Large websites are often conflicted. They want users to see more things on the homepage, but they don’t want to waste too much server traffic. For example, a homepage with 3 screens. Maybe 50% of users enter the homepage to click on the link on the homepage to go to the sub-page.
Then our website loads all content for 3 screens for 100% of users. If content can be loaded on demand. You can save more resources and make more good applications.
2: Solution
Use client language to determine the user's current visible range, and only load content within the user's visible range. The main thing is the pictures. Because text information is relatively small, other multimedia content takes up more server traffic.
3: Demonstration example (provided at the end)
4: Analysis
First we need to analyze that this effect will have an outermost container. He included that some content needs to be delayed loaded. The container may generally be the browser window itself (window), or a DIV with scroll bars.
OK, we have to get some parameters of this container. For example, visible width, visible height, horizontal roll to width, vertical roll to height. I use the following program.
4.1: Get container object properties
_this.docInfo=function(){//Get container-related information
var d={},db= (wf)? document.body : warpper,
dd=(wf) ? document.documentElement : warpper ;
if(sys.ie){
d.offh=dd.offsetHeight;//Visible area H
d.offw=dd.offsetWidth;//Visible area W
}else {
if(wf){
d.offw=window.innerWidth;//Visible area H
d.offh=window.innerHeight;//Visible area W
}else{
d.offh=dd.offsetHeight;//Visible area H
d.offw=dd.offsetWidth;//Visible area W
}
}
d.jtop=(wf ) ? db.scrollTop dd.scrollTop : db.scrollTop ;//Scroll vertically to remove height
d.jleft=(wf) ? db.scrollLeft dd.scrollLeft : db.scrollLeft;//Scroll horizontally to remove width
//The width of the rolled window. If you use two added divs to curl, just use scrollLeft.
$j("bbb").innerHTML=d.offh ',' d.offw ',' d.jtop ',' d.jleft
return d;
}
//Note that to obtain the visible area of a non-window object in a non-IE browser, use offsetHeight and offsetWidth (the same as IE)
// To obtain the visible area of the window object under non-IE, you need to use window.innerWidth and window.innerHeight
//That is to say, the visual area acquisition of window and non-window objects under non-IE is different.
4.2: Get information about loading content
We mainly get the distance between the loading object and the page container object.
There will be a BUG in IE 6 and 7
wtop= sys.ie ? (sys.ie[1]=='6.0' || sys.ie[1]=='7.0') ? 0 : warpper.offsetTop : warpper.offsetTop,
wleft=sys.ie ? (sys.ie[1]=='6.0' || sys.ie[1]=='7.0') ? 0 : warpper.offsetLeft : warpper.offsetLeft,
getoff=function(o){//Get the offw and offh of the IMG object
o.innerHTML=(o.offsetTop-wtop) ',' (o.offsetLeft-wleft);
return (o.offsetTop-wtop) ',' (o.offsetLeft-wleft);
//Note o.offsetTop Under chrome, you have to wait for window.onload before you can correctly obtain
};
4.3: Load the main program
He is mainly responsible for loading the objects currently within the visible range. Then we must go through all the objects to be loaded. Determine whether the object is currently loading.
Then load him. I will have a picture below. (The method may not be very good)
_this.Load=function(){
var hereline=[];
hereline[1]=doc.offh doc.jtop;
hereline[2]=doc.offw doc .jleft;
for(i=0;i
 if(imgs[i][1] != undefined){//Determine whether the current object has been loaded
if(imgs[i][1] != undefined){//Determine whether the current object has been loaded var jj=hereline[1] - imgs[i][1] 0 ? true : false,
jjj=hereline[2 ] - imgs[i][2] 0 ? true : false;
if(jj && jjj){
imgall [i].innerHTML ='th' (j) 'load';
imgs[i][1]=undefined;
}
}
}
if( j > = imgs.length){//Determine whether all loading has been completed
//Cancel time binding
alert("All loading has been completed, the program will no longer be executed")
warpper.onscroll=null;
warpper.onresize=null;
}
}
I don’t really like my judgment program, but I haven’t found it yet, or I don’t understand a better algorithm. So I’ll use this first.
