Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >JavaScript Basics 4 window object, DOM_basic knowledge
JavaScript Basics 4 window object, DOM_basic knowledge
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOriginal
- 2016-05-16 17:55:26997browse
他的属性也很丰富,因为我很懒,我就直接复制手册里的东西了:
| closed | 获取引用窗口是否已关闭。 |
| defaultStatus | 设置或获取要在窗口底部的状态栏上显示的缺省信息。 |
| dialogArguments | 设置或获取传递给模式对话框窗口的变量或变量数组。 |
| dialogHeight | 设置或获取模式对话框的高度。 |
| dialogLeft | 设置或获取模式对话框的左坐标。 |
| dialogTop | 设置或获取模式对话框的顶坐标。 |
| dialogWidth | 设置或获取模式对话框的宽度。 |
| frameElement | 获取在父文档中生成 window 的 frame或 iframe 对象。 |
| length | 设置或获取集合中对象的数目。 |
| name | 设置或获取表明窗口名称的值。 |
| offscreenBuffering | 设置或获取对象在对用户可见之前是否要先在屏幕外绘制。 |
| opener | 设置或获取创建当前窗口的窗口的引用。 |
| parent | 获取对象层次中的父窗口。 |
| returnValue | 设置或获取从模式对话框返回的值。 |
| screenLeft | 获取浏览器客户区左上角相对于屏幕左上角的 x 坐标。 |
| screenTop | 获取浏览器客户区左上角相对于屏幕左上角的 y 坐标。 |
| self | 获取对当前窗口或框架的引用。 |
| status | 设置或获取位于窗口底部状态栏的信息。 |
| top | 获取最顶层的祖先窗口。 |
The body element will serve as the host for the following window object events: onblur, onbeforeunload, onfocus, onload and onunload.
The following uses window to create a prompt when leaving the page:
We usually have prompts when leaving the page. For example, whether to confirm leaving, etc., in fact, just add a sentence to the body node:
In this case, there will be a message when leaving. hint.
In this example, we pay attention to three points:
You must write return ‘xxxxx’ with or without a semicolon. If you only write a string, there will be no prompt.
The problem emphasized before, because there are double quotes after the onbeforeunload event, the return must be enclosed in single quotes.
This sentence is valid for FF, chrome, and IE. The triggering mechanisms of chrome and IE are the same. The phenomenon is: write the return string in the confirmation bar. I guess the process should be like this: the user clicks the close button to trigger the onbeforeunload object. At this time, if the return value of the onbeforeunload object is a string, then a warning will be issued upwards and the string will be displayed. But FF is different, only the default warning is displayed.
There is the following prompt in chrome:

The returned sentence appears above the navigation, with the same effect as IE (if IE does not display, just click to allow the script to run.).
If it is FF, only the upper level prompt will appear, which has nothing to do with the sentence we wrote. However, we still have to write it, otherwise there will be no prompt in FF.
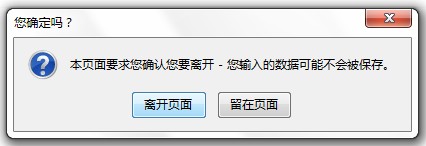
So if we want to make its confirmation box appear with our own things, I tried many times and found that FF cannot replace its default box with other dialog boxes, so we can only add a confirm silently , but in this case FF will prompt twice. Both IE and Chrome will enter the return string of the function in the exit prompt, which is good. The following is the modified code after feedback from the first floor.
After testing, this code only displays a prompt in chrome 16.0.912.0, but dual prompts of FF and chrome will appear in some chrome-based browsers (such as sunchrome). I guess it is because these browsers include Other kernels have been removed, and I don’t quite understand what’s going on.
Anyway, just contact me~ Hey~
testing
那个方法一的意思是:如果在这里写了这个节点,那么IE运行的时候就会运行这个部分的代码,但是如果没有这个节点,那么这段代码在FF和chrome正常,但是在IE里,会出现两个提示都出现的情况,这是因为它既会执行window.confirm这句,也会返回chrome那句。
以下是上面代码在各浏览器的测试:

