JavaScript talks about closures from the scope chain_javascript skills
Shenma is a closure
Regarding the concept of closure, it makes sense.
A closure refers to a function that has access to variables in the scope of another function
This concept is a bit convoluted, so let’s break it down. Conceptually, closures have two characteristics:
- 1. Function
- 2. Can access variables in another function scope
Before ES 6, Javascript only had the concept of function scope and no concept of block-level scope (but exceptions caught by catch can only be accessed in the catch block) (IIFE can create local scope). Each function scope is closed, that is, variables in the function scope cannot be accessed from the outside.
function getName() {
var name = "美女的名字";
console.log(name); //"美女的名字"
}
function displayName() {
console.log(name); //报错
}
But in order to get the name of the beautiful woman, the single guy who refused to give up changed the code to this:
function getName() {
var name = "美女的名字";
function displayName() {
console.log(name);
}
return displayName;
}
var 美女 = getName();
美女() //"美女的名字"
Now, the beauty is a closed person, and the single guy can have fun as he wants. (However, it is not recommended for singles to write variable names in Chinese, so please don’t learn it).
Regarding closures, I would like to say three more points:
1. Closures can access variables outside the current function
function getOuter(){
var date = '815';
function getDate(str){
console.log(str + date); //访问外部的date
}
return getDate('今天是:'); //"今天是:815"
}
getOuter();
getDate is a closure. When this function is executed, a scope A will be formed. The variable date is not defined in A, but it can find the definition of the variable in the parent scope.
2. Even if the external function has returned, the closure can still access the variables defined by the external function
function getOuter(){
var date = '815';
function getDate(str){
console.log(str + date); //访问外部的date
}
return getDate; //外部函数返回
}
var today = getOuter();
today('今天是:'); //"今天是:815"
today('明天不是:'); //"明天不是:815"
3. Closures can update the values of external variables
function updateCount(){
var count = 0;
function getCount(val){
count = val;
console.log(count);
}
return getCount; //外部函数返回
}
var count = updateCount();
count(815); //815
count(816); //816
Scope chain
Why can closures access variables of external functions? This is about the scope chain in Javascript.
There is a concept of execution context in Javascript, which defines other data that variables or functions have access to, and determines their respective behaviors. Each execution environment has a variable object associated with it, and all variables and functions defined in the environment are stored in this object. You can treat it as an ordinary object in Javascript, but you can only modify its properties, but not reference it.
Variable objects also have parent scopes. When accessing a variable, the interpreter will first search for the identifier in the current scope. If it is not found, it will go to the parent scope until it finds the identifier of the variable or the parent scope no longer exists. This is the scope chain. .
Scope chain is somewhat similar to prototypal inheritance, but there is a slight difference: if you search for a property of a common object and cannot find it in the current object or its prototype, undefined will be returned; but the property you are looking for is in If it does not exist in the scope chain, a ReferenceError will be thrown.
The top of the scope chain is the global object. For code in the global environment, the scope chain contains only one element: the global object. Therefore, when variables are defined in the global environment, they will be defined in the global object. When a function is called, the scope chain will contain multiple scope objects.
- Global environment
We talk a little bit more about scope chain (the red book has a detailed explanation of scope and execution environment), let’s look at a simple example:
// my_script.js "use strict"; var foo = 1; var bar = 2;
In the global environment, two simple variables are created. As mentioned before, the variable object is a global object at this time.