The general meaning: use the visible height of the container, the scroll height of the container - the distance between the object and the distance from the container > The container is visible and the height or width of the object itself proves that it is within the loading range. (Tongue twister)
We must also exclude objects that have already been loaded. Because the loaded objects also satisfy the above formula, there can be less judgment at the same time.
imgs[i][1]=undefined;
if(imgs[i][1] != undefined){//Determine whether the current object has been loaded
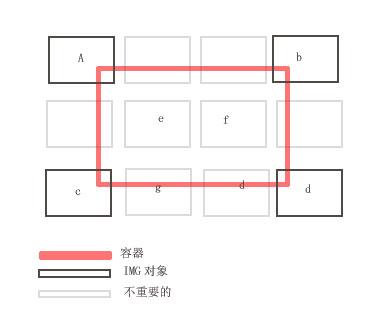
Special attention (see picture)

Look at A B C D above. There are 4 different corners exposed within the visual range. So these 4 objects need to be loaded.
If you only consider a certain point of the object or a certain line to determine whether the object is within the visible range, it may bring a bad experience.
Due to the above situation, it also adds difficulty to our programming (judging whether it is within the visible range).
My above method can be completed. (If you find any bugs, please give me some pointers. In fact, I’m a little dizzy too.)
Finally there are a few tricks, such as
1: Load all objects It's over. You should remove the container object event triggering.
2: Try to optimize the algorithm for judging whether the object is within the visible range or the traversed object. Can save a lot of browser resources.
3: cloudgamer also mentioned a delayed trigger, which is to quickly slide the scroll bar. Delaying it is also a small optimization.
5: Recommended articles
by cloudgamer He explained it in detail and did it better than me. So it is recommended to learn this effect of his. I also borrowed many things from him.
Also, thank you for his advice. Lazyload delay loading effect
6: My source code
 Javascript Data Types : Is there any difference between Browser and NodeJs?May 14, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Javascript Data Types : Is there any difference between Browser and NodeJs?May 14, 2025 am 12:15 AMJavaScript core data types are consistent in browsers and Node.js, but are handled differently from the extra types. 1) The global object is window in the browser and global in Node.js. 2) Node.js' unique Buffer object, used to process binary data. 3) There are also differences in performance and time processing, and the code needs to be adjusted according to the environment.
 JavaScript Comments: A Guide to Using // and /* */May 13, 2025 pm 03:49 PM
JavaScript Comments: A Guide to Using // and /* */May 13, 2025 pm 03:49 PMJavaScriptusestwotypesofcomments:single-line(//)andmulti-line(//).1)Use//forquicknotesorsingle-lineexplanations.2)Use//forlongerexplanationsorcommentingoutblocksofcode.Commentsshouldexplainthe'why',notthe'what',andbeplacedabovetherelevantcodeforclari
 Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AMThe main difference between Python and JavaScript is the type system and application scenarios. 1. Python uses dynamic types, suitable for scientific computing and data analysis. 2. JavaScript adopts weak types and is widely used in front-end and full-stack development. The two have their own advantages in asynchronous programming and performance optimization, and should be decided according to project requirements when choosing.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AMWhether to choose Python or JavaScript depends on the project type: 1) Choose Python for data science and automation tasks; 2) Choose JavaScript for front-end and full-stack development. Python is favored for its powerful library in data processing and automation, while JavaScript is indispensable for its advantages in web interaction and full-stack development.
 Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMPython and JavaScript each have their own advantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1. Python is easy to learn, with concise syntax, suitable for data science and back-end development, but has a slow execution speed. 2. JavaScript is everywhere in front-end development and has strong asynchronous programming capabilities. Node.js makes it suitable for full-stack development, but the syntax may be complex and error-prone.
 JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AMJavaScriptisnotbuiltonCorC ;it'saninterpretedlanguagethatrunsonenginesoftenwritteninC .1)JavaScriptwasdesignedasalightweight,interpretedlanguageforwebbrowsers.2)EnginesevolvedfromsimpleinterpreterstoJITcompilers,typicallyinC ,improvingperformance.
 JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript can be used for front-end and back-end development. The front-end enhances the user experience through DOM operations, and the back-end handles server tasks through Node.js. 1. Front-end example: Change the content of the web page text. 2. Backend example: Create a Node.js server.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AMChoosing Python or JavaScript should be based on career development, learning curve and ecosystem: 1) Career development: Python is suitable for data science and back-end development, while JavaScript is suitable for front-end and full-stack development. 2) Learning curve: Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners; JavaScript syntax is flexible. 3) Ecosystem: Python has rich scientific computing libraries, and JavaScript has a powerful front-end framework.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools






