 Web Front-end
Web Front-end JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial JavaScript Basics 3 categories, callback functions, built-in objects, event processing_Basic knowledge
JavaScript Basics 3 categories, callback functions, built-in objects, event processing_Basic knowledgeJavaScript Basics 3 categories, callback functions, built-in objects, event processing_Basic knowledge
function class name (parameter list) {
this.attribute;
......
this.function;
}
In this way, functions and data members are implemented using "this."
Let’s define a simple class student ourselves, then construct it and implement an output function.
> ;
(Hey, this is too simple, right? Hundan(||| ̄— ̄)==o(#) ̄▽ ̄)∕ )
Yeah. . Anyway, it’s good to understand the general meaning. .
Anonymous function:
It is a function without a name (parameter list) {.....} Anonymous functions are discarded after use (so pitiful TvT)
Callback function:
It often appears that the parameter of a function is another function. In fact, this situation is often encountered. For example, when adding a listener to a control in Java, the parameter of the listener is actually a function.
For this function, we can directly add new in the parameter, which is an anonymous function. Because each response is targeted at this control, it will generally not be needed again.
But let’s take an example and follow the normal path.
(非常感谢二楼Arliang 指出错误!)
此处注意事项:
1.typeof a的类型function是小写,因为js大小写敏感,所以必须注意。
2.Huidiao(test) test不需要写出括号,因为它的参数就仅仅是一个变量,如果写成(test()),那么函数会执行test();这个函数,但是Huidao函数不执行,因为test()没有返回值,那个么Huidiao的参数其实是未定义的。
输出大家都想得到的。。
然后再说一句:Javascript中没有重载。不要痴心妄想了骚年~ㄟ( ̄v ̄ㄟ)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
接下来学习js里面的内置对象,其实我们已经接触过几个了。
常用的内置对象: String Date Math Array Number Globle
String大家都很懂的,var s="xxxxx"; 或者 var= new String("xxxx"); 意思差不多,至于String里涵盖的一些操作函数的话。。请自行下载javascript的API文档亲,我就不给连接了亲,自己搜搜吧~
提供一个在线的参考手册连接:点这里 http://www.jb51.net/w3school/js/jsref_obj_string.htm (这个网站不错,有空可以看看~)
每个对象的数据成员和函数成员就都有了,老师在这里一直讲那些个函数,我都睡着了,其实根本没必要讲,用的时候看看就行了,熟了以后都不需要看就知道有什么啦~
然后稍微说一下Array这个对象,实际上JS并没有提供二维数组,but,我们可以通过嵌套来实现,比如
var array2=new Array(new Array(4), new Array(), new Array(1,2,3,4));
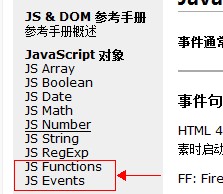
最后,除了这些常用对象外,
还有一些全局的函数和事件也需要熟悉起来,
对应到文档里就是function和event两个部分。
事件处理:
事件处理是什么我觉得应该没有人不清楚吧,我也懒得写概念了,因为写了也没人会记住的╮(╯▽╰)╭
然后,指定事件处理程序有三种方法:
第一:直接在HTML标记中指定
第二:编写特定对象特定之间的javascript
第三:在javascript中说明 =;
常用的事件罗列一下:
| 鼠标事件 | 键盘事件 | HTML事件 | 变动事件 |
|
onclick 单击事件 ondblClick 双击事件 onmouseover 鼠标移到上方 onmouseout 鼠标离开事件 onmousedown 鼠标按下事件 onmouseup 鼠标放开事件 onselect 选中事件 |
onkeydown 按键事件 onkeypress 按下键事件 onkeyup 放开键事件 |
onload 窗口加载事件 onunload 窗口离开事件 onresize 改变窗口大小触发事件 onabort 中断事件 onerror 异常事件 onreset 按下重置按钮事件 onsubmit 提交事件 |
onblur 失去焦点事件 onfocus 获得焦点事件 onchange 值改变触发事件 |
Define a button and then give it a response event. This is actually the first method. Of course, because this response is very simple, you can also directly use it in the button control. Write like this:
(Note here that the string in alert() uses single quotes. Cannot use double double quotes)
The two have the same effect.

After my careful research, many events, such as "onbeforeunload", etc., are only feasible in IE, so we will give up this method without hesitation. Just know it.
PS Use Baidu to search for "Complete Web Page Production Manual". It is a CHM help file. You can download the Sina file that comes out first. It has a lot of information. If necessary, download it for reference~
OK, The third type is said to be widely used in the Ajax framework, but as a person who does not know ajax. . . Okay, let's learn slowly.
The third type slightly involves the DOM that will be discussed in the next part. But it doesn’t matter, it doesn’t affect the overall situation. The third format looks more complicated, but it’s actually very simple.
When adding a control, give the control an ID, and then use the ID to get the control in JavaScript, and then operate its various events, such as:
In this way, we have added the text text box An event response, one thing to emphasize here: script response must be written after the control declaration, otherwise the compiler will not be able to find the control based on the ID.
PS, in fact, you can also find the control based on its name, but it is still recommended to use ID, because the name can be the same, but the id cannot be the same
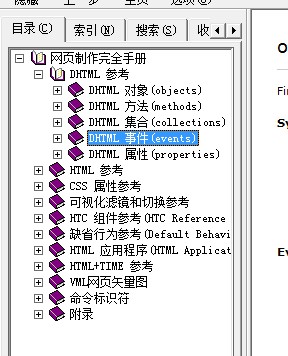
Regarding the responses of each control, you can browse on the previous website, or download the manual I mentioned. The screenshot below is the event list of the input text control in the manual~ Of course, it is not just this. Click, there is a drop-down bar on the right~

In fact, I still recommend downloading this manual. It is a very good tool.
After a brief introduction to event processing, let's learn about the Event object
The event object represents the event status, such as the element where the event occurs, keyboard status, mouse position and mouse button status.
You can use window.event to obtain it in IE, but not FF, so for the sake of compatibility, the following strategy is adopted. . The wisdom of programmers is great.
function eventName(event){
event=event|| window.event;
.............
}
Event program binding:
Because it is more abstract, we still Write a code and feel more at ease.
< ;script type="text/javascript" src="js/output.js">
< ;/body>
Note, thanks to Aleax on the third floor for his help. I quoted his words directly and gave an example, regarding the attribute innerText in the div:
The innerText in FF is not available, alternative method: textContent
IE: oDiv.innerText = aString; oDiv.innerHTML = aString;
FF: oDiv.textContent = aString; oDiv.innerHTML = aString;
Since the browser will ignore unfamiliar statements, we can just write two lines of code to accommodate these two lines as I wrote above. At the same time, there is another way to shorten it to one sentence, which is obj.innerHTML=s;
By the way, here is the difference between innerText and innerHTML: innerText only accepts text and then outputs it directly, but innerHTML recognizes HTML statements, that is, if you write
innerText="< ;br>Hello" ; Then the output is:
Hello If you write innerHTML="
Hello" then the output is Hello after line breaks.

Event bubbling problem
Event bubbling problem is actually that one operation triggers multiple responses. For example, the body defines the onclick event, and the div below the body also defines the onclick event. Then After clicking on the div, the div's event response is first made, and then bubbles up, and the body's click event is also triggered.
The solution is not troublesome, but it still has to accommodate the conflict between the two good friends IE and FF:
To prevent bubbling in IE, use: event object.cancelBubble=true;
To prevent bubbling in FF Bubble, use: event object.stopPropagation(); (I just checked, propagation [,prɔpə'ɡeiʃən] means reproduction, reproduction... Forgive my vocabulary, TvT)
Okay, in order to make this pair good Gay friends live in harmony, we have to make another judgment:
function xxxxx(event){
..........;
if(event&&event.stopPropagation) //Indicates it is a Firefox
event.stopPropagation();
else
event .cancleBubble=true;
}
Of course, this judgment must be written in the lower node. For example, in the example just now, if it is written in the click event of the body, that is It's useless work.
-------------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
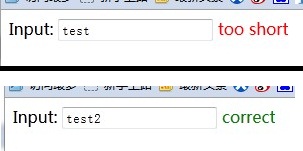
Finally, a small application is to judge the input situation. We Commonly encountered when registering a website:
The code is as follows:
Input:
效果如下:
 Java vs JavaScript: A Detailed Comparison for DevelopersMay 16, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Java vs JavaScript: A Detailed Comparison for DevelopersMay 16, 2025 am 12:01 AMJavaandJavaScriptaredistinctlanguages:Javaisusedforenterpriseandmobileapps,whileJavaScriptisforinteractivewebpages.1)Javaiscompiled,staticallytyped,andrunsonJVM.2)JavaScriptisinterpreted,dynamicallytyped,andrunsinbrowsersorNode.js.3)JavausesOOPwithcl
 Javascript Data Types : Is there any difference between Browser and NodeJs?May 14, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Javascript Data Types : Is there any difference between Browser and NodeJs?May 14, 2025 am 12:15 AMJavaScript core data types are consistent in browsers and Node.js, but are handled differently from the extra types. 1) The global object is window in the browser and global in Node.js. 2) Node.js' unique Buffer object, used to process binary data. 3) There are also differences in performance and time processing, and the code needs to be adjusted according to the environment.
 JavaScript Comments: A Guide to Using // and /* */May 13, 2025 pm 03:49 PM
JavaScript Comments: A Guide to Using // and /* */May 13, 2025 pm 03:49 PMJavaScriptusestwotypesofcomments:single-line(//)andmulti-line(//).1)Use//forquicknotesorsingle-lineexplanations.2)Use//forlongerexplanationsorcommentingoutblocksofcode.Commentsshouldexplainthe'why',notthe'what',andbeplacedabovetherelevantcodeforclari
 Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AMThe main difference between Python and JavaScript is the type system and application scenarios. 1. Python uses dynamic types, suitable for scientific computing and data analysis. 2. JavaScript adopts weak types and is widely used in front-end and full-stack development. The two have their own advantages in asynchronous programming and performance optimization, and should be decided according to project requirements when choosing.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AMWhether to choose Python or JavaScript depends on the project type: 1) Choose Python for data science and automation tasks; 2) Choose JavaScript for front-end and full-stack development. Python is favored for its powerful library in data processing and automation, while JavaScript is indispensable for its advantages in web interaction and full-stack development.
 Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMPython and JavaScript each have their own advantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1. Python is easy to learn, with concise syntax, suitable for data science and back-end development, but has a slow execution speed. 2. JavaScript is everywhere in front-end development and has strong asynchronous programming capabilities. Node.js makes it suitable for full-stack development, but the syntax may be complex and error-prone.
 JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AMJavaScriptisnotbuiltonCorC ;it'saninterpretedlanguagethatrunsonenginesoftenwritteninC .1)JavaScriptwasdesignedasalightweight,interpretedlanguageforwebbrowsers.2)EnginesevolvedfromsimpleinterpreterstoJITcompilers,typicallyinC ,improvingperformance.
 JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript can be used for front-end and back-end development. The front-end enhances the user experience through DOM operations, and the back-end handles server tasks through Node.js. 1. Front-end example: Change the content of the web page text. 2. Backend example: Create a Node.js server.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!





