Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >Detailed explanation of JavaScript time formatting_javascript skills
Detailed explanation of JavaScript time formatting_javascript skills
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOriginal
- 2016-05-16 15:23:551460browse
Thanks to a senior for writing the JS format date and time JS code, it is very good and powerful! ! !
Foreword:
Although js provides various different attribute methods for obtaining time Date objects, such as: getDate method | getDay method | getFullYear method | getHours method... etc., it does not provide a method like Java does. It allows users to format the specified time object according to the template (pattern) provided by themselves, so I have encapsulated a small method, just for everyone to laugh at -.-. If you have good suggestions, please generously recommend it.
Knowledge points used:
• arguments: This object represents the parameters of the function being executed and the function that calls it. It cannot be created explicitly. Although it has a length attribute and can be retrieved using the "[]" syntax like an array, it is not an array.
•typeof object: operator, returns a string used to represent the data type of the expression. Six possibilities: "number," "string," "boolean," "object," "function," and "undefined."
• object.constructor: Represents a function that creates an object. object must be the name of an object or function. The underlying data does not have this attribute.
• exec method: Runs a search in a string using a regular expression pattern and returns an array containing the results of the search. If no match is found, it returns null. Matching elements of the same type will not appear repeatedly in the array.
• str.split(Rex|str): Use a regular object or substring to split a string into substrings, and then return the result as a string array.
• throw Error('msg'): Throw an Error with Message information. throw can be followed by any expression.
• There are also some usages of for..in, ternary operator, substr, which I won’t go into, they are relatively simple.
Code snippet:
/**
* ***js时间日期格式化*** <br>
* <p>
* 模版字符串采用严谨格式,超出则会抛出异常,且每类格式只可出现一次,如:yyyy-mm-yyyy 格式会抛异常
* </p>
* y-年 length: 2/4位 <br>
* q-季度 length: 1位 <br>
* M-月 length: 1~2位 <br>
* d-日 length: 1~2位 <br>
* H-时 length: 1~2位24小时制,h:12小时制 <br>
* m-分 length: 1~2位 <br>
* s-秒 length: 1~2位 <br>
* S-毫秒 length: 固定1位
* @param {Date类型对象} date
* @param {String类型模板字符串} fmt
* @return 格式化后时间日期字符串
* @author lyt
* blongs: http://www.cnblogs.com/liuyitian/
*/
function DateFormat(date, fmt){
if (arguments.length != 2) // 参数个数校验
throw Error('arguments长度不合法');
if (!date || (typeof date != 'object') || (d.constructor != Date)) // 参数合法性校验
throw Error(arguments[0] + ':类型不为Date类型');
if (/H+/.test(fmt) && /h+/.test(fmt))
throw Error("小时格式错误,同类型只能连续出现一次!");
/* 模板参数校验,正则验证方法 */
var verify = function(Rex ){
var arr = new RegExp(Rex).exec(fmt); // 获得匹配结果数组
if (!arr) // 匹配失败返回
return "";
if (fmt.split(Rex).length > 2) // 同一类型间隔出现多次
throw Error("fmt格式错误:同类型只能连续出现一次!");
return arr[0];
};
/**
* 提供月、天、时、分、秒通用匹配替换
* @param {对象o属性key} r
* @param {r对应正则对象} rex
**/
var common = function(r, rex) {
if(len !=1 && len !=2)
throw Error("月份格式错误:M只能出现1/2次");
len == 2 ? fmt=fmt.replace(rex, o[r].length==1 ? "0"+o[r] : o[r]) : fmt=fmt.replace(rex, o[r]);
}
var o = { // 数据存储对象
"y+": date.getFullYear() + "", // 年
"q+": Math.floor((date.getMonth() + 3) / 3), // 季度
"M+": date.getMonth() + 1 + "", // 月
"d+": date.getDate() + "", // 日
"H+": date.getHours() + "", // 24时
"h+": date.getHours() + "", // 12时
"m+": date.getMinutes() + "", // 分
"s+": date.getSeconds() + "", // 秒
"S+": date.getMilliseconds() // 毫秒
}
for(var r in o) {
var rex, len, temp;
rex = new RegExp(r);
temp = verify(rex); // 匹配所得字符串
len = temp.length; // 长度
if(!len || len == 0)
continue;
if(r == "y+") {
if(len !=2 && len != 4)
throw Error("年份格式错误:y只能出现2/4次");
len == 2 ? fmt=fmt.replace(rex, o[r].substr(2,3)) : fmt=fmt.replace(rex, o[r]);
} else if(r == "q+") {
if(len != 1)
throw Error("季度格式错误:q只能出现1次");
fmt=fmt.replace(rex, o[r]);
} else if(r == "h+") {
if(len !=1 && len !=2)
throw Error("小时格式错误:h只能出现1/2次");
var h = (o[r] > 12 ? o[r]-12 : o[r]) + "";
len == 2 ? fmt=fmt.replace(rex, h.length==1 ? "0"+h : h) : fmt=fmt.replace(rex, h);
} else if(r == "S+") {
if(len != 1)
throw Error("毫秒数格式错误:S只能出现1次");
fmt=fmt.replace(rex, o[r]);
}else { // (r=="M+" || r=="d+" || r=="H+" || r=="m+" || r=="s+")
common(r, rex)
}
}
return fmt;
}
Here are some demonstration effects for your reference:
console.log(DateFormat(new Date(),'Yyyy year q quarter M month dd day HH hour m minute s second S millisecond'));
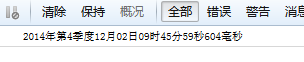
console.log(DateFormat(new Date(),'yyyy year yy q quarter M month dd day HH hour m minute s second S millisecond'));
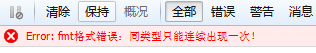
console.log(DateFormat(new Date(),'yyyy year q quarter M month dd day Hh hour m minute s second S millisecond'));
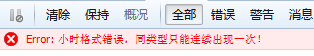
console.log(DateFormat("I am not a time object",'Yyyy year Q quarter M month dd day Hh hour m minute s second S millisecond'));
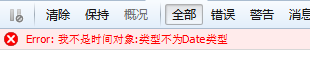
console.log(DateFormat(new Date(),'yyyy year q quarter MMM month dd day HH hour m minute s second S millisecond'));

I won’t list other effects one by one. If you are interested, you can just copy the code and test it directly. If there are any bugs or areas that need to be optimized, please feel free to correct them.
Through the above content, I have given you a detailed explanation of JavaScript time formatting knowledge. I hope you will like it.
Related articles
See more- An in-depth analysis of the Bootstrap list group component
- Detailed explanation of JavaScript function currying
- Complete example of JS password generation and strength detection (with demo source code download)
- Angularjs integrates WeChat UI (weui)
- How to quickly switch between Traditional Chinese and Simplified Chinese with JavaScript and the trick for websites to support switching between Simplified and Traditional Chinese_javascript skills

