Home >Java >javaTutorial >Analysis of the implementation principle of Java8 HashMap
Analysis of the implementation principle of Java8 HashMap
- 高洛峰Original
- 2017-01-19 09:57:501286browse
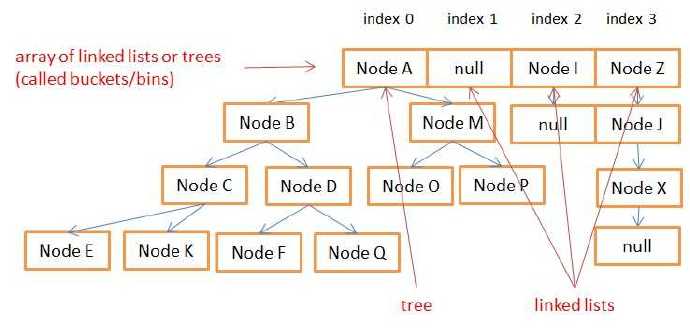
The storage structure of HashMap is as shown in the figure: if there are more than 8 nodes in a bucket, the storage structure is a red-black tree, and if there are less than 8 nodes, it is a one-way linked list.
1: Some attributes of HashMap
public class HashMap<k,v> extends AbstractMap<k,v> implements Map<k,v>, Cloneable, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 362498820763181265L;
// 默认的初始容量是16
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4;
// 最大容量
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
// 默认的填充因子(以前的版本也有叫加载因子的)
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
// 这是一个阈值,当桶(bucket)上的链表数大于这个值时会转成红黑树,put方法的代码里有用到
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
// 也是阈值同上一个相反,当桶(bucket)上的链表数小于这个值时树转链表
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
// 看源码注释里说是:树的最小的容量,至少是 4 x TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 32 然后为了避免(resizing 和 treeification thresholds) 设置成64
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
// 存储元素的数组,总是2的倍数
transient Node<k,v>[] table;
transient Set<map.entry<k,v>> entrySet;
// 存放元素的个数,注意这个不等于数组的长度。
transient int size;
// 每次扩容和更改map结构的计数器
transient int modCount;
// 临界值 当实际大小(容量*填充因子)超过临界值时,会进行扩容
int threshold;
// 填充因子
final float loadFactor;
2: The construction method of HashMap
// 指定初始容量和填充因子的构造方法
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
// 指定的初始容量非负
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(Illegal initial capacity: +
initialCapacity);
// 如果指定的初始容量大于最大容量,置为最大容量
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
// 填充比为正
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException(Illegal load factor: +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
// 指定容量后,tableSizeFor方法计算出临界值,put数据的时候如果超出该值就会扩容,该值肯定也是2的倍数
// 指定的初始容量没有保存下来,只用来生成了一个临界值
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
// 该方法保证总是返回大于cap并且是2的倍数的值,比如传入999 返回1024
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1;
// 向右做无符号位移
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
// 三目运算符的嵌套
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}
//构造函数2
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
//构造函数3
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted
}
3: Determine the position of the element in the array when getting and putting
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
Determine the position
The first step: First, calculate the hash code of the key, which is an int type number. The following h >>> 16 source code comments say: In order to avoid hash collisions (hash collisons), the high bits are dispersed to the low bits. This is done after comprehensive consideration of various factors such as speed and performance.
Step 2: h is the hash code, length is the length of the Node[] array above, and do the AND operation h & (length-1). Since length is a multiple of 2 -1, its binary code is all 1, and the result of 1 and other numbers above may be 0 or 1, thus ensuring uniformity after the operation. That is to say, the hash method ensures the uniformity of the results, which is very important and will greatly affect the put and get performance of HashMap. Look at the comparison below:
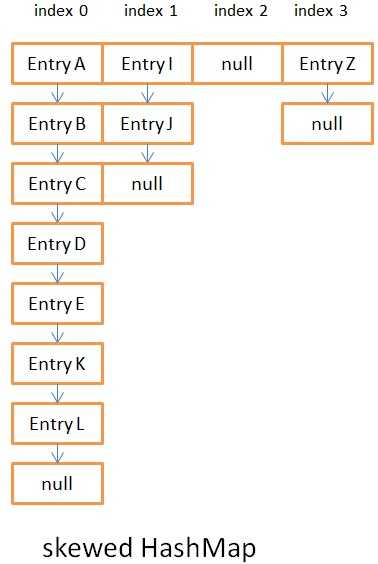
Figure 3.1 is the asymmetric hash result
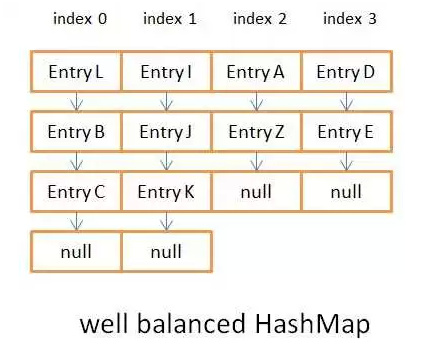
Figure 3.2 is the balanced hash result
There is not a lot of data in these two pictures. If the length of the linked list exceeds 8, it will be converted into a red-black tree. It will be more obvious at that time. Before jdk8, it has always been a linked list. The complexity of linked list query is O(n), while the query complexity of red-black tree is O(log(n)) due to its own characteristics. If the hash results are uneven, it will greatly affect the complexity of the operation. Related knowledge here is72e1214e15ec42bfc5f5aa5e4f182c03Red-Black Tree Basic Knowledge Blog5db79b134e9f6b82c0b36e0489ee08edThere is also an example on the Internet To verify: Customize an object as the key, adjust the hashCode() method to see the put value time
public class MutableKeyTest {
public static void main(String args[]){
class MyKey {
Integer i;
public void setI(Integer i) {
this.i = i;
}
public MyKey(Integer i) {
this.i = i;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
// 如果返回1
// return 1
return i;
}
// object作为key存map里,必须实现equals方法
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof MyKey) {
return i.equals(((MyKey)obj).i);
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
// 我机器配置不高,25000的话正常情况27毫秒,可以用2500万试试,如果hashCode()方法返回1的话,250万就卡死
Map<MyKey,String> map = new HashMap<>(25000,1);
Date begin = new Date();
for (int i = 0; i < 20000; i++){
map.put(new MyKey(i), "test " + i);
}
Date end = new Date();
System.out.println("时间(ms) " + (end.getTime() - begin.getTime()));
4: get method
public V get(Object key) {
Node<k,v> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
final Node<k,v> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<k,v>[] tab; Node<k,v> first, e; int n; K k;
// hash & (length-1)得到红黑树的树根位置或者是链表的表头
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
// 如果是树,遍历红黑树复杂度是O(log(n)),得到节点值
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<k,v>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
// else是链表结构
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
5: put method, when putting, locate the bucket according to h & (length – 1) and then check whether it is a red-black tree or a linked list and then putVal
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<k,v>[] tab; Node<k,v> p; int n, i;
// 如果tab为空或长度为0,则分配内存resize()
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
// (n - 1) & hash找到put位置,如果为空,则直接put
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<k,v> e; K k;
// 第一节节点hash值同,且key值与插入key相同
if (p.hash == hash &&((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
// 红黑树的put方法比较复杂,putVal之后还要遍历整个树,必要的时候修改值来保证红黑树的特点
e = ((TreeNode<k,v>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
// 链表
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
// e为空,表示已到表尾也没有找到key值相同节点,则新建节点
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
// 新增节点后如果节点个数到达阈值,则将链表转换为红黑树
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
// 容许空key空value
if (e.hash == hash &&((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
// 更新hash值和key值均相同的节点Value值
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
6: resize method
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
// 这一句比较重要,可以看出每次扩容是2倍
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // preserve order
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
The above is the implementation of Java8 HashMap introduced by the editor The relevant knowledge of principle analysis, I hope it will be helpful to everyone!
For more articles related to the analysis of the implementation principles of Java8 HashMap, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website!

