaining it to clients, the same question pops up: "Will my users be
 The Simplest Ways to Handle HTML IncludesApr 21, 2025 am 11:09 AM
The Simplest Ways to Handle HTML IncludesApr 21, 2025 am 11:09 AMIt's extremely surprising to me that HTML has never had any way to include other HTML files within it. Nor does there seem to be anything on the horizon that
 Change Color of SVG on HoverApr 21, 2025 am 11:04 AM
Change Color of SVG on HoverApr 21, 2025 am 11:04 AMThere are a lot of different ways to use SVG. Depending on which way, the tactic for recoloring that SVG in different states or conditions — :hover,


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool





