Home >Web Front-end >CSS Tutorial >css positioning z-index problem
css positioning z-index problem
- 高洛峰Original
- 2016-11-24 11:55:222677browse
-
There is a bug in element level masking in some browsers;
The z-index of a certain element is set too large, causing it to never be covered;
js dynamically calculates z-index, causing the element coverage relationship to be uncontrollable
vc+hozxicj4KPGJyPgo8YnI+CmZmL2Nocm9tZSB6LWluZGV4IElFNi83IElFOC85IDxicj4KsrvJ6NbDICAwICBhdXRvICBhdXRvICA8YnI+Cm51bWJlciAgbnVtYmVyIC Buddhist pzdGF0aWMpx+m/9s/CzsS1tcH3uvPD5rXE1KrL2LvhuLK4x8eww+a1xDs8YnI+Cjxicj4KMi4gttTT2s2svLbUqsvYo6xwb3NpdGlvbrK7zqpzdGF0aWPH0notaW5kZXi05tTatcTH6b /2z8J6LWluZGV4tPO1xNSqy9i74biyuMd6LWluZGV40KG1xNSqy9ijrLy0ei1pbmRleNS9tPP Txc/IvLbUvbjfOzxicj4KPGJyPgozLiBJRTYvN8/CcG9zaXRpb26yu86qc3RhdGljo6zH0not aW5kZXiyu7Tm1NrKsXotaW5kZXjOqjCjrLP9tMvWrs3itcTkr8DAxvd6LWluZGV4zqphdXR vPGJyPgo8YnI+CjQuIHotaW5kZXjOqmF1dG+1xNSqy9iyu7LO0+uy47y2udjPtbXEsci9z6O s08nP8snPsenA+tbBtMvH0notaW5kZXiyu86qYXV0b7XE1KrL2MC0ss7T67HIvc+hozxicj4KPGJyPgrU2snPw+YyteO94cLbtcS7+bShyc+ JRM7SW8FS/CJROBC2QM67yvehSSI3X3CZY7NZT720YRVJKBXEUMXE7SC01/AY47Y2TCSXYL3POAM8YNI+CJXICJ4K1NQ2QM67yvfv4RJ2UMXE7S/CO6ZKR8DAXVV Fu2UTWYL5KB2292RXJYRGJRLP9WCVJ+RPJZG9TyVFWRS3IO6Y7UBVHUPM+3WRVBCR31xLaozrvUQSVC2L0AW9USRVYXRPYYYYYYYYYNJ+RPJOBC2QM66 7yvehsao6pgjypgpkb23k96gitqJou8r3ttsxymjnz8ioxutw0lhfyc/T0LRSYAVUSSIMTCSX7CQ+ DXICJ4KPGLTZYBZCMM9 "http://www.2cto.com/uploadFile/collfiles/20140321/20140321125539169.png" alt = "" & gt;

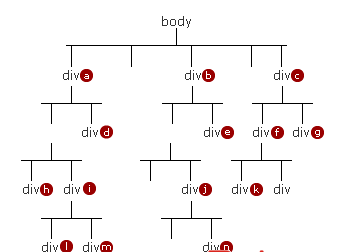
;It can be understood like this: the positioning tree contains all elements in the dom tree whose position is not staitc. The hierarchical relationship between non-sibling elements can be compared as follows:
1. Traverse the parent node of the positioning tree upward until two elements are sibling elements.
2. Let’s make the final comparison based on the above conclusion. Higher-level elements will move closer to the user's display and cover lower-level elements.
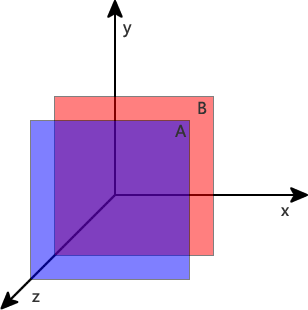
Example 1: Assume that the positions of all elements marked in red in the above picture are not static; and z-index=1. According to the above comparison rules, we can know:
1. c > (b && b *) > (a && a *) That is, the level of all positioned elements of elements c and c is higher than a and b
2. m > h, g > k, d > m
Example 2: Assume that the position of a is not static, the z-index attribute does not exist. The z-index of the sub-elements of a in the positioning tree are 1, 2, 3, 4... Other positioning elements z-index: 1:
1. According to the following three conclusions: Under IE6/7, b > (a && a *) means that the level of element b is higher than a and all positioned elements of a. Under other browsers: i > h > b > d. Please indicate the source for reprinting: css positioning z-index problem