- Non-nested functions
Change the code to create a function without function nesting:
"use strict";
var foo = 1;
var bar = 2;
function myFunc() {
//-- define local-to-function variables
var a = 1;
var b = 2;
var foo = 3;
console.log("inside myFunc");
}
console.log("outside");
//-- and then, call it:
myFunc();
当myFunc被定义的时候,myFunc的标识符(identifier)就被加到了当前的作用域对象中(在这里就是全局对象),并且这个标识符所引用的是一个函数对象(function object)。函数对象中所包含的是函数的源代码以及其他的属性。其中一个我们所关心的属性就是内部属性[[scope]]。[[scope]]所指向的就是当前的作用域对象。也就是指的就是函数的标识符被创建的时候,我们所能够直接访问的那个作用域对象(在这里就是全局对象)。
比较重要的一点是:myFunc所引用的函数对象,其本身不仅仅含有函数的代码,并且还含有指向其被创建的时候的作用域对象。
当myFunc函数被调用的时候,一个新的作用域对象被创建了。新的作用域对象中包含myFunc函数所定义的本地变量,以及其参数(arguments)。这个新的作用域对象的父作用域对象就是在运行myFunc时我们所能直接访问的那个作用域对象。
- Nested functions
如前面所说,当函数返回没有被引用的时候,就会被垃圾回收器回收。但是对于闭包(函数嵌套是形成闭包的一种简单方式)呢,即使外部函数返回了,函数对象仍会引用它被创建时的作用域对象。
"use strict";
function createCounter(initial) {
var counter = initial;
function increment(value) {
counter += value;
}
function get() {
return counter;
}
return {
increment: increment,
get: get
};
}
var myCounter = createCounter(100);
console.log(myCounter.get()); // 返回 100
myCounter.increment(5);
console.log(myCounter.get()); // 返回 105
当调用createCounter(100)时,内嵌函数increment和get都有指向createCounter(100) scope的引用。如果createCounter(100)没有任何返回值,那么createCounter(100) scope不再被引用,于是就可以被垃圾回收。但是因为createCounter(100)实际上是有返回值的,并且返回值被存储在了myCounter中,所以对象之间的引用关系发生变化。
需要用点时间思考的是:即使createCounter(100)已经返回,但是其作用域仍在,并能且只能被内联函数访问。可以通过调用myCounter.increment() 或 myCounter.get()来直接访问createCounter(100)的作用域。
当myCounter.increment() 或 myCounter.get()被调用时,新的作用域对象会被创建,并且该作用域对象的父作用域对象会是当前可以直接访问的作用域对象。
当执行到return counter;时,在get()所在的作用域并没有找到对应的标示符,就会沿着作用域链往上找,直到找到变量counter,然后返回该变量,调用increment(5)则会更有意思。当单独调用increment(5)时,参数value会存贮在当前的作用域对象。函数要访问value,能马上在当前作用域找到该变量。但是当函数要访问counter时,并没有找到,于是沿着作用域链向上查找,在createCounter(100)的作用域找到了对应的标示符,increment()就会修改counter的值。除此之外,没有其他方式来修改这个变量。闭包的强大也在于此,能够存贮私有数据。
Similar function objects, different scope objects
对于上面的counter示例,再说点扩展的事。看代码:
//myScript.js
"use strict";
function createCounter(initial) {
/* ... see the code from previous example ... */
}
//-- create counter objects
var myCounter1 = createCounter(100);
var myCounter2 = createCounter(200);
myCounter1 和 myCounter2创建之后,关系图是酱紫的:
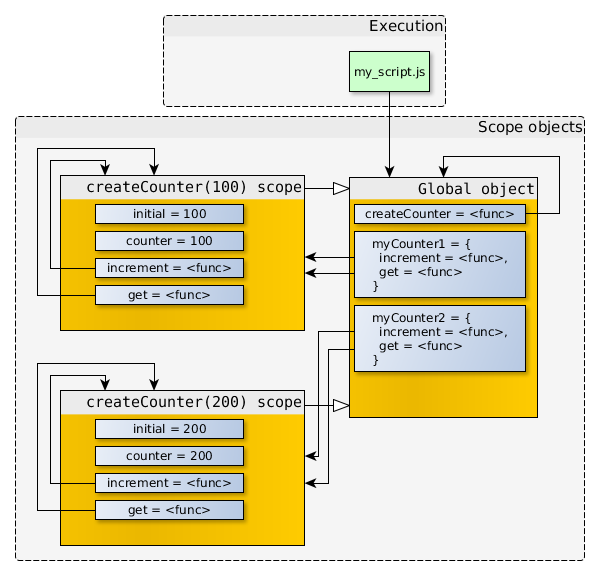
在上面的例子中,myCounter1.increment和myCounter2.increment的函数对象拥有着一样的代码以及一样的属性值(name,length等等),但是它们的[[scope]]指向的是不一样的作用域对象。
这才有了下面的结果:
var a, b; a = myCounter1.get(); // a 等于 100 b = myCounter2.get(); // b 等于 200 myCounter1.increment(1); myCounter1.increment(2); myCounter2.increment(5); a = myCounter1.get(); // a 等于 103 b = myCounter2.get(); // b 等于 205
作用域和this
作用域会存储变量,但this并不是作用域的一部分,它取决于函数调用时的方式。关于this指向的总结,可以看这篇文章:JavaScript面试问题:事件委托和this
 Javascript Data Types : Is there any difference between Browser and NodeJs?May 14, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Javascript Data Types : Is there any difference between Browser and NodeJs?May 14, 2025 am 12:15 AMJavaScript core data types are consistent in browsers and Node.js, but are handled differently from the extra types. 1) The global object is window in the browser and global in Node.js. 2) Node.js' unique Buffer object, used to process binary data. 3) There are also differences in performance and time processing, and the code needs to be adjusted according to the environment.
