Ray: A Powerful Framework for Scaling AI and Python Applications
Ray is a revolutionary open-source framework designed to effortlessly scale AI and Python applications. Its intuitive API allows researchers and developers to transition their code from single-machine environments to powerful clusters with minimal adjustments, often requiring only a few decorator changes. This guide delves into Ray's architecture, capabilities, and practical applications within modern machine learning workflows.
Key Learning Objectives:
- Grasp Ray's architecture and its role in distributed AI/ML computing.
- Master Ray's ecosystem (Train, Tune, Serve, Data) for comprehensive ML workflows.
- Compare Ray's strengths against other distributed computing frameworks.
- Design robust distributed training pipelines for large language models (LLMs).
- Optimize resource allocation and effectively debug distributed applications.
(This article is part of the Data Science Blogathon.)
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Ray and Distributed Computing
- The Challenge of Scaling Python Applications
- The Ray Framework Architecture
- Getting Started with Ray
- Ray's Programming Model: Tasks and Actors
- Understanding Ray Cluster Architecture
- Ray Object Store and Memory Management
- Leveraging Ray for AI and ML Workloads
- Distributed Fine-tuning of an LLM with Ray
- Environment Setup and Configuration
- Model Evaluation and Performance Metrics
- Real-World Applications and Case Studies
- Ray's Impact at OpenAI: Powering LLMs
- Advanced Ray Features and Best Practices
- Comparative Analysis: Ray vs. Other Frameworks
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction to Ray and Distributed Computing:
Ray's open-source nature and unified API make it a powerful tool for scaling AI and Python applications, seamlessly transitioning from laptops to clusters. Originally developed at UC Berkeley's RISELab and now maintained by Anyscale, Ray has become a cornerstone for training and deploying advanced AI models.
The increasing reliance on distributed computing in AI is driven by:
- Massive Model Sizes: Modern LLMs boast billions or trillions of parameters.
- Expanding Datasets: Training data volumes often surpass single-machine processing capabilities.
- Intense Computational Demands: Complex algorithms require substantial computational resources.
- Deployment Scalability: Serving models effectively demands distributed infrastructure.
Unlike traditional frameworks that necessitate extensive code rewrites, Ray's simplicity streamlines the transition to multi-machine computation.
The Challenge of Scaling Python Applications:
While Python dominates data science and machine learning, its inherent design doesn't inherently support distributed computing. Scaling Python applications often presents these hurdles:
- Low-Level Distribution Complexity: Managing processes, load balancing, and fault tolerance.
- Data Transfer Efficiency: Moving data between machines efficiently.
- Resource Allocation: Managing CPU, GPU, and memory across a cluster.
- Code Complexity: Rewriting algorithms for distributed environments.
Ray addresses these challenges by providing a unified framework that simplifies complexity while offering fine-grained control.
The Ray Framework Architecture:
Ray's architecture comprises three core components:

- Ray AI Libraries: A collection of Python libraries tailored for various ML applications.
- Ray Core: The foundation—a general-purpose distributed computing library.
- Ray Clusters: Multiple worker nodes connected to a central head node, scalable in size.
This modular design allows for efficient application building and management.
(Continue with the remaining sections, adapting the text similarly to maintain the original meaning while varying the phrasing and sentence structure. Remember to keep the images in their original positions and format.)
The above is the detailed content of Guide to Ray for Scalable AI and Machine Learning Applications. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 The Hidden Dangers Of AI Internal Deployment: Governance Gaps And Catastrophic RisksApr 28, 2025 am 11:12 AM
The Hidden Dangers Of AI Internal Deployment: Governance Gaps And Catastrophic RisksApr 28, 2025 am 11:12 AMThe unchecked internal deployment of advanced AI systems poses significant risks, according to a new report from Apollo Research. This lack of oversight, prevalent among major AI firms, allows for potential catastrophic outcomes, ranging from uncont
