Unlock the Power of Excel's GROUPBY Function for Enhanced Data Analysis! This function simplifies data grouping, summarization, sorting, and filtering, all within a single formula. Say goodbye to complex outlines, subtotals, and pivot tables – GROUPBY streamlines your workflow.
Excel's data analysis capabilities just got a significant boost. While features like outlines and pivot tables have long been staples for organizing and interpreting data, the new GROUPBY function offers a more streamlined approach, all within the convenience of your formula bar.
- Understanding the Excel GROUPBY Function: Syntax and Basic Applications
- GROUPBY Function Availability and Compatibility
- Constructing a Basic GROUPBY Formula
- Mastering GROUPBY: Advanced Formula Examples
- Selecting the Right Aggregation Function
- Displaying Headers Effectively
- Grouping Rows Using Multiple Columns
- Grouping with Non-Adjacent Columns
- Controlling the Display of Totals and Subtotals
- Sorting Grouped Data
- Filtering Results
- Aggregating Multiple Columns (Adjacent and Non-Adjacent)
- Multiple Aggregations on a Single Dataset
- Handling Comma-Separated Text Strings
- Auto-Formatting GROUPBY Results with Conditional Formatting
- Troubleshooting GROUPBY Function Issues
The Excel GROUPBY Function
The GROUPBY function efficiently groups and aggregates data rows based on values in one or more columns. It also supports sorting and filtering of grouped data. As a dynamic array function, it returns multiple results, spilling into adjacent cells. The output resembles a pivot table without the formatting; the spill range dynamically recalculates with data changes. This is particularly beneficial for large datasets requiring summarized data through functions like SUM, AVERAGE, or COUNT.

Note: GROUPBY is similar to PIVOTBY, but GROUPBY exclusively groups data in rows.
Function Syntax
GROUPBY(row_fields, values, function, [field_headers], [total_depth], [sort_order], [filter_array])
Seven arguments are available, but only the first three are mandatory:
-
row_fields(required): The range of values to group by. -
values(required): The values to aggregate. -
function(required): The aggregation function (e.g.,SUM,AVERAGE,COUNT,MIN,MAX). -
field_headers(optional): Controls header display (0: No headers, 1: Yes, but don't show, 2: No headers, but generate, 3: Yes, and show). -
total_depth(optional): Controls total/subtotal display (0: No totals, 1: Grand total at bottom, 2: Grand and subtotals at bottom, -1: Grand total at top, -2: Grand and subtotals at top). -
sort_order(optional): Sorts by column index (positive for ascending, negative for descending). Arrays allow multi-column sorting. -
filter_array(optional): Filters rows using a Boolean array.
Usage Tips
- Dynamic Updates: The formula dynamically adjusts to dataset changes within its range. Adding new rows requires including them in the argument ranges or using an Excel table for automatic expansion.
-
Header Detection: If
field_headersis omitted, Excel infers headers based on thevaluesargument (text followed by a number suggests headers). -
Range Consistency:
row_fieldsandvaluesmust have equal lengths to avoid#VALUE!errors. - Conditional Formatting: Enhance readability by using conditional formatting to highlight totals and subtotals.
Note: GROUPBY is under development; thorough testing is recommended.
GROUPBY Function Availability
Currently available in Excel for Microsoft 365 (Insider Beta Channel).
Basic GROUPBY Formula
Let's assume a dataset with project names (Column A), types (Column B), and revenues (Column C). To summarize revenues by project type:
=GROUPBY(B2:B32, C2:C32, SUM)
This yields a list of unique project types with their revenue sums. Defaults are used for optional arguments (no headers, ascending sort, grand total at bottom).

Advanced GROUPBY Formula Examples
This section expands on the basic example, demonstrating the function's versatility.
Choosing the Aggregation Function
GROUPBY supports 16 aggregation functions, including standard functions (SUM, AVERAGE, COUNT, etc.) and specialized ones (PERCENTOF, ARRAYTOTEXT). These are eta-reduced lambdas, simplifying usage. Custom lambda functions are also supported. Multiple aggregations are possible using vectors (vertical for column stacking, horizontal for row stacking).
Displaying Headers
Use the field_headers argument (set to 3) to include headers in the output.
=GROUPBY(B2:B32, C2:C32, SUM, 3)

Grouping by Multiple Columns
Include a multi-column range in row_fields to group by multiple columns. For example, grouping by project type and status:
=GROUPBY(B2:C32, D2:D32, COUNT)

Grouping by Non-Adjacent Columns
Use CHOOSECOLS to select non-adjacent columns for grouping:
=GROUPBY(CHOOSECOLS(A2:D32, 2, 4), C2:C32, COUNT)

Controlling Totals and Subtotals
Use total_depth to control total/subtotal display. Setting it to 2 shows both grand and subtotals.
=GROUPBY(B2:C32, D2:D32, SUM, 3, 2)

Sorting Grouped Rows
Use sort_order for custom sorting (positive for ascending, negative for descending). Arrays enable multi-column sorting.
=GROUPBY(B2:B32, C2:C32, SUM, , , 2) (Sorts by values)

=GROUPBY(B2:C32, D2:D32, SUM, , , {-1,2}) (Multi-column sort)

Filtering Results
Use filter_array (Boolean array) to filter rows.
=GROUPBY(B2:B32, C2:C32, SUM, , , , B2:B32"Design")

Aggregating Multiple Columns
Aggregate adjacent columns directly:
=GROUPBY(B2:B32, D2:E32, AVERAGE, 3)

For non-adjacent columns, use CHOOSECOLS:
=GROUPBY(B2:B32, CHOOSECOLS(C2:E32, 1, 3), AVERAGE, 3)

Multiple Aggregations on the Same Data
Use HSTACK or VSTACK for multiple aggregations:
=GROUPBY(B3:B32, C3:C32, HSTACK(SUM, AVERAGE, PERCENTOF))

=GROUPBY(B3:B32, C3:C32, VSTACK(SUM, AVERAGE, MIN, MAX),, 0)

Grouping Comma-Separated Text Values
Use ARRAYTOTEXT to group comma-separated text:
=GROUPBY(B3:B23, A3:A23, ARRAYTOTEXT, 0, 0)

Conditional Formatting of GROUPBY Results
Enhance visual clarity using conditional formatting to highlight headers, totals, and subtotals.
Troubleshooting GROUPBY Function Issues
- Function Unavailability: Ensure you have a Microsoft 365 subscription and the latest updates.
-
#VALUE!Error: Check for equal lengths inrow_fieldsandvaluesarguments, and ensure correctfilter_arraylength. Also, verify thattotal_depthis appropriate for the number of columns inrow_fields. -
#SPILL!Error: Clear adjacent cells to allow spill range.
In conclusion, the GROUPBY function significantly enhances Excel's data analysis capabilities, providing a powerful and efficient tool for various data manipulation tasks. With practice, you'll unlock its full potential for insightful data analysis.
The above is the detailed content of Excel GROUPBY function to group rows and aggregate values. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examplesApr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examplesApr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PMThis tutorial explains how to calculate the median of numerical data in Excel using the MEDIAN function. The median, a key measure of central tendency, identifies the middle value in a dataset, offering a more robust representation of central tenden
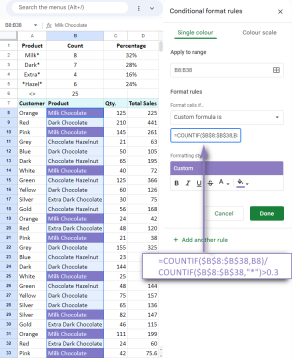 Google Spreadsheet COUNTIF function with formula examplesApr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
Google Spreadsheet COUNTIF function with formula examplesApr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PMMaster Google Sheets COUNTIF: A Comprehensive Guide This guide explores the versatile COUNTIF function in Google Sheets, demonstrating its applications beyond simple cell counting. We'll cover various scenarios, from exact and partial matches to han
 Excel shared workbook: How to share Excel file for multiple usersApr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AM
Excel shared workbook: How to share Excel file for multiple usersApr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AMThis tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to sharing Excel workbooks, covering various methods, access control, and conflict resolution. Modern Excel versions (2010, 2013, 2016, and later) simplify collaborative editing, eliminating the need to m
 How to convert Excel to JPG - save .xls or .xlsx as image fileApr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AM
How to convert Excel to JPG - save .xls or .xlsx as image fileApr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AMThis tutorial explores various methods for converting .xls files to .jpg images, encompassing both built-in Windows tools and free online converters. Need to create a presentation, share spreadsheet data securely, or design a document? Converting yo
 Excel names and named ranges: how to define and use in formulasApr 11, 2025 am 11:13 AM
Excel names and named ranges: how to define and use in formulasApr 11, 2025 am 11:13 AMThis tutorial clarifies the function of Excel names and demonstrates how to define names for cells, ranges, constants, or formulas. It also covers editing, filtering, and deleting defined names. Excel names, while incredibly useful, are often overlo
 Standard deviation Excel: functions and formula examplesApr 11, 2025 am 11:01 AM
Standard deviation Excel: functions and formula examplesApr 11, 2025 am 11:01 AMThis tutorial clarifies the distinction between standard deviation and standard error of the mean, guiding you on the optimal Excel functions for standard deviation calculations. In descriptive statistics, the mean and standard deviation are intrinsi
 Square root in Excel: SQRT function and other waysApr 11, 2025 am 10:34 AM
Square root in Excel: SQRT function and other waysApr 11, 2025 am 10:34 AMThis Excel tutorial demonstrates how to calculate square roots and nth roots. Finding the square root is a common mathematical operation, and Excel offers several methods. Methods for Calculating Square Roots in Excel: Using the SQRT Function: The
 Google Sheets basics: Learn how to work with Google SpreadsheetsApr 11, 2025 am 10:23 AM
Google Sheets basics: Learn how to work with Google SpreadsheetsApr 11, 2025 am 10:23 AMUnlock the Power of Google Sheets: A Beginner's Guide This tutorial introduces the fundamentals of Google Sheets, a powerful and versatile alternative to MS Excel. Learn how to effortlessly manage spreadsheets, leverage key features, and collaborate


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.






