How to highlight duplicates in Excel
To highlight duplicates in Excel, you can use the Conditional Formatting feature. This tool allows you to visually distinguish between duplicate and unique entries in your data set. Here’s how you can do it:
- Select the range of cells where you want to highlight duplicates. This could be a single column, multiple columns, or an entire sheet.
- Go to the Home tab on the Excel ribbon and click on “Conditional Formatting” in the Styles group.
- Choose “Highlight Cells Rules” from the dropdown menu, then select “Duplicate Values...”.
- In the Duplicate Values dialog box, you will see two dropdown menus. The first one is set to “Duplicate” by default. The second one allows you to choose the format for highlighting the duplicates. You can choose from preset options like “Light Red Fill with Dark Red Text” or customize it by selecting “Custom Format...”.
- Click OK to apply the formatting. Now, any duplicates within the selected range will be highlighted according to the format you chose.
What are the steps to use conditional formatting for highlighting duplicates in Excel?
The steps to use conditional formatting for highlighting duplicates in Excel are as follows:
- Select the cells you want to analyze for duplicates. This can be a single column, multiple columns, or a range of cells.
- Navigate to the Home tab on the Excel ribbon and find the “Conditional Formatting” button in the Styles group.
- Click on “Conditional Formatting” and from the dropdown, select “Highlight Cells Rules”, then choose “Duplicate Values...”.
- In the “Duplicate Values” dialog box, the first dropdown is set to “Duplicate” by default. Use the second dropdown to choose a formatting style or click “Custom Format...” to create your own.
- After selecting your desired format, click “OK”. The selected cells will now be formatted to highlight any duplicates based on your chosen style.
Can you highlight duplicates across multiple columns in Excel, and if so, how?
Yes, you can highlight duplicates across multiple columns in Excel using conditional formatting. Here’s how to do it:
- Select the columns you want to check for duplicates. For example, if you want to highlight duplicates in columns A, B, and C, click on the header of column A, hold down the Shift key, and click on the headers of columns B and C to select all three.
- Go to the Home tab, click on “Conditional Formatting” in the Styles group, and then select “Highlight Cells Rules” followed by “Duplicate Values...”.
- In the “Duplicate Values” dialog box, choose your preferred format for highlighting the duplicates from the second dropdown menu, or select “Custom Format...” to specify your own.
- Click OK. Excel will now highlight any duplicates that appear in the selected columns, no matter which column they are in.
Is there a way to automatically highlight new duplicates as they are entered in an Excel spreadsheet?
While Excel's built-in Conditional Formatting does not automatically update to highlight new duplicates as they are entered, you can use a combination of Conditional Formatting and Excel's VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) to achieve this. Here’s how you can set it up:
- First, set up your Conditional Formatting to highlight existing duplicates as previously described.
- Press Alt F11 to open the VBA Editor.
- Insert a new module by right-clicking on any of the objects in the Project Explorer, selecting “Insert”, and then “Module”.
- Copy and paste the following VBA code into the module:
Private Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range)
Dim KeyCells As Range
Set KeyCells = Range("YourRangeHere") ' Replace "YourRangeHere" with the actual range, e.g., "A1:C100"
If Not Intersect(Target, KeyCells) Is Nothing Then
KeyCells.FormatConditions.Delete
KeyCells.FormatConditions.AddUniqueValues
KeyCells.FormatConditions(1).DupeUnique = xlDuplicate
KeyCells.FormatConditions(1).Interior.Color = RGB(255, 0, 0) ' Red color, adjust as needed
End If
End Sub- Close the VBA Editor and return to Excel.
- Right-click on the sheet tab where you want this to work and select “View Code”. In the VBA window that appears, paste the following code to connect the Worksheet_Change event to your sheet:
Private Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range)
Call YourModuleName.Worksheet_Change(Target) ' Replace "YourModuleName" with the actual name of your module
End Sub- Close the VBA window and save your workbook as a macro-enabled file (.xlsm).
Now, every time you enter new data into the specified range, Excel will automatically check for and highlight any new duplicates in real-time.
The above is the detailed content of how to highlight duplicates in excel. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examplesApr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examplesApr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PMThis tutorial explains how to calculate the median of numerical data in Excel using the MEDIAN function. The median, a key measure of central tendency, identifies the middle value in a dataset, offering a more robust representation of central tenden
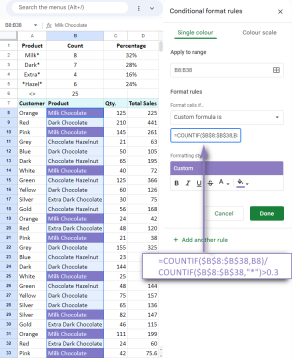 Google Spreadsheet COUNTIF function with formula examplesApr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
Google Spreadsheet COUNTIF function with formula examplesApr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PMMaster Google Sheets COUNTIF: A Comprehensive Guide This guide explores the versatile COUNTIF function in Google Sheets, demonstrating its applications beyond simple cell counting. We'll cover various scenarios, from exact and partial matches to han
 Excel shared workbook: How to share Excel file for multiple usersApr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AM
Excel shared workbook: How to share Excel file for multiple usersApr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AMThis tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to sharing Excel workbooks, covering various methods, access control, and conflict resolution. Modern Excel versions (2010, 2013, 2016, and later) simplify collaborative editing, eliminating the need to m
 How to convert Excel to JPG - save .xls or .xlsx as image fileApr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AM
How to convert Excel to JPG - save .xls or .xlsx as image fileApr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AMThis tutorial explores various methods for converting .xls files to .jpg images, encompassing both built-in Windows tools and free online converters. Need to create a presentation, share spreadsheet data securely, or design a document? Converting yo
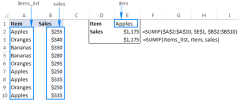 Excel names and named ranges: how to define and use in formulasApr 11, 2025 am 11:13 AM
Excel names and named ranges: how to define and use in formulasApr 11, 2025 am 11:13 AMThis tutorial clarifies the function of Excel names and demonstrates how to define names for cells, ranges, constants, or formulas. It also covers editing, filtering, and deleting defined names. Excel names, while incredibly useful, are often overlo
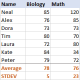 Standard deviation Excel: functions and formula examplesApr 11, 2025 am 11:01 AM
Standard deviation Excel: functions and formula examplesApr 11, 2025 am 11:01 AMThis tutorial clarifies the distinction between standard deviation and standard error of the mean, guiding you on the optimal Excel functions for standard deviation calculations. In descriptive statistics, the mean and standard deviation are intrinsi
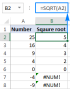 Square root in Excel: SQRT function and other waysApr 11, 2025 am 10:34 AM
Square root in Excel: SQRT function and other waysApr 11, 2025 am 10:34 AMThis Excel tutorial demonstrates how to calculate square roots and nth roots. Finding the square root is a common mathematical operation, and Excel offers several methods. Methods for Calculating Square Roots in Excel: Using the SQRT Function: The
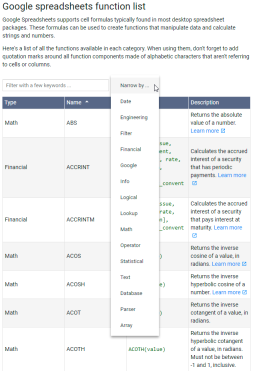 Google Sheets basics: Learn how to work with Google SpreadsheetsApr 11, 2025 am 10:23 AM
Google Sheets basics: Learn how to work with Google SpreadsheetsApr 11, 2025 am 10:23 AMUnlock the Power of Google Sheets: A Beginner's Guide This tutorial introduces the fundamentals of Google Sheets, a powerful and versatile alternative to MS Excel. Learn how to effortlessly manage spreadsheets, leverage key features, and collaborate


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.







