Introduction
Imagine preparing a dish with a specific desired flavor profile; the correct sequence of steps is crucial. Similarly, in mathematics and programming, calculating the factorial of a number necessitates a precise sequence of multiplications involving a series of descending positive integers. Factorials are fundamental in various fields, including combinatorics, algebra, and computer science.
This article guides you through calculating factorials in Python, explaining the underlying logic and exploring different approaches.

Key Learning Objectives
- Understand the concept of a factorial and its mathematical significance.
- Implement factorial calculations in Python using iterative and recursive methods.
- Effectively address factorial computations in Python.
Table of contents
- Defining Factorials
- Practical Applications of Factorials
- Python Factorial Implementations
- Iterative Approach
- Recursive Approach
- Utilizing Python's Built-in Function
- Performance Analysis: Efficiency and Complexity
- Frequently Asked Questions
Defining Factorials
The factorial of a non-negative integer n, denoted as n!, is the product of all positive integers less than or equal to n.
Example:
- 5! = 5 × 4 × 3 × 2 × 1 = 120
Special Case:
- 0! = 1 (by definition)
Practical Applications of Factorials
Factorials find extensive use in:
- Permutations and Combinations: Determining the number of ways to arrange or select items.
- Probability Calculations: Modeling probabilistic events.
- Algebra and Calculus: Solving equations and series expansions.
- Computer Algorithms: Implementing various mathematical algorithms.
Python Factorial Implementations
Several methods exist for computing factorials in Python. We'll examine the most prevalent: iterative and recursive approaches.
Iterative Approach
This method employs a loop to perform the multiplications in descending order.
def factorial_iterative(n):
result = 1
for i in range(1, n 1):
result *= i
return result
# Example
number = 5
print(f"The factorial of {number} is {factorial_iterative(number)}")
Output:
<code>The factorial of 5 is 120</code>
Recursive Approach
Recursion involves a function calling itself to solve smaller instances of the same problem until a base case is reached.
def factorial_recursive(n):
if n == 0 or n == 1:
return 1
else:
return n * factorial_recursive(n - 1)
# Example
number = 5
print(f"The factorial of {number} is {factorial_recursive(number)}")
Output:
<code>The factorial of 5 is 120</code>
Utilizing Python's Built-in Function
Python's math module offers a built-in factorial function.
import math
number = 5
print(f"The factorial of {number} is {math.factorial(number)}")
Output:
<code>The factorial of 5 is 120</code>
Performance Analysis: Efficiency and Complexity
- Iterative Method: Time complexity O(n), space complexity O(1). Efficient for large inputs.
- Recursive Method: Time complexity O(n), space complexity O(n) due to the call stack. Less efficient for very large inputs due to potential stack overflow.
- Built-in Method: Generally the most efficient and optimized solution.
Conclusion
Calculating factorials is a fundamental task in mathematics and programming. Python provides multiple approaches, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these methods allows you to choose the most appropriate technique based on the specific context and input size. Whether tackling combinatorial problems or implementing algorithms, mastering factorial computation is a valuable skill.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is a factorial?
A: The factorial of a non-negative integer n is the product of all positive integers less than or equal to n, denoted as n!.
Q2: How can I calculate factorials in Python?
A: Use iterative loops, recursion, or Python's built-in math.factorial function.
Q3: Which method is most efficient for calculating factorials in Python?
A: Python's built-in math.factorial function is generally the most efficient.
Q4: Are there limitations to the recursive method?
A: Recursion can be limited by Python's recursion depth and stack size, making it less suitable for extremely large inputs.
Q5: What are some real-world applications of factorials?
A: Factorials are used in permutations, combinations, probability, algebra, calculus, and various computer algorithms.
The above is the detailed content of Factorial Program in Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Sam's Club Bets On AI To Eliminate Receipt Checks And Enhance RetailApr 22, 2025 am 11:29 AM
Sam's Club Bets On AI To Eliminate Receipt Checks And Enhance RetailApr 22, 2025 am 11:29 AMRevolutionizing the Checkout Experience Sam's Club's innovative "Just Go" system builds on its existing AI-powered "Scan & Go" technology, allowing members to scan purchases via the Sam's Club app during their shopping trip.
 Nvidia's AI Omniverse Expands At GTC 2025Apr 22, 2025 am 11:28 AM
Nvidia's AI Omniverse Expands At GTC 2025Apr 22, 2025 am 11:28 AMNvidia's Enhanced Predictability and New Product Lineup at GTC 2025 Nvidia, a key player in AI infrastructure, is focusing on increased predictability for its clients. This involves consistent product delivery, meeting performance expectations, and
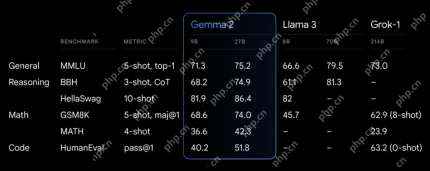 Exploring the Capabilities of Google's Gemma 2 ModelsApr 22, 2025 am 11:26 AM
Exploring the Capabilities of Google's Gemma 2 ModelsApr 22, 2025 am 11:26 AMGoogle's Gemma 2: A Powerful, Efficient Language Model Google's Gemma family of language models, celebrated for efficiency and performance, has expanded with the arrival of Gemma 2. This latest release comprises two models: a 27-billion parameter ver
 The Next Wave of GenAI: Perspectives with Dr. Kirk Borne - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:21 AM
The Next Wave of GenAI: Perspectives with Dr. Kirk Borne - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:21 AMThis Leading with Data episode features Dr. Kirk Borne, a leading data scientist, astrophysicist, and TEDx speaker. A renowned expert in big data, AI, and machine learning, Dr. Borne offers invaluable insights into the current state and future traje
 AI For Runners And Athletes: We're Making Excellent ProgressApr 22, 2025 am 11:12 AM
AI For Runners And Athletes: We're Making Excellent ProgressApr 22, 2025 am 11:12 AMThere were some very insightful perspectives in this speech—background information about engineering that showed us why artificial intelligence is so good at supporting people’s physical exercise. I will outline a core idea from each contributor’s perspective to demonstrate three design aspects that are an important part of our exploration of the application of artificial intelligence in sports. Edge devices and raw personal data This idea about artificial intelligence actually contains two components—one related to where we place large language models and the other is related to the differences between our human language and the language that our vital signs “express” when measured in real time. Alexander Amini knows a lot about running and tennis, but he still
 Jamie Engstrom On Technology, Talent And Transformation At CaterpillarApr 22, 2025 am 11:10 AM
Jamie Engstrom On Technology, Talent And Transformation At CaterpillarApr 22, 2025 am 11:10 AMCaterpillar's Chief Information Officer and Senior Vice President of IT, Jamie Engstrom, leads a global team of over 2,200 IT professionals across 28 countries. With 26 years at Caterpillar, including four and a half years in her current role, Engst
 New Google Photos Update Makes Any Photo Pop With Ultra HDR QualityApr 22, 2025 am 11:09 AM
New Google Photos Update Makes Any Photo Pop With Ultra HDR QualityApr 22, 2025 am 11:09 AMGoogle Photos' New Ultra HDR Tool: A Quick Guide Enhance your photos with Google Photos' new Ultra HDR tool, transforming standard images into vibrant, high-dynamic-range masterpieces. Ideal for social media, this tool boosts the impact of any photo,
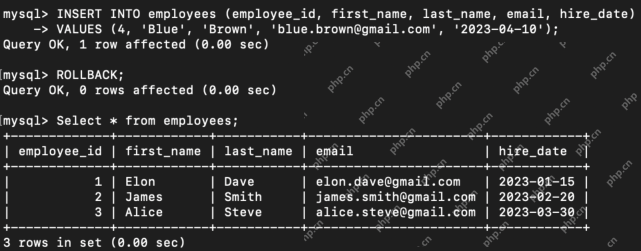 What are the TCL Commands in SQL? - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:07 AM
What are the TCL Commands in SQL? - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:07 AMIntroduction Transaction Control Language (TCL) commands are essential in SQL for managing changes made by Data Manipulation Language (DML) statements. These commands allow database administrators and users to control transaction processes, thereby


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor






