
Dynex, a company from Liechtenstein, recently launched its Quantum Diffusion Large Language Model (qdLLM) in its SXSW 2025 Innovation Award final, becoming a compelling development. The company claims its qdLLM is able to generate generative AI output faster and more efficiently than traditional Transformer-based systems that rely on current technology infrastructure.
How does this compare to other emerging approaches? What does this mean for the broader future of AI?
The significance of quantum computing to AI
The core difference of quantum computing is that it uses qubits, which can exist in multiple states at the same time due to quantum superposition. This allows quantum computers to evaluate a large number of potential solutions in parallel, which may have advantages in tasks such as large-scale optimization, simulation, or pattern recognition.
In the field of AI, researchers have explored how quantum features can improve tasks such as natural language processing, machine learning optimization, and model training efficiency. However, most of these efforts are still in their early stages. For example, IBM and MIT have studied how hybrid quantum classical models reduce training time for specific deep learning tasks, while startups such as Zapata AI are experimenting with quantum enhancement models for sentiment analysis and prediction.
In this context, Dynex's approach introduces a new architecture that uses quantum heuristic algorithms to run LLM more efficiently through decentralized hardware.
Dynex's qdLLM: A diffusion-based parallel approach
Unlike Transformer-based models that use autoregression techniques to generate one tag at a time, Dynex's qdLLM is built on a diffusion model that creates output tags in parallel. According to Dynex, this approach is more computationally efficient and produces better contextual consistency.
“Traditional models like GPT-4 or DeepSeek work sequentially, word after word,” said Daniela Herrmann, Dynex co-founder and task leader at Dynex Moonshots. "qdLLM works in parallel. It thinks more like the human brain, processing all patterns at once. That's the power of quantum."
Several academic projects including Stanford University and Google DeepMind, as well as initiatives from major AI technology providers, have recently begun exploring the diffusion-based Transformer.
Dynex further differentiates itself by integrating quantum annealing, a quantum optimization form, to improve mark selection during text generation. This increases consistency and reduces computational overhead compared to traditional LLMs, the company claims.
Decentralized and analog quantum hardware
One unique feature of the Dynex model is that it relies on a decentralized GPU network that simulates quantum behavior rather than requiring access to actual quantum hardware. This design allows the system to scale to up to one million algorithmic qubits described by Dynex.
"Any quantum algorithm, such as qdLLM, is being computed on the decentralized network of the GPU, which effectively simulate quantum computing," Herrmann explained.
This type of simulation has some similarities with the work of TensorFlow Quantum (Google and X) which also simulates quantum circuits on classic hardware to create algorithm prototypes. Similarly, many tech startups and vendors are developing platforms to simulate quantum logic at scale before physical hardware is ready.
In addition to software, Dynex plans to launch its own neuromorphic quantum chip Apollo in 2025. Unlike superconducting quantum chips that require low temperature cooling, Apollo is designed to operate at room temperature and supports integration into edge devices.
"Using neuromorphic circuits allows Dynex to simulate quantum computing at scale, up to 1 million algorithmic qubits," Herrmann explained. “Dynex will start producing actual quantum chips that are also based on neuromorphic paradigms.”
Quantum impact on AI efficiency and environmental impact
Dynex says qdLLM achieves 90% smaller model sizes, 10 times faster, and uses only 10% of the GPU resources typically used for equivalent tasks. These are important statements, especially given the increasing concern about AI energy consumption.
"The efficiency and parallelism of quantum algorithms reduce energy consumption because it is 10 times faster and requires only 10% of the number of GPUs," Herrmann said.
While independent verification is still required, Dynex's approach echoes the efforts of Cerebras Systems, which has created wafer-level chips that use less energy for training tasks. Another example is Graphcore, whose Intelligent Processing Unit (IPU) is designed to reduce the energy footprint of AI workloads through a dedicated parallel architecture.
Dynex reports that qdLLM performs strongly in benchmarks requiring strong inference, outperforming leading models, including ChatGPT and Grok. While public benchmark data has not been released yet, the company said it will release a comparative study as it is closer to the 2025 market launch. Dynex's performance assertions remain anecdotal, but interesting until it is provided with peer-reviewed benchmarks.
“We publish qdLLM benchmarks regularly and have proven that certain questions that require strong reasoning cannot be answered correctly by ChatGPT, Grok or DeepSeek,” Herrmann noted.
A bigger picture: How will quantum affect AI?
In the long run, Dynex believes that quantum computing will become the core of the AI field.
"We think quantum will dominate AI for the next five years," Herrmann said.
This prediction remains speculative, although not without precedent. Analysts at McKinsey, Boston Consulting Group and Gartner all point out that quantum computing can greatly improve optimization and simulation tasks, but for most use cases, it may not be possible until after 2030. A more cautious view suggests that quantum-AI hybrids will first appear in niche applications such as drug discovery, financial risk modeling, or cybersecurity.
Currently, Dynex is in a growing field that is experimenting with quantum augmentation or quantum heuristic AI methods. Whether their decentralized, diffusion-based qdLLM can surpass benchmarks remains to be seen, but its emergence suggests that searching for new foundations of AI is far from over.
The above is the detailed content of Can Quantum-Inspired AI Compete With Today's Large Language Models?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Tesla's Robovan Was The Hidden Gem In 2024's Robotaxi TeaserApr 22, 2025 am 11:48 AM
Tesla's Robovan Was The Hidden Gem In 2024's Robotaxi TeaserApr 22, 2025 am 11:48 AMSince 2008, I've championed the shared-ride van—initially dubbed the "robotjitney," later the "vansit"—as the future of urban transportation. I foresee these vehicles as the 21st century's next-generation transit solution, surpas
 Sam's Club Bets On AI To Eliminate Receipt Checks And Enhance RetailApr 22, 2025 am 11:29 AM
Sam's Club Bets On AI To Eliminate Receipt Checks And Enhance RetailApr 22, 2025 am 11:29 AMRevolutionizing the Checkout Experience Sam's Club's innovative "Just Go" system builds on its existing AI-powered "Scan & Go" technology, allowing members to scan purchases via the Sam's Club app during their shopping trip.
 Nvidia's AI Omniverse Expands At GTC 2025Apr 22, 2025 am 11:28 AM
Nvidia's AI Omniverse Expands At GTC 2025Apr 22, 2025 am 11:28 AMNvidia's Enhanced Predictability and New Product Lineup at GTC 2025 Nvidia, a key player in AI infrastructure, is focusing on increased predictability for its clients. This involves consistent product delivery, meeting performance expectations, and
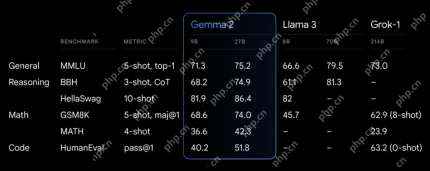 Exploring the Capabilities of Google's Gemma 2 ModelsApr 22, 2025 am 11:26 AM
Exploring the Capabilities of Google's Gemma 2 ModelsApr 22, 2025 am 11:26 AMGoogle's Gemma 2: A Powerful, Efficient Language Model Google's Gemma family of language models, celebrated for efficiency and performance, has expanded with the arrival of Gemma 2. This latest release comprises two models: a 27-billion parameter ver
 The Next Wave of GenAI: Perspectives with Dr. Kirk Borne - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:21 AM
The Next Wave of GenAI: Perspectives with Dr. Kirk Borne - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:21 AMThis Leading with Data episode features Dr. Kirk Borne, a leading data scientist, astrophysicist, and TEDx speaker. A renowned expert in big data, AI, and machine learning, Dr. Borne offers invaluable insights into the current state and future traje
 AI For Runners And Athletes: We're Making Excellent ProgressApr 22, 2025 am 11:12 AM
AI For Runners And Athletes: We're Making Excellent ProgressApr 22, 2025 am 11:12 AMThere were some very insightful perspectives in this speech—background information about engineering that showed us why artificial intelligence is so good at supporting people’s physical exercise. I will outline a core idea from each contributor’s perspective to demonstrate three design aspects that are an important part of our exploration of the application of artificial intelligence in sports. Edge devices and raw personal data This idea about artificial intelligence actually contains two components—one related to where we place large language models and the other is related to the differences between our human language and the language that our vital signs “express” when measured in real time. Alexander Amini knows a lot about running and tennis, but he still
 Jamie Engstrom On Technology, Talent And Transformation At CaterpillarApr 22, 2025 am 11:10 AM
Jamie Engstrom On Technology, Talent And Transformation At CaterpillarApr 22, 2025 am 11:10 AMCaterpillar's Chief Information Officer and Senior Vice President of IT, Jamie Engstrom, leads a global team of over 2,200 IT professionals across 28 countries. With 26 years at Caterpillar, including four and a half years in her current role, Engst
 New Google Photos Update Makes Any Photo Pop With Ultra HDR QualityApr 22, 2025 am 11:09 AM
New Google Photos Update Makes Any Photo Pop With Ultra HDR QualityApr 22, 2025 am 11:09 AMGoogle Photos' New Ultra HDR Tool: A Quick Guide Enhance your photos with Google Photos' new Ultra HDR tool, transforming standard images into vibrant, high-dynamic-range masterpieces. Ideal for social media, this tool boosts the impact of any photo,


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor





