 Web Front-end
Web Front-end JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial Introduction to the use of Javascript reference pointers_javascript tips
Introduction to the use of Javascript reference pointers_javascript tipsPlease try to complete the following cloze:
/* Create a Queue, head is head0, tail is tail0 */
function IntList(head0, tail0){
this.head = head0 || 0;
this.tail = tail0 || null;
}
/* Return an IntList containing all the numbers in the array*/
IntList.list = function(__args){
var sentinel = new IntList(),
len = __args.length,
p = sentinel;
for(var i = 0; i p.tail = new IntList(__args[i]);
p = p.tail ;
}
return sentinel.tail;
};
/* Return the string representation of the object*/
IntList.prototype.toString = function(){
var temp = "";
temp = "[";
for(var L = this; L !== null; L = L.tail){
temp = temp " " L.head;
}
temp = " ]";
return temp;
};
/**Returns an IntList containing IntList A and IntList B,
* where the elements of B are after A. The new keyword cannot be used.
*/
function dcatenate(A, B){
/* Complete function*/
}
/**Returns a new IntList with length len,
* starting with the #start element (where #0 is the first element),
* cannot change L.
*/
function sublist(L, start, len){
/* Complete function*/
}
This is a linked list question written in Javascript. Since linked lists have relatively complex reference operations, they can be used to examine the understanding of Javascript references. Comes with a simple test case:
/* Test dcatenate and sublist Is the function correct*/
function test(){
var A = IntList.list([4,6,7,3,8]),
B = IntList.list([3,2, 5,9]);
dcatenate(A, B);
if(A.toString() === "[ 4 6 7 3 8 3 2 5 9 ]"){
alert(" The dcatenate function is correct. ");
}else{
alert("The dcatenate function is wrong.");
}
var L = IntList.list([3,4,5,2,6 ,8,1,9]),
result = sublist(L, 3, 3);
if(result.toString() === "[ 2 6 8 ]"){
alert( "The sublist function is correct.");
}else{
alert("The sublist function is correct.");
}
}
Javascript reference?
In fact, when assigning a reference type instance to a variable, the variable holds a reference to the instance:
var temp = new Object();
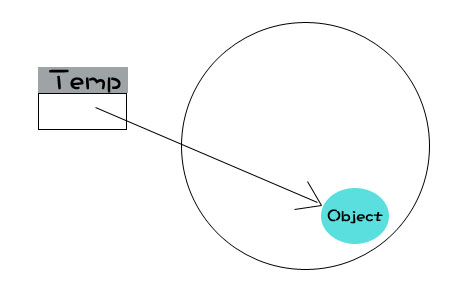
This behavior is very consistent with its name, reference type, and its instances are of course referenced.
And when the variable is assigned to another variable, it is actually just a copy of the reference:
var temp2 = temp;
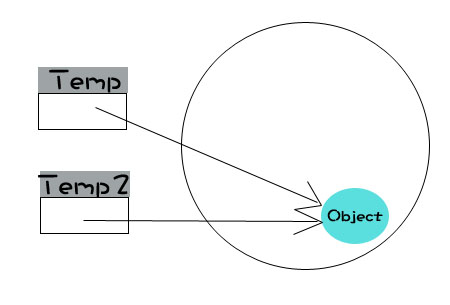
So although from the definition: temp2 = temp, they are not directly related. For example, the reference of temp is modified:
var temp = {
name: "temp"
};
var temp2 = temp;
temp = {
name: "not temp2"
};
temp === temp2; //false
Of course, if we modify only the instance pointed to by the pointer, then temp2 is still equal to temp:
var temp = {
name: " temp"
};
var temp2 = temp;
temp.name = "also temp2";
temp === temp2; //true
What is IntList?
Let’s analyze the picture below:
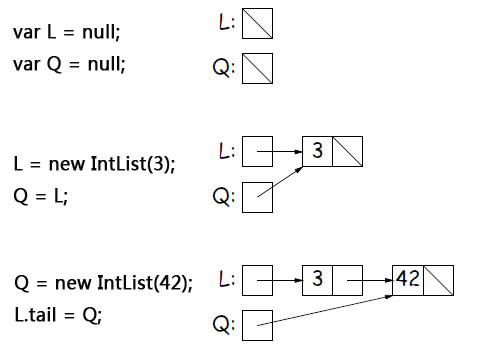
- Create two empty variables, so L and Q in the picture on the right are empty. Create a new IntList with a head of 3 and an empty tail, and assign the value referenced by L to Q, so both L and Q point to this new IntList. Q points to a newly created IntList whose head is 42 and whose tail is empty. The pointer of Q is assigned to L.tail, so that the two IntLists are nested.
It can be seen that IntList is a data structure that achieves multiple nesting through pointers, which is called a Linked List.
