Home >Web Front-end >H5 Tutorial >Quick start guide for calling HTML5's Canvas API to draw graphics
Quick start guide for calling HTML5's Canvas API to draw graphics
- 黄舟Original
- 2017-02-24 14:02:571652browse
1. Canvas element
The following html code defines a canvas element.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Canvas快速入门</title>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
</head>
<body>
<p>
<canvas id="mainCanvas" width="640" height="480"></canvas>
</p>
</body>
</html>
Access the canvas element through the following Javascript statement:
//DOM写法
window.onload = function () {
var canvas = document.getElementById("mainCanvas");
var context = canvas.getContext("2d");
};
//jQuery写法
$(document).ready(function () {
var canvas = $("#mainCanvas");
var context = canvas.get(0).getContext("2d");
});
//接下来就可以调用context的方法来调用绘图API
2. Basic API
2.1 Coordinate system
The Canvas 2D rendering context uses a flat Cartesian coordinate system, with the upper left corner as the origin (0,0), and 1 unit of the coordinate system is equivalent to 1 pixel of the screen. The details are as follows: 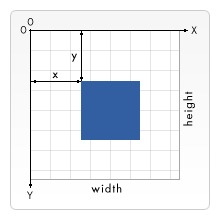
##2.2 Draw basic graphics2.2.1 Rectangle
//绘制一个填充矩形
context.fillRect(x, y, width, height)
//绘制一个边框矩形
context.strokeRect(x, y, width, height)
//清除一个矩形区域
context.clearRect(x, y, width, height)
2.2.2 Lines
There are some differences between drawing lines and drawing graphics. Lines are actually called paths. To draw a simple path, you must first call the beginPath method, then call moveTo to set the starting point coordinates of the path, then call lineTo to set the end point coordinates of the line segment (can be set multiple times), and then call closePath to complete the path drawing. Finally, call stroke to draw the outline (or call fill to fill the path). The following is an example:
//示例
context.beginPath(); //开始路径
context.moveTo(40, 40); //移动到点(40,40)
context.lineTo(300, 40); //画线到点(300,30)
context.lineTo(40, 300); //画线到点(40,300)
context.closePath(); //结束路径
context.stroke(); //绘制轮廓
//或者填充用context.fill();
2.2.3 Circle
Canvas actually does not have a special method for drawing a circle. You can simulate a circle by drawing an arc. Since an arc is a path, the API for drawing arcs should be included between beginPath and closePath.
2.3 Style2.3.1 Modify line color
var color;
//指定RGB值
color = "rgb(255, 0, 0)";
//指定RGBA值(最后一个参数为alpha值,取值0.0~1.0)
color = "rgba(255, 0, 0, 1)";
//指定16进制码
color = "#FF0000";
//用单词指定
color = "red";
//设置填充颜色
context.fillStyle = color;
//设置边框颜色
context.strokeStyle = color;
2.3.2 Modify line width
//指定线宽值
var value= 3;
//设置边框颜色
context.linewidth = value;
2.4 Draw text
//指定字体样式
context.font = "italic 30px 黑体";
//在点(40,40)处画文字
context.fillText("Hello world!", 40, 40);
2.5 Draw image
Drawing Before the image, the image needs to be defined and loaded.
var img = new Image();
img.src = "myImage.png";
img.onload = function () {
//图像加载完毕执行
};
The following is the drawImage API explanation:
//在(x,y)出绘制图像image
context.drawImage(image, x, y)
//在(x,y)出绘制width*height的图像image
context.drawImage(image, x, y, width, height)
//在image的(sx,sy)处截取sWidth*sHeight的图像,在(dx,dy)处绘制dWidth*dHeight的图像
context.drawImage(image, sx, sy, sWidth, sHeight, dx, dy, dWidth, dHeight)
3. Advanced features3.1 Make Canvas fill the browser window
The simplest way is to set the width and height of the canvas element exactly to the width and height of the browser window, and use CSS to eliminate the white space. CSS code:
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
html, body {
height: 100%;
width: 100%;
}
canvas {
display: block;
}Javascript code: function resizeCanvas() {
//canvas由jQuery获取
canvas.attr("width", $(window).get(0).innerWidth);
canvas.attr("height", $(window).get(0).innerHeight);
context.fillRect(0, 0, canvas.width(), canvas.height());
}
$(window).resize(resizeCanvas);
resizeCanvas();
3.2 Drawing status
In canvas, drawing status The graph refers to the entire set of properties that describe the appearance of the 2D rendering context at a certain moment, including: transformation matrix, clipping area, globalAlpha, globalCompositeOperation, strokeStyle, fillStyle, lineWidth, lineCap, lineJoin, miterLimit, shadowOffsetX, shadowOffsetY, shadowBlur, shadowColor, font, textAlign and textBaseline. When you need to change the global state of the canvas, you generally save the current state first - call the save method to push the state into the drawing state stack). After completing the operation, call the restore method to restore the drawing state.
//示例
context.save();
context.globalAlpha = 0.5;
context.fillRect(0, 0, 200, 100);
context.restore();
3.3 Transformation3.3.1 Translation
Moves the origin of the 2D rendering context from one position to another. Note that what is moved here is the coordinate origin, which is the global drawing position. The API is as follows:
//将坐标原点移动到(x,y)
context.translate(x, y)
3.3.2 Zoom
//将全局横纵尺寸缩放至x,y倍(即在原有数值乘上倍乘因子)
context.scale(x, y)
3.3.3 Rotation
//将画布绕着原点旋转radius弧度
context.rotate(radius) The above is the content of the quick start guide for calling HTML5’s Canvas API to draw graphics. For more related content, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website (www.php.cn)! Related articles
See more- AlloyTouch full-screen scrolling plug-in creates a smooth H5 page in 30 seconds
- HTML5 actual combat and analysis of touch events (touchstart, touchmove and touchend)
- Detailed explanation of image drawing examples in HTML5 canvas 9
- Regular expressions and new HTML5 elements
- How to combine NodeJS and HTML5 to drag and drop multiple files to upload to the server