 Building The AI PolygraphApr 28, 2025 am 11:11 AM
Building The AI PolygraphApr 28, 2025 am 11:11 AMTraditional lie detectors are outdated. Relying on the pointer connected by the wristband, a lie detector that prints out the subject's vital signs and physical reactions is not accurate in identifying lies. This is why lie detection results are not usually adopted by the court, although it has led to many innocent people being jailed. In contrast, artificial intelligence is a powerful data engine, and its working principle is to observe all aspects. This means that scientists can apply artificial intelligence to applications seeking truth through a variety of ways. One approach is to analyze the vital sign responses of the person being interrogated like a lie detector, but with a more detailed and precise comparative analysis. Another approach is to use linguistic markup to analyze what people actually say and use logic and reasoning. As the saying goes, one lie breeds another lie, and eventually
 Is AI Cleared For Takeoff In The Aerospace Industry?Apr 28, 2025 am 11:10 AM
Is AI Cleared For Takeoff In The Aerospace Industry?Apr 28, 2025 am 11:10 AMThe aerospace industry, a pioneer of innovation, is leveraging AI to tackle its most intricate challenges. Modern aviation's increasing complexity necessitates AI's automation and real-time intelligence capabilities for enhanced safety, reduced oper
 Watching Beijing's Spring Robot RaceApr 28, 2025 am 11:09 AM
Watching Beijing's Spring Robot RaceApr 28, 2025 am 11:09 AMThe rapid development of robotics has brought us a fascinating case study. The N2 robot from Noetix weighs over 40 pounds and is 3 feet tall and is said to be able to backflip. Unitree's G1 robot weighs about twice the size of the N2 and is about 4 feet tall. There are also many smaller humanoid robots participating in the competition, and there is even a robot that is driven forward by a fan. Data interpretation The half marathon attracted more than 12,000 spectators, but only 21 humanoid robots participated. Although the government pointed out that the participating robots conducted "intensive training" before the competition, not all robots completed the entire competition. Champion - Tiangong Ult developed by Beijing Humanoid Robot Innovation Center
 The Mirror Trap: AI Ethics And The Collapse Of Human ImaginationApr 28, 2025 am 11:08 AM
The Mirror Trap: AI Ethics And The Collapse Of Human ImaginationApr 28, 2025 am 11:08 AMArtificial intelligence, in its current form, isn't truly intelligent; it's adept at mimicking and refining existing data. We're not creating artificial intelligence, but rather artificial inference—machines that process information, while humans su
 New Google Leak Reveals Handy Google Photos Feature UpdateApr 28, 2025 am 11:07 AM
New Google Leak Reveals Handy Google Photos Feature UpdateApr 28, 2025 am 11:07 AMA report found that an updated interface was hidden in the code for Google Photos Android version 7.26, and each time you view a photo, a row of newly detected face thumbnails are displayed at the bottom of the screen. The new facial thumbnails are missing name tags, so I suspect you need to click on them individually to see more information about each detected person. For now, this feature provides no information other than those people that Google Photos has found in your images. This feature is not available yet, so we don't know how Google will use it accurately. Google can use thumbnails to speed up finding more photos of selected people, or may be used for other purposes, such as selecting the individual to edit. Let's wait and see. As for now
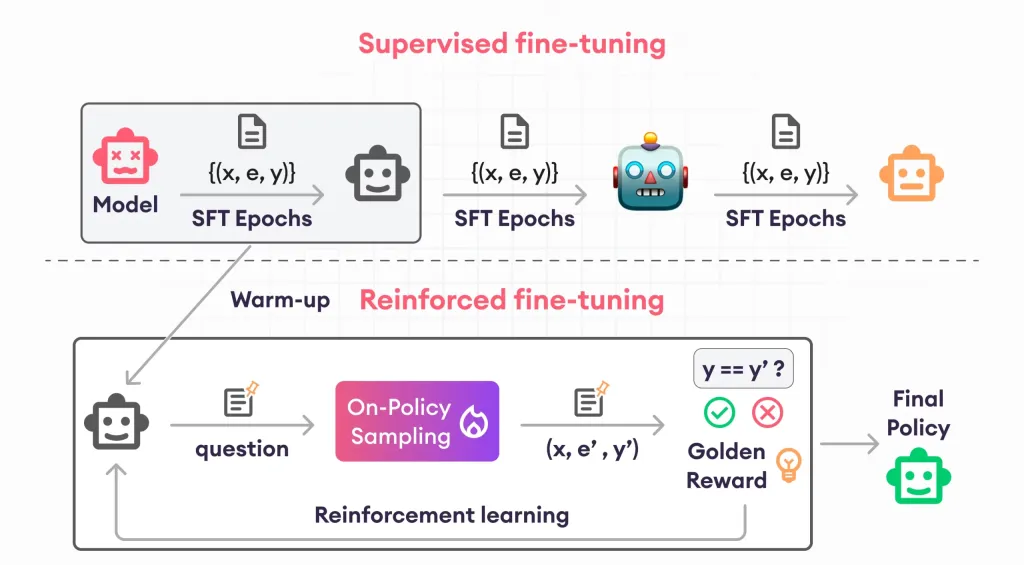 Guide to Reinforcement Finetuning - Analytics VidhyaApr 28, 2025 am 09:30 AM
Guide to Reinforcement Finetuning - Analytics VidhyaApr 28, 2025 am 09:30 AMReinforcement finetuning has shaken up AI development by teaching models to adjust based on human feedback. It blends supervised learning foundations with reward-based updates to make them safer, more accurate, and genuinely help
 Let's Dance: Structured Movement To Fine-Tune Our Human Neural NetsApr 27, 2025 am 11:09 AM
Let's Dance: Structured Movement To Fine-Tune Our Human Neural NetsApr 27, 2025 am 11:09 AMScientists have extensively studied human and simpler neural networks (like those in C. elegans) to understand their functionality. However, a crucial question arises: how do we adapt our own neural networks to work effectively alongside novel AI s


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.






