Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >JavaScript Document Object Model-DOM Level 2 Style
JavaScript Document Object Model-DOM Level 2 Style
- 黄舟Original
- 2017-01-20 14:52:341390browse
There are three ways to define styles in HTML: refer to external style sheet files through the tag, use the
var supportsDOM2CSS = document.implementation.hasFeature("CSS","2.0");
var supportsDOM2CSS2 = document.implementation.hasFeature("CSS2","2.0");If the browser supports DOM2-level CSS capabilities, the variable value returned by the above code is true.
Access the style of the element
Any HTML element that supports the style attribute has a corresponding style attribute in JavaScript. This style object is an instance of CSSStyleDeclaration and contains all style information specified through the style attribute of HTML, but does not include styles cascaded with external style sheets or embedded style sheets. Any CSS properties specified in the style attribute will appear as corresponding properties of this style object.
It should be noted that in JavaScript, the camel case format is used to access CSS properties, while the CSS properties in CSS styles use the "-" connection form. Therefore, when using it, you must convert the CSS properties in the "-" connection form into the JavaScript properties in the camel case form, such as the following example:
There is an exception to the CSS property: The float attribute, because it is a reserved word in JavaScript, cannot be used as an attribute name. The "DOM2-level style" specification stipulates that the JavaScript attribute corresponding to this attribute is cssFloat. Firefox, Chrome, Safari and Opera browsers all support this attribute, but IE browser supports the styleFloat attribute.
As long as we obtain a reference to a valid DOM element, we can use JavaScript to add styles to it at any time. For example, the following example:
<div id="myDiv"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var div = document.getElementById("myDiv");
//设置DIV元素的背景颜色
div.style.backgroundColor = "#f00";
//修改DIV元素的大小
div.style.width = "100px";
div.style.height = "150px";
//指定DIV元素的边框
div.style.border = "1px solid #00f";
</script>Through the style object, we can also obtain the CSS style specified in the style attribute, such as the following example:
<div id="myDiv" style="background-color:#f00;width:200px;height:300px;"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var div = document.getElementById("myDiv");
console.info(div.style.backgroundColor);
console.info(div.style.width);
console.info(div.style.height);
</script>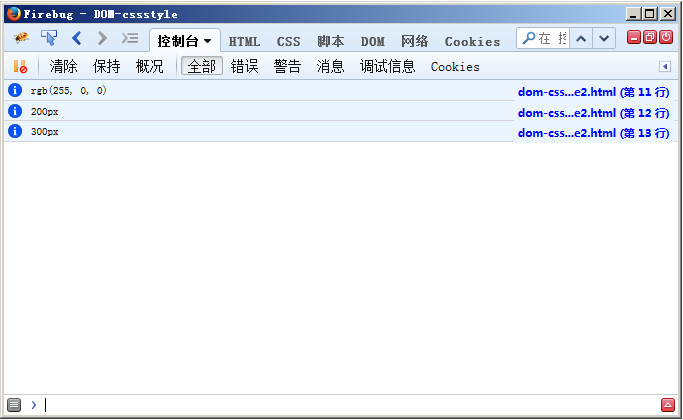
DOM Style attributes and methods
The "DOM2-level style" specification also defines some attributes and methods for the style object. These properties and methods can also modify the element's style while providing the element's style attribute value.
cssText: This property allows you to access the CSS code in the style attribute.
length: The number of CSS properties applied to the element.
parentRule: CSSRule object representing CSS information.
getPropertyCSSValue(propertyName): Returns a CSSRule object containing the specified property value.
getPropertyPriority(propertyName): If the given CSS property uses !important setting, return important, otherwise return an empty string.
getPropertyValue(propertyName): Returns the string value of the specified property.
item(index): Returns the name of the CSS property at the specified position.
removeProperty(propertyName): Remove the specified property from the style.
setProperty(propertyName,value,priority): Set the specified property to the corresponding value and add the priority flag (important or an empty string).
The CSS code in the style attribute of the specified element can be read through the cssText attribute, and the style attribute of the specified element can also be set. For example:
var div = document.getElementById("myDiv");
div.style.cssText = "background-color:#f00;width:200px;height:300px;";
console.info(div.style.cssText);cssText property can quickly set multiple CSS properties for elements at once.
The length property can get the number of CSS properties applied to the element. You can use this property to traverse CSS properties. It is often used in conjunction with the item() method. When using the length attribute and item() method, the style object is actually a collection. You can also use square bracket syntax instead of item() to get the CSS property at the specified position, such as the following example:
for(var i = 0,len = div.style.length; i < len; i++){
console.info(div.style[i]);
//或者使用item()
//console.info(div.style.item(i));
}Through the item() method or the square bracket method, we can get the CSS attribute name (note: the obtained CSS attribute name is in dash form, not camel case). After getting the CSS property name, we can get the value corresponding to this property through the getPropertyValue() method.
