Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >Detailed explanation of how to use offset, client and scroll in javascript_javascript skills
Detailed explanation of how to use offset, client and scroll in javascript_javascript skills
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOriginal
- 2016-05-16 17:45:551082browse
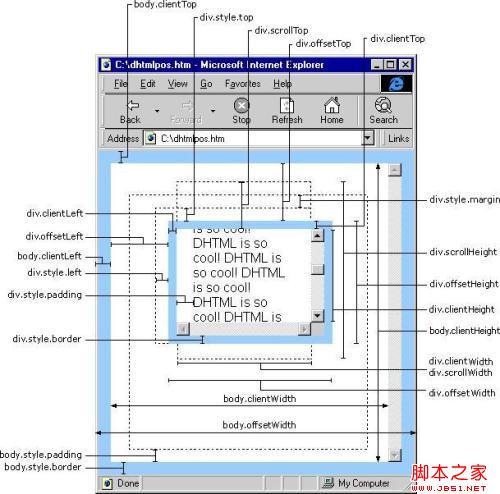
offsetTop 指元素距离上方或上层控件的位置,整型,单位像素。
offsetLeft 指元素距离左方或上层控件的位置,整型,单位像素。
offsetWidth 指元素控件自身的宽度,整型,单位像素。
offsetHeight 指元素控件自身的高度,整型,单位像素。
网页可见区域宽:document.body.clientWidth
网页可见区域高:document.body.clientHeight
网页可见区域宽:document.body.offsetWidth (包括边线的宽)
网页可见区域高:document.body.offsetHeight (包括边线的宽)
网页正文全文宽:document.body.scrollWidth
网页正文全文高:document.body.scrollHeight
网页被卷去的高:document.body.scrollTop
网页被卷去的左:document.body.scrollLeft
网页正文部分上:window.screenTop
网页正文部分左:window.screenLeft
屏幕分辨率的高:window.screen.height
屏幕分辨率的宽:window.screen.width
屏幕可用工作区高度:window.screen.availHeight
屏幕可用工作区宽度:window.screen.availWidth
这里说说四种浏览器对 document.body 的 clientHeight、offsetHeight 和 scrollHeight 的解释。
这四种浏览器分别为IE(Internet Explorer)、NS(Netscape)、Opera、FF(FireFox)。
clientHeight
四种浏览器对 clientHeight 的解释都没有什么异议,都认为是内容可视区域的高度,也就是说页面浏览器中可以看到内容的这个区域的高度,一般是最后一个工具条以下到状态栏以上的这个区域,与页面内容无关。
offsetHeight
IE、Opera 认为 offsetHeight = clientHeight + 滚动条 + 边框。
NS、FF 认为 offsetHeight 是网页内容实际高度,可以小于 clientHeight。
scrollHeight
IE、Opera 认为 scrollHeight 是网页内容实际高度,可以小于 clientHeight。
NS、FF 认为 scrollHeight 是网页内容高度,不过最小值是 clientHeight
介绍:
1、offsetLeft
假设 obj 为某个 HTML 控件。
obj.offsetTop 指 obj 距离上方或上层控件的位置,整型,单位像素。
obj.offsetLeft 指 obj 距离左方或上层控件的位置,整型,单位像素。
obj.offsetWidth 指 obj 控件自身的宽度,整型,单位像素。
obj.offsetHeight 指 obj 控件自身的高度,整型,单位像素。
我们对前面提到的“上方或上层”与“左方或上层”控件作个说明。
例如:
“提交”按钮的 offsetTop 指“提交”按钮距“tool”层上边框的距离,因为距其上边最近的是 “tool” 层的上边框。
“重置”按钮的 offsetTop 指“重置”按钮距“tool”层上边框的距离,因为距其上边最近的是 “tool” 层的上边框。
“提交”按钮的 offsetLeft 指“提交”按钮距“tool”层左边框的距离,因为距其左边最近的是 “tool” 层的左边框。
“重置”按钮的 offsetLeft 指“重置”按钮距“提交”按钮右边框的距离,因为距其左边最近的是“提交”按钮的右边框。
以上属性在 FireFox 中也有效。
另 外:我们这里所说的是指 HTML 控件的属性值,并不是 document.body,document.body 的值在不同浏览器中有不同解释(实际上大多数环境是由于对 document.body 解释不同造成的,并不是由于对 offset 解释不同造成的),点击这里查看不同点。
标题:offsetTop 与 style.top 的区别
预备知识:offsetTop、offsetLeft、offsetWidth、offsetHeight
我们知道 offsetTop 可以获得 HTML 元素距离上方或外层元素的位置,style.top 也是可以的,二者的区别是:
一、offsetTop 返回的是数字,而 style.top 返回的是字符串,除了数字外还带有单位:px。
二、offsetTop 只读,而 style.top 可读写。
三、如果没有给 HTML 元素指定过 top 样式,则 style.top 返回的是空字符串。
offsetLeft 与 style.left、offsetWidth 与 style.width、offsetHeight 与 style.height 也是同样道理。
标题:clientHeight、offsetHeight和scrollHeight
我们这里说说四种浏览器对 document.body 的 clientHeight、offsetHeight 和 scrollHeight 的解释,这里说的是 document.body,如果是 HTML 控件,则又有不同,点击这里查看。
这四种浏览器分别为IE(Internet Explorer)、NS(Netscape)、Opera、FF(FireFox)。
2、clientHeight
clientHeight
大家对 clientHeight 都没有什么异议,都认为是内容可视区域的高度,也就是说页面浏览器中可以看到内容的这个区域的高度,一般是最后一个工具条以下到状态栏以上的这个区域,与页面内容无关。
offsetHeight
IE、Opera 认为 offsetHeight = clientHeight + 滚动条 + 边框。
NS、FF 认为 offsetHeight 是网页内容实际高度,可以小于 clientHeight。
scrollHeight
IE、Opera 认为 scrollHeight 是网页内容实际高度,可以小于 clientHeight。
NS、FF 认为 scrollHeight 是网页内容高度,不过最小值是 clientHeight。
简单地说
clientHeight 就是透过浏览器看内容的这个区域高度。
NS、 FF 认为 offsetHeight 和 scrollHeight 都是网页内容高度,只不过当网页内容高度小于等于 clientHeight 时,scrollHeight 的值是 clientHeight,而 offsetHeight 可以小于 clientHeight。
IE、Opera 认为 offsetHeight 是可视区域 clientHeight 滚动条加边框。scrollHeight 则是网页内容实际高度。
同理
clientWidth、offsetWidth 和 scrollWidth 的解释与上面相同,只是把高度换成宽度即可。
但是
FF 在不同的 DOCTYPE 中对 clientHeight 的解释不同, xhtml 1 trasitional 中则不是如上解释的。其它浏览器则不存在此问题。
标题:scrollTop、scrollLeft、scrollWidth、scrollHeight
3、scrollLeft
scrollTop 是“卷”起来的高度值,示例:
如果为 p 设置了 scrollTop,这些内容可能不会完全显示。
Since scrollTop is set for the outer element p, the inner element will scroll upward.
scrollLeft is similar.
We already know that offsetHeight is the width of its own element.
And scrollHeight is the absolute width of the inner element, including the hidden part of the inner element.
In the above, the scrollHeight of p is 300, and the offsetHeight of p is 100.
scrollWidth is similar.
IE and FireFox fully support, while Netscape and Opera do not support scrollTop and scrollLeft (except document.body).
Title: offsetTop, offsetLeft, offsetWidth, offsetHeight
4. clientLeft
Returns the distance between the offsetLeft attribute value of the object and the real value to the left side of the current window, you can Understood as the length of the border
I have always been confused about the methods of offsetLeft, offsetTop, scrollLeft, and scrollTop. I spent a day studying them carefully. The following results were obtained:
1.offsetTop:
The distance from the current object to the top of its superior layer.
cannot be assigned a value. Please set the distance from the object to the top of the page. Use the style.top attribute.
2.offsetLeft:
The distance between the current object and the left side of its parent layer.
Cannot be assigned a value. Set the object to the left of the page Please use the style.left attribute for the distance.
3.offsetWidth:
The width of the current object. The difference between
and the style.width attribute is: if the width of the object is set The fixed value is the percentage width, no matter the page becomes larger or smaller, style.width returns this percentage, while offsetWidth returns the width value of the object in different pages instead of the percentage value
4. offsetHeight: The difference between
and the style.height property is that if the width of the object is set to a percentage height, no matter the page becomes larger or smaller, style.height will return this percentage, while offsetHeight will return the percentage. The height value of the object in different pages instead of the percentage value
5.offsetParent :
The parent object of the current object.
Note. If the object is included in a DIV , this DIV will not be regarded as the upper level of this object (that is, the upper level of the object will skip the DIV object). When the upper level is a Table, there will be no problem.
Using this attribute, you can get the location of the current object. Absolute position in pages of different sizes.
Get the absolute position script code
Copy the code The code is as follows:
function GetPosition(obj )
{
var left = 0;
var top = 0;
while(obj != document.body)
{
left = obj.offsetLeft;
top = obj.offsetTop;
obj = obj.offsetParent;
}
alert("Left Is : " left "rn" "Top Is : " top);
}
6.scrollLeft:
The distance from the far left side of the object to the left side of the object within the range displayed in the current window.
That is, when a horizontal scroll bar appears, the distance the scroll bar is pulled.
7.scrollTop
The distance from the top of the object to the top edge of the object within the range displayed in the current window.
That is, when a vertical scroll bar appears, the distance the scroll bar is pulled.
Here we talk about the interpretation of clientHeight, offsetHeight and scrollHeight of document.body by four browsers. Here we are talking about document.body. If it is an HTML control, it is different. Click here to view.
The four browsers are IE (Internet Explorer), NS (Netscape), Opera, and FF (FireFox).
clientHeight
No one has any objection to clientHeight. They all think it is the height of the visible area of the content, which means the height of the area where the content can be seen in the page browser. , generally the area below the last toolbar to above the status bar, has nothing to do with the page content.
offsetHeight
IE and Opera consider offsetHeight = clientHeight scroll bar border.
NS and FF consider offsetHeight to be the actual height of the web page content, which can be smaller than clientHeight.
scrollHeight
IE and Opera believe that scrollHeight is the actual height of the web page content and can be smaller than clientHeight.
NS and FF consider scrollHeight to be the height of web page content, but the minimum value is clientHeight.
Simply put
clientHeight is the height of the area where the content is viewed through the browser.
NS and FF believe that offsetHeight and scrollHeight are both web page content heights, but when the web page content height is less than or equal to clientHeight, the value of scrollHeight is clientHeight, and offsetHeight can be less than clientHeight.
IE and Opera believe that offsetHeight is the visible area clientHeight scroll bar plus
Statement:
The content of this article is voluntarily contributed by netizens, and the copyright belongs to the original author. This site does not assume corresponding legal responsibility. If you find any content suspected of plagiarism or infringement, please contact admin@php.cn
Previous article:Javascript deletes array elements based on specified subscript or object_javascript skillsNext article:Javascript deletes array elements based on specified subscript or object_javascript skills
Related articles
See more- An in-depth analysis of the Bootstrap list group component
- Detailed explanation of JavaScript function currying
- Complete example of JS password generation and strength detection (with demo source code download)
- Angularjs integrates WeChat UI (weui)
- How to quickly switch between Traditional Chinese and Simplified Chinese with JavaScript and the trick for websites to support switching between Simplified and Traditional Chinese_javascript skills