 JavaScript Comments: A Guide to Using // and /* */May 13, 2025 pm 03:49 PM
JavaScript Comments: A Guide to Using // and /* */May 13, 2025 pm 03:49 PMJavaScriptusestwotypesofcomments:single-line(//)andmulti-line(//).1)Use//forquicknotesorsingle-lineexplanations.2)Use//forlongerexplanationsorcommentingoutblocksofcode.Commentsshouldexplainthe'why',notthe'what',andbeplacedabovetherelevantcodeforclari
 Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AMThe main difference between Python and JavaScript is the type system and application scenarios. 1. Python uses dynamic types, suitable for scientific computing and data analysis. 2. JavaScript adopts weak types and is widely used in front-end and full-stack development. The two have their own advantages in asynchronous programming and performance optimization, and should be decided according to project requirements when choosing.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AMWhether to choose Python or JavaScript depends on the project type: 1) Choose Python for data science and automation tasks; 2) Choose JavaScript for front-end and full-stack development. Python is favored for its powerful library in data processing and automation, while JavaScript is indispensable for its advantages in web interaction and full-stack development.
 Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMPython and JavaScript each have their own advantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1. Python is easy to learn, with concise syntax, suitable for data science and back-end development, but has a slow execution speed. 2. JavaScript is everywhere in front-end development and has strong asynchronous programming capabilities. Node.js makes it suitable for full-stack development, but the syntax may be complex and error-prone.
 JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AMJavaScriptisnotbuiltonCorC ;it'saninterpretedlanguagethatrunsonenginesoftenwritteninC .1)JavaScriptwasdesignedasalightweight,interpretedlanguageforwebbrowsers.2)EnginesevolvedfromsimpleinterpreterstoJITcompilers,typicallyinC ,improvingperformance.
 JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript can be used for front-end and back-end development. The front-end enhances the user experience through DOM operations, and the back-end handles server tasks through Node.js. 1. Front-end example: Change the content of the web page text. 2. Backend example: Create a Node.js server.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AMChoosing Python or JavaScript should be based on career development, learning curve and ecosystem: 1) Career development: Python is suitable for data science and back-end development, while JavaScript is suitable for front-end and full-stack development. 2) Learning curve: Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners; JavaScript syntax is flexible. 3) Ecosystem: Python has rich scientific computing libraries, and JavaScript has a powerful front-end framework.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment






