OpenAI releases a new function call guide to help developers expand their model capabilities! This guide integrates user feedback, reduces 50% shorter, has clearer content, and contains complete examples of best practices, in-document function generation, and use of the weather API. OpenAI is committed to simplifying AI tools to make them easier for developers to use, thereby making it more efficient to utilize function calling capabilities.
OpenAI releases a brand new guide to function calling!
We have made important improvements based on your feedback:
-- 50% shorter, making it clearer and easier to understand – New best practices (see below for details?) – Supports in-document function generation! – Provides a complete feature example of using the weather API
View the guide and share your thoughts... pic.twitter.com/Id89E9PEff
— ilan bigio (@ilanbigio) January 13, 2025
Catalog
- How does OpenAI function call work?
- Quick Example: Weather API
- Step 1: Define the function
- Step 2: Call the model using the defined function
- Step 3: Execute the function
- Step 4: Provide results to the model
- Step 5: Get the final response
- Best Practice for Function Calls
- Summary
How does OpenAI function call work?
Function calls allow the OpenAI model to interact with developer-defined tools, enabling it to perform more tasks beyond text or audio generation. The following is a simplified process:
- Define function: Create a function that the model can call (for example, get_weather).
- Model determines calling functions: Based on system prompts and user input, the model determines when to call functions.
- Execute function: Run the function code and return the result.
- Integration Results: The model uses the output of the function to generate the final response.
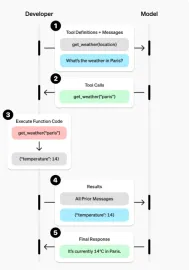
This image shows the process of function calls between the developer and the AI model. Here are the step-by-step instructions:
- Tool Definition Message: The developer defines the tool (function) and sends a message. In this example, the get_weather(location) function is defined, and the user asks: "What is the weather in Paris?"
- Tool call: Model recognition requires the use of the parameter "paris" to call the get_weather function.
- Execute function code: The developer (or system) executes the actual get_weather("paris") function. The function returns the response, for example: {"temperature": 14}.
- Result: The result of the function ({"temperature": 14}) is returned to the model with all previous messages.
- Final response: The model uses the function results to generate a natural language response, for example: "The current temperature in Paris is 14°C."
Please read also: 6 top LLMs that support function calls
Quick Example: Weather API
Let's look at a practical example using the get_weather function. This function retrieves the current temperature of the given coordinates.
Step 1: Define the function
<code>import requests
def get_weather(latitude, longitude):
response = requests.get(f"https://api.open-meteo.com/v1/forecast?latitude={latitude}&longitude={longitude}¤t=temperature_2m,wind_speed_10m&hourly=temperature_2m,relative_humidity_2m,wind_speed_10m")
data = response.json()
return data['current']['temperature_2m']</code>
Step 2: Call the model using the defined function
<code>from openai import OpenAI
import json
client = OpenAI(api_key="sk-api_key”)
tools = [{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "获取提供的坐标(摄氏度)的当前温度。",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"latitude": {"type": "number"},
"longitude": {"type": "number"}
},
"required": ["latitude", "longitude"],
"additionalProperties": False
},
"strict": True
}
}]
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": "今天巴黎的天气怎么样?"}]
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=messages,
tools=tools,
)</code>
Step 3: Execute the function
<code>tool_call = completion.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0] args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments) result = get_weather(args["latitude"], args["longitude"])</code>
Step 4: Provide results to the model
<code># 附加模型的工具调用消息
messages.append(completion.choices[0].message)
# 将结果消息作为字符串附加
messages.append({
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
"content": json.dumps({"temperature": result}) # 将结果转换为JSON字符串
})
# 创建第二个聊天完成
completion_2 = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=messages,
tools=tools,
)</code>
Step 5: Get the final response
<code>print(completion_2.choices[0].message.content)</code>
Output:
<code>巴黎目前的温度是-2.8°C。</code>
Best Practice for Function Calls
To help you make the most of your function calls, here are some professional tips:
-
Writing a clear and detailed description
- Clearly describe the purpose, parameters and output of the function.
- Use the system prompts to guide the model when (and when not) to use functions.
-
Best Practice of Application Software Engineering
- Make the function intuitive and easy to understand.
- Use enumerations and object structures to prevent invalid states.
-
Reduce the burden on the model
- Do not let the model fill in parameters you know.
- Merge functions that are always called sequentially.
-
The number of functions is small
- To improve accuracy, use up to less than 20 functions at a time.
-
Utilize OpenAI resources
- Use Playground to generate and iterate function patterns.
- Consider fine-tuning for complex tasks or large numbers of functions.
For more information, please visit OpenAI.
Summary
OpenAI's improved function call guide enables developers to seamlessly integrate custom tools to make AI easier to access and use. By simplifying processes, providing clear examples, and prioritizing user feedback, OpenAI enables developers to innovate and build solutions that leverage the full potential of AI, thereby driving real-world applications and creativity.
The above is the detailed content of Checkout the OpenAI Function Calling Guide. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Meta's New AI Assistant: Productivity Booster Or Time Sink?May 01, 2025 am 11:18 AM
Meta's New AI Assistant: Productivity Booster Or Time Sink?May 01, 2025 am 11:18 AMMeta has joined hands with partners such as Nvidia, IBM and Dell to expand the enterprise-level deployment integration of Llama Stack. In terms of security, Meta has launched new tools such as Llama Guard 4, LlamaFirewall and CyberSecEval 4, and launched the Llama Defenders program to enhance AI security. In addition, Meta has distributed $1.5 million in Llama Impact Grants to 10 global institutions, including startups working to improve public services, health care and education. The new Meta AI application powered by Llama 4, conceived as Meta AI
 80% Of Gen Zers Would Marry An AI: StudyMay 01, 2025 am 11:17 AM
80% Of Gen Zers Would Marry An AI: StudyMay 01, 2025 am 11:17 AMJoi AI, a company pioneering human-AI interaction, has introduced the term "AI-lationships" to describe these evolving relationships. Jaime Bronstein, a relationship therapist at Joi AI, clarifies that these aren't meant to replace human c
 AI Is Making The Internet's Bot Problem Worse. This $2 Billion Startup Is On The Front LinesMay 01, 2025 am 11:16 AM
AI Is Making The Internet's Bot Problem Worse. This $2 Billion Startup Is On The Front LinesMay 01, 2025 am 11:16 AMOnline fraud and bot attacks pose a significant challenge for businesses. Retailers fight bots hoarding products, banks battle account takeovers, and social media platforms struggle with impersonators. The rise of AI exacerbates this problem, rende
 Selling To Robots: The Marketing Revolution That Will Make Or Break Your BusinessMay 01, 2025 am 11:15 AM
Selling To Robots: The Marketing Revolution That Will Make Or Break Your BusinessMay 01, 2025 am 11:15 AMAI agents are poised to revolutionize marketing, potentially surpassing the impact of previous technological shifts. These agents, representing a significant advancement in generative AI, not only process information like ChatGPT but also take actio
 How Computer Vision Technology Is Transforming NBA Playoff OfficiatingMay 01, 2025 am 11:14 AM
How Computer Vision Technology Is Transforming NBA Playoff OfficiatingMay 01, 2025 am 11:14 AMAI's Impact on Crucial NBA Game 4 Decisions Two pivotal Game 4 NBA matchups showcased the game-changing role of AI in officiating. In the first, Denver's Nikola Jokic's missed three-pointer led to a last-second alley-oop by Aaron Gordon. Sony's Haw
 How AI Is Accelerating The Future Of Regenerative MedicineMay 01, 2025 am 11:13 AM
How AI Is Accelerating The Future Of Regenerative MedicineMay 01, 2025 am 11:13 AMTraditionally, expanding regenerative medicine expertise globally demanded extensive travel, hands-on training, and years of mentorship. Now, AI is transforming this landscape, overcoming geographical limitations and accelerating progress through en
 Key Takeaways From Intel Foundry Direct Connect 2025May 01, 2025 am 11:12 AM
Key Takeaways From Intel Foundry Direct Connect 2025May 01, 2025 am 11:12 AMIntel is working to return its manufacturing process to the leading position, while trying to attract fab semiconductor customers to make chips at its fabs. To this end, Intel must build more trust in the industry, not only to prove the competitiveness of its processes, but also to demonstrate that partners can manufacture chips in a familiar and mature workflow, consistent and highly reliable manner. Everything I hear today makes me believe Intel is moving towards this goal. The keynote speech of the new CEO Tan Libo kicked off the day. Tan Libai is straightforward and concise. He outlines several challenges in Intel’s foundry services and the measures companies have taken to address these challenges and plan a successful route for Intel’s foundry services in the future. Tan Libai talked about the process of Intel's OEM service being implemented to make customers more
 AI Gone Wrong? Now There's Insurance For ThatMay 01, 2025 am 11:11 AM
AI Gone Wrong? Now There's Insurance For ThatMay 01, 2025 am 11:11 AMAddressing the growing concerns surrounding AI risks, Chaucer Group, a global specialty reinsurance firm, and Armilla AI have joined forces to introduce a novel third-party liability (TPL) insurance product. This policy safeguards businesses against


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.