1. Create two empty variables, so L and Q in the picture on the right are empty.2. Create a new IntList with a head of 3 and an empty tail. Assign the value referenced by L to Q, so both L and Q point to this new IntList.
3.Q points to a newly created IntList whose head is 42 and whose tail is empty. Assign the pointer of Q to L.tail, so that the two IntLists are nested.
It can be seen that IntList is a data structure that achieves multiple nesting through pointers, which is called a Linked List.
IntList merge
We just need to point the tail of one to the other. In this way, the two IntLists are connected:
/**Returns an IntList containing IntList A and IntList B,
* where the elements of B are after A. The new keyword cannot be used.
*/
function dcatenate(A, B){
var p;
for(p = A; p != null; p = p.tail){
if(p.tail === null){
p.tail = B;
break;
}
}
return A
}
IntList interception
Since the question requires that the original IntList cannot be changed, we can only take out the data from the original IntList and reconstruct new data.
/**Returns a new IntList with length len,
* starting with the #start element (where #0 is the first element),
* cannot change L.
*/
function sublist(L, start, len){
var K,
P,
J;
var i = 0,
end = start len;
for(P = L; i if(i continue;
}else if(i === start){
K = new IntList(P.head);
J = K;
}else if(i > start && i J.tail = new IntList(P.head);
J = J.tail;
}else if(i >= end){
break;
}
}
return K;
}
Thinking Questions
1. How do functions pass parameters when they are passed? For example, what is the citation process for the following code?
var obj = {
name: "anything"
};
function getName(__obj){
return __obj.name;
}
var name = getName(obj);
 JavaScript Engines: Comparing ImplementationsApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScript Engines: Comparing ImplementationsApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AMDifferent JavaScript engines have different effects when parsing and executing JavaScript code, because the implementation principles and optimization strategies of each engine differ. 1. Lexical analysis: convert source code into lexical unit. 2. Grammar analysis: Generate an abstract syntax tree. 3. Optimization and compilation: Generate machine code through the JIT compiler. 4. Execute: Run the machine code. V8 engine optimizes through instant compilation and hidden class, SpiderMonkey uses a type inference system, resulting in different performance performance on the same code.
 Beyond the Browser: JavaScript in the Real WorldApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Beyond the Browser: JavaScript in the Real WorldApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AMJavaScript's applications in the real world include server-side programming, mobile application development and Internet of Things control: 1. Server-side programming is realized through Node.js, suitable for high concurrent request processing. 2. Mobile application development is carried out through ReactNative and supports cross-platform deployment. 3. Used for IoT device control through Johnny-Five library, suitable for hardware interaction.
 Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AMI built a functional multi-tenant SaaS application (an EdTech app) with your everyday tech tool and you can do the same. First, what’s a multi-tenant SaaS application? Multi-tenant SaaS applications let you serve multiple customers from a sing
 How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AMThis article demonstrates frontend integration with a backend secured by Permit, building a functional EdTech SaaS application using Next.js. The frontend fetches user permissions to control UI visibility and ensures API requests adhere to role-base
 JavaScript: Exploring the Versatility of a Web LanguageApr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
JavaScript: Exploring the Versatility of a Web LanguageApr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AMJavaScript is the core language of modern web development and is widely used for its diversity and flexibility. 1) Front-end development: build dynamic web pages and single-page applications through DOM operations and modern frameworks (such as React, Vue.js, Angular). 2) Server-side development: Node.js uses a non-blocking I/O model to handle high concurrency and real-time applications. 3) Mobile and desktop application development: cross-platform development is realized through ReactNative and Electron to improve development efficiency.
 The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future ProspectsApr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future ProspectsApr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AMThe latest trends in JavaScript include the rise of TypeScript, the popularity of modern frameworks and libraries, and the application of WebAssembly. Future prospects cover more powerful type systems, the development of server-side JavaScript, the expansion of artificial intelligence and machine learning, and the potential of IoT and edge computing.
 Demystifying JavaScript: What It Does and Why It MattersApr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Demystifying JavaScript: What It Does and Why It MattersApr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AMJavaScript is the cornerstone of modern web development, and its main functions include event-driven programming, dynamic content generation and asynchronous programming. 1) Event-driven programming allows web pages to change dynamically according to user operations. 2) Dynamic content generation allows page content to be adjusted according to conditions. 3) Asynchronous programming ensures that the user interface is not blocked. JavaScript is widely used in web interaction, single-page application and server-side development, greatly improving the flexibility of user experience and cross-platform development.
 Is Python or JavaScript better?Apr 06, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Is Python or JavaScript better?Apr 06, 2025 am 12:14 AMPython is more suitable for data science and machine learning, while JavaScript is more suitable for front-end and full-stack development. 1. Python is known for its concise syntax and rich library ecosystem, and is suitable for data analysis and web development. 2. JavaScript is the core of front-end development. Node.js supports server-side programming and is suitable for full-stack development.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft




