Home >Web Front-end >CSS Tutorial >css float
css float
- 高洛峰Original
- 2016-10-09 15:43:041450browse
Standard document flow
Divides the form into rows from top to bottom, and arranges the elements in each row from left to right, which is the document flow. Each non-floating block-level element occupies its own row, and floating elements Then it floats at one end of the line as specified. If the current line cannot fit, start a new line and float again.
Microscopic phenomenon of standard flow
Blank folding phenomenon
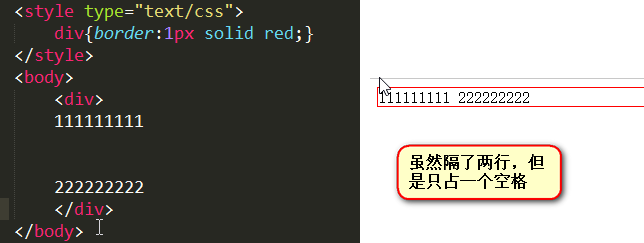
The same goes for pictures, pictures and form elements can Seen as text

uneven height, aligned at the bottom

automatic line wrapping, cannot be written in one line, write line wrapping

block-level elements and inline elements
block-level elements
occupy one line , cannot be juxtaposed with any other elements
You can set the width and height. If the width is not set, the width will default to 100% of the parent.
Inline elements
are placed side by side with other inline elements
The width and height cannot be set. The default width is the width of the text.
Tag classification
In HTML, tags can be divided into: text level and container level.
Text level: p, span, a, b, i, u, em
Container level: p, h series, li, dt, dd
CSS classification is very similar to the above, but p is different:
All text-level tags are inline elements, except p, which is a text-level but a block-level element.
All container-level tags are block-level elements.
Conversion between block-level elements and inline elements
Block-level elements can be set as inline elements, and inline elements can be set as block-level elements
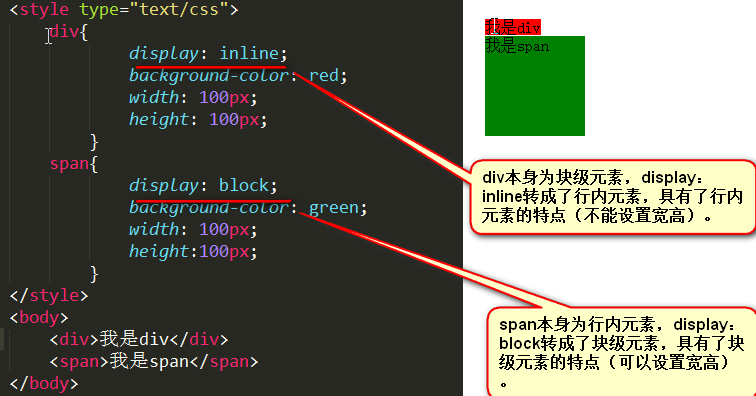
display: inline;/*块级元素转为行内元素*/
Once a p is set to display: inline; at this time, the width of this p cannot be set. height; then, this p will immediately become an inline element. At this time it is no different from a span, and this p can be placed side by side with other tags.
display: block;/*行内元素转为块级元素*/
Once you set display: block; to a span, the span becomes a block-level element. At this time, this label is no different from a p. At this time, the span can set the width and height; at this time, the span must occupy a line, and others cannot be side by side with it; if the width is not set, it will fill up the father.
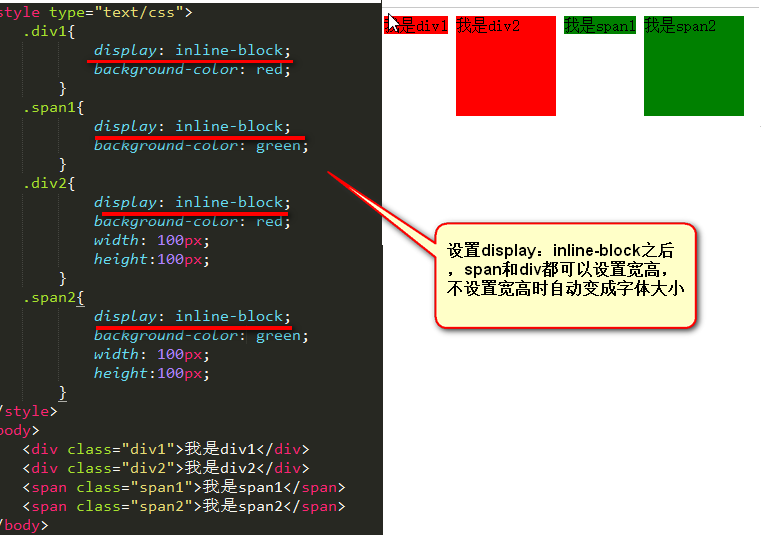
display: inline-block;/*元素既能并排,又能设置宽高*/
标准文档流无法布局,所以需要元素脱离文档流,css中一共有三种手段,使一个元素脱离标准文档流:
浮动
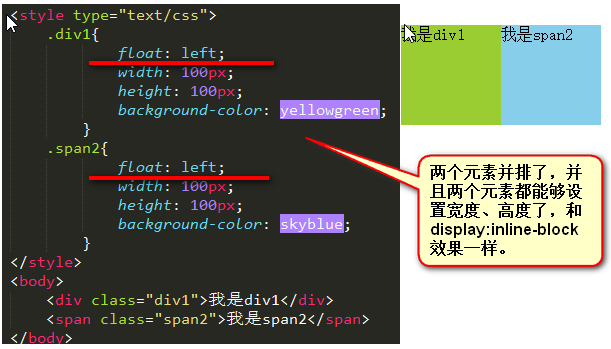
浮动的三个性质
浮动的元素脱离标准文档流
.p1{
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
}
.p2{
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: green;
}我是p1我是p2效果如下:p1浮动之后,脱离了标准文档流,p2就是标准文档流中的第一个盒子,所以就渲染在了页面的左上方。
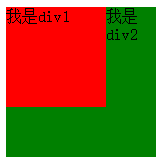
浮动之后,一个span标签不需要转成块级元素,就能够设置宽度、高度了。所以能够证明一件事儿,就是所有标签已经不区分行内、块了。也就是说,一旦一个元素浮动了,那么将能够并排了,并且能够设置宽高了。无论它原来是个p还是个span。参考浮动的第一个图。
浮动的元素互相贴靠
body{font-size: 60px;}
.p1{float: left;width: 100px;height: 100px;background-color: red;}
.p2{float: left;width: 150px;height: 150px;background-color: green;}
.p3{float: left;width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: blue;}123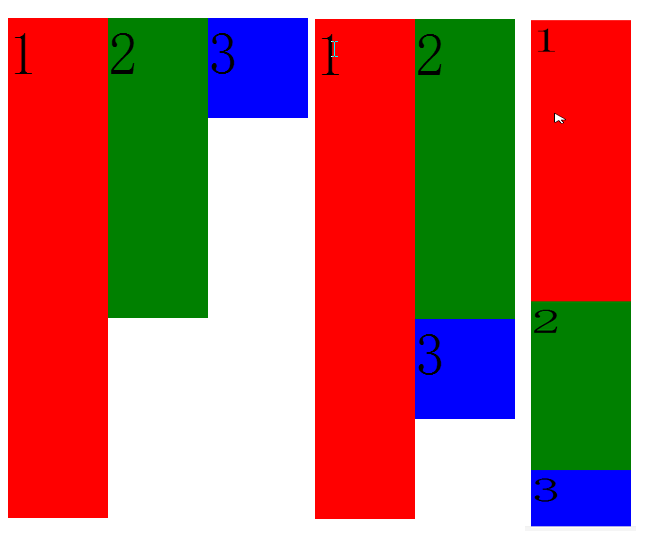
如果有足够空间,那么p3就会靠着p2。如果没有足够的空间,那么p3会靠着p1,如果没有足够的空间靠着p1,自己去贴页面左边。
浮动的元素有“字围”效果

p{float: left;width: 320px;height: 320px;background-color: orange;} 此处省略一万字p挡住了p,但是p中的文字不会被挡住,形成“字围”效果。
浮动的清除
先看看不清除浮动的效果
Document ul {list-style: none; }
li { float: left;margin-left: 5px;padding: 0;}
.p1 li {background-color: red;}
.p2 li {background-color: green; }
园子 新闻 博问 首页 精华 候选
本想让p1和p2分成两行显示,但是结果显示在了一行,第二组中的第1个li,去贴靠第一组中的最后一个li了。看看两个p的高度,显示为0,原因就是因为p没有高度,不能给自己浮动的子元素们一个容器。
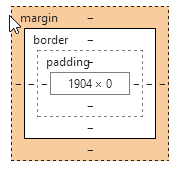
清除浮动方法
清除浮动方法1.给浮动的元素的祖先元素加高度
如果一个元素要浮动,那么它的祖先元素一定要有高度,有高度的盒子,才能关住浮动。只要浮动在一个有高度的盒子中,那么这个浮动就不会影响后面的浮动元素。所以就是清除浮动带来的影响了。
上面的代码,为了让p1浮动的子元素不影响p2,给p1增加 .p1{height: 50px;} 或者给p1的任何一个父级加上高度就达到了想要的结果。
网页制作中,高度height很少出现。因为能被内容撑高(浮动的元素不能撑高父元素),所以这种清除浮动的方法不太适用。
清除浮动方法2:clear:both;
clear:both; 清除左右浮动,这种方法有一个非常大的问题,margin失效了。
Document ul{list-style: none;}
li{float: left;margin-left: 5px;padding: 0;background-color: green;}
.p1{margin-bottom: 100px;}/*margin失效*/
.p2{margin-top: 100px;clear:both;}/*margin失效*/
园子 新闻 博问 首页 精华 候选
清除浮动方法3:隔墙法
外墙法
Document ul{list-style: none;}
li{float: left;margin-left: 5px;padding: 0;background-color: green;}
.p1{margin-bottom: 100px;}/*margin失效*/
.both { clear: both;margin-top:100px; }/*margin失效*/
.h10{height:10px;}
园子 新闻 博问 首页 精华 候选margin仍然失效,但是可以给
设置高度,充当margin效果。

内墙法
放到p1的内部,好处是内容可以撑出父级的高了,margin也不会失效了。
Document ul{list-style: none;}
li{float: left;margin-left: 5px;padding: 0;background-color: green;}
.both { clear: both; }
.h10{height:10px;}
园子 新闻 博问 首页 精华 候选清除浮动方法4:overflow:hidden;
一个父元素不能被自己浮动的子元素撑出高度。但是只要给父级元素加上 overflow:hidden ; 父亲就能被子元素撑出高了。
IE6不支持用 overflow:hidden;来清除浮动的,解决办法是追加一条 _zoom:1;
Document ul{list-style: none;}
li{float: left;margin-left: 5px;padding: 0;background-color: green;}
.p1{overflow:hidden;}
园子 新闻 博问 首页 精华 候选