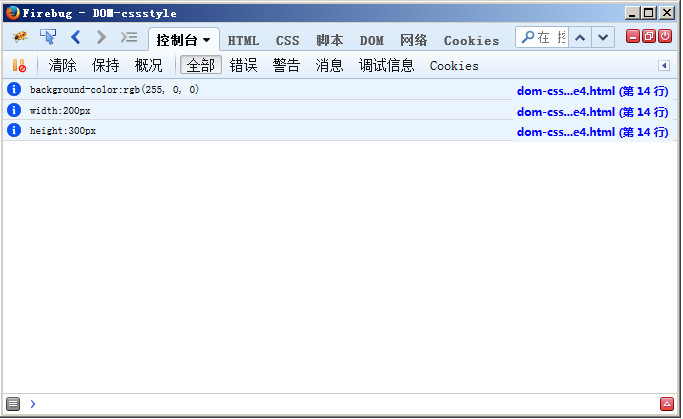
for(var i = 0,len = div.style.length; i < len; i++){
var prop = div.style[i];//或者:var prop = div.style.item(i);
var value = div.style.getPropertyValue(prop);
console.info(prop+":"+value);
}
getPropertyValue()方法会返回CSS属性的字符串表示。如果你需要得到更多的信息,可以使用getPropertyCSSValue()方法。该方法返回一个包含2个属性的CSSValue对象,这两个属性分别是:cssText和cssValueType。其中,cssText属性的值和使用getPropertyValue()方法获取的值相同,而cssValueType则是一个数值常量,表示值的类型:0表示继承的值,1表示基本的值,2表示值列表,3表示自定义的值。
只有Safari 3+和Chrome浏览器支持getPropertyCSSValue()这个方法。
要从元素样式中移除某个CSS属性,可以使用removeProperty()方法。使用该方法一次只移除一个属性,被移除后的属性将使用默认的样式。例如,要想移除元素的背景颜色,可以像下面这样写代码:
div.style.removeProperty("backgroundColor");Firefox、Chrome、Safari和Opera 9+都支持以上的属性和方法,但是IE浏览器只支持cssText属性。Safari 3+和Chrome浏览器是唯一支持getPropertyCSSValue()方法的浏览器。
计算的样式
虽然style对象能够提供支持style特性的任何元素的样式信息,但是它不包含那些从其它样式表层叠过来的样式。“DOM2级样式”增强了document.defaultView,提供了一个getComputedStyle()方法。该方法接收2个参数:要取得计算样式的元素和一个伪元素字符串(如":after")。如果不需要伪元素信息,第二个参数可以为null。getComputedStyle()方法返回一个CSSStyleDelaration对象。其中包含了当前元素的所有计算的样式。下面是一个例子:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>getComputedStyle()</title>
<style type="text/css">
#myDiv{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #ff0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="myDiv" style="background-color:#f00;border:1px solid #f00;"></div>
</body>
</html>在上面的HTML代码中,应用到div#myDiv元素上的CSS样式一方面来自嵌入的样式表,另一方面来自元素本身的style样式。但是style特性中设置了background-color和border两个属性,没有设置width和height这两个属性。通过下面的代码可以获得这个元素计算后的CSS样式:
var div = document.getElementById("myDiv");
var computedStyle = document.defaultView.getComputedStyle(div,null);
console.info(computedStyle.backgroundColor);
console.info(computedStyle.width);
console.info(computedStyle.height);
console.info(computedStyle.border);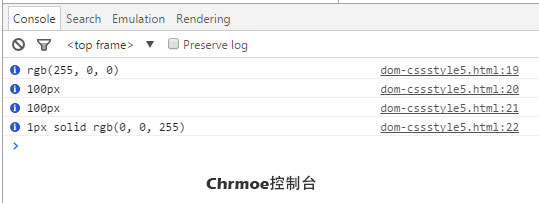
由于在设置border属性的时候,实际上是设置4个边框的宽度、颜色和样式属性:border-left-width、border-top-color、border-right-style等,所以在不同的浏览器上computedStyle.border的返回值是不同的,在Firefox浏览器中执行上面的代码computedStyle.border的返回值就是一个空字符串。所以实际使用getComputedStyle()方法的时候最好在多种浏览器上测试一下。
IE浏览器不支持getComputedStyle()方法,但是它有一个类似的概念。在IE浏览器中,每个具有style属性的元素还有一个currentStyle属性。这个属性是CSSStyleDelaration的实例,它包含当前元素全部的计算后的样式。要获取这些样式的方法和前面也类似:
var div = document.getElementById("myDiv");
var computedStyle = document.currentStyle;
console.info(computedStyle.backgroundColor);
console.info(computedStyle.width);
console.info(computedStyle.height);
console.info(computedStyle.border);和DOM版本相同,IE也没有返回border样式,因为它是一个综合性的属性。
无论在哪个浏览器中,所有的计算样式都是只读的,不能修改计算后样式对象中的CSS属性。另外,计算后的样式也包括属于浏览器内部样式表的样式信息。例如,所有的浏览器的visibility属性都有一个默认值,但这个值会因为浏览器的不同而不同。默认情况下,有的浏览器visibility属性的值设置为visible,而有的浏览器则将它设置为inherit,所以,如果你需要某个元素具有某个特定值,需要手动设置它。
以上就是JavaScript文档对象模型-DOM2级样式的内容,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网(www.php.cn)!
Related articles
See more- An in-depth analysis of the Bootstrap list group component
- Detailed explanation of JavaScript function currying
- Complete example of JS password generation and strength detection (with demo source code download)
- Angularjs integrates WeChat UI (weui)
- How to quickly switch between Traditional Chinese and Simplified Chinese with JavaScript and the trick for websites to support switching between Simplified and Traditional Chinese_javascript skills