哈哈,怎么样,不错吧~
好,接下在就是万众期待(其实只有LZ期待吧= =+)的DOM
DOM的全称是document object model,怎么理解这个东西挺关键的,我看了不少定义,有的说它是个平台,有的说它是个接口,anyway,我打开了它的官方guide网站:http://www.w3.org/DOM/
它对DOM的定义是:
The Document Object Model is a platform- and language-neutral interface that will allow programs and scripts to dynamically access and update the content, structure and style of documents. The document can be further processed and the results of that processing can be incorporated back into the presented page.
我来简单翻译下好了:DOM是个平台/语言的中间接口,它可以允许程序和脚本动态的访问和更新内容、架构以及文件style。文件可以被进一步处理并将结果返回到显示页面。
其实这么说我看了也还是云里雾里,所以可以这么理解,DOM是个大家为了编程方便,传输速度快而统一起来的,基于树规范,它跟浏览器是没有关系的。DOM的基本思想就是树形结构,比如HTML文件,就是一个树形结构。DOM是没有跟任何语言绑定的,我们利用js可以对html dom进行动态的修改。
DOM有三个级别,可以分为:core Dom, XML DOM(*), HTML DOM三部分。中间那个是作为文档传输标准,使用很广泛的,但是这里就着重讲HTML DOM。
DOM把文档分为带有:元素、属性、文本 的树形结构,然后将这些作为结点来构造文档的树形结构,这样,就可以通过一个结点访问到所有的结点。
之前给出的那个网站(http://www.jb51.net/w3school/js/jsref_obj_string.htm)里面有比较全的DOM的玩意儿,可以用来参考,但是用来做教程还是有点生硬。
我打算先介绍节点类型,然后再对应到代码里。
节点类型介绍(复制来自http://www.jb51.net/w3schools/jsref/dom_obj_node.htm)
| Node type | Description | Children | Value | Constant |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | Represents an element | Element, Text, Comment, ProcessingInstruction, CDATASection, EntityReference | 1 | ELEMENT_NODE |
| Attr | Represents an attribute | Text, EntityReference | 2 | ATTRIBUTE_NODE |
| Text | Represents textual content in an element or attribute | None | 3 | TEXT_NODE |
| CDATASection | Represents a CDATA section in a document (text that will NOT be parsed by a parser) | None | 4 | CDATA_SECTION_NODE |
| EntityReference | Represents an entity reference | Element, ProcessingInstruction, Comment, Text, CDATASection, EntityReference | 5 | ENTITY_REFERENCE_NODE |
| Entity | Represents an entity | Element, ProcessingInstruction, Comment, Text, CDATASection, EntityReference | 6 | ENTITY_NODE |
| ProcessingInstruction | Represents a processing instruction | None | 7 | PROCESSING_INSTRUCTION_NODE |
| Comment | Represents a comment | None | 8 | COMMENT_NODE |
| Document | Represents the entire document (the root-node of the DOM tree) | Element, ProcessingInstruction, Comment, DocumentType | 9 | DOCUMENT_NODE |
| DocumentType | Provides an interface to the entities defined for the document | None | 10 | DOCUMENT_TYPE_NODE |
| DocumentFragment | Represents a "lightweight" Document object, which can hold a portion of a document | Element, ProcessingInstruction, Comment, Text, CDATASection, EntityReference | 11 | DOCUMENT_FRAGMENT_NODE |
| Notation | Represents a notation declared in the DTD | None | 12 | NOTATION_NODE |
Ok, after knowing this, we use a small html file to view the tree structure of the DOM:
HTML text
Tree structure analysis

PS: Theoretically br is not a node, but I’m not sure. I hope someone who knows can tell me~.
1. The file is always the root node. To obtain the document node, you can directly use document.documentElement or document.body to obtain it.
2.script is also a node. Everything in <> is a node, including comments.
3. The name of the node, which is similar to hear title, is the tagName of the node.
For a method to get other nodes from one node, it is nothing more than upward, downward, or parallel directions. For details, you can check the properties and methods of the DOM Node object in the website given above. I have different opinions. One list. (Many of the above things are not available in IE. You should consider how to use them after testing.)
After roughly looking at the various methods of nodes in the DOM, we make a small application:
The user clicks , you can add open or closed sub-options.

Additional point: In addition to adding and deleting, nodes can also be cloned. The function is cloneNode. In addition to setAttribute, events can also be attached. For example, this node has Events such as onclick can be implemented using the addEvent function. I won’t write down the specifics, the principles are the same~.
Related articles
See more- An in-depth analysis of the Bootstrap list group component
- Detailed explanation of JavaScript function currying
- Complete example of JS password generation and strength detection (with demo source code download)
- Angularjs integrates WeChat UI (weui)
- How to quickly switch between Traditional Chinese and Simplified Chinese with JavaScript and the trick for websites to support switching between Simplified and Traditional Chinese_javascript skills

