
The upward rounding function is a valuable mathematical tool used by professionals in finance, analytics, and programming. This function ensures numbers are rounded up to a specified level, preventing underestimation. Businesses benefit significantly from this in budgeting, pricing, and statistical analysis. This article explores Python's upward rounding capabilities and its real-world applications.
Learning Objectives
- Define the upward rounding function and its purpose.
- Understand the syntax and parameters of upward rounding functions.
- Apply upward rounding in various contexts (spreadsheets, programming).
- Identify practical applications of upward rounding in real-world scenarios.
Table of contents
- What is the Upward Rounding Function?
- Methods for Upward Rounding in Python
- Real-World Applications
- Method Summary
- Practical Use Cases
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Upward Rounding Function?
The upward rounding function rounds numbers to precise decimal places or multiples of specific values. Unlike traditional rounding, it always results in a value equal to or greater than the input, eliminating underestimation.
Key Characteristics
- Guaranteed Upward Rounding: Always rounds up to the next integer or specified decimal place.
- Underestimation Prevention: Crucial for financial applications where underestimation can lead to budget shortfalls.
Syntax and Parameters
The syntax varies depending on the platform (Excel, Python). A general structure is:
-
Excel:
ROUNDUP(number, num_digits)-
number: The value to round up. -
num_digits: The number of decimal places (positive), or the number of places to the left of the decimal point (negative). 0 rounds to the nearest whole number.
-
-
Python:
math.ceil(x)- Rounds the floating-point number
xup to the nearest integer.
- Rounds the floating-point number
Methods to Round Up a Number in Python
Python offers several ways to round up, each with its strengths:
Using the math.ceil() Function
The math.ceil() function (from the math module) is the simplest method for rounding up to the nearest integer.
Example:
import math number = 5.3 rounded_number = math.ceil(number) print(rounded_number) # Output: 6
Custom Upward Rounding Function
For more control, create a custom function:
Example:
import math
def round_up(n, decimals=0):
multiplier = 10 ** decimals
return math.ceil(n * multiplier) / multiplier
# Usage
result = round_up(3.14159, 2)
print(result) # Output: 3.15
This function handles rounding to a specified number of decimal places.
Using NumPy's ceil() Function
NumPy offers efficient upward rounding for arrays:
Example:
import math number = 5.3 rounded_number = math.ceil(number) print(rounded_number) # Output: 6
Using the decimal Module
For high-precision applications (e.g., finance), the decimal module provides accurate rounding:
Example:
import math
def round_up(n, decimals=0):
multiplier = 10 ** decimals
return math.ceil(n * multiplier) / multiplier
# Usage
result = round_up(3.14159, 2)
print(result) # Output: 3.15
Rounding Up with the Built-in round() Function (Approximation)
While round() doesn't directly round up, a workaround is possible:
import numpy as np array = np.array([1.1, 2.5, 3.7]) rounded_array = np.ceil(array) print(rounded_array) # Output: [2. 3. 4.]
Real-World Applications
Here are some practical examples:
Retail Pricing
Rounding up prices simplifies transactions and ensures whole-number charges.
Expense Calculation
Rounding up project expenses ensures the budget covers all potential costs.
Project Management Time Estimation
Rounding up time estimates ensures sufficient resource allocation.
Inventory Management
Rounding up inventory levels ensures sufficient stock to meet demand.
Travel Planning
Rounding up distances improves fuel cost and travel time estimations.
Summary of Methods
| Method | Description | Example Code | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
math.ceil() |
Rounds up to the nearest integer | math.ceil(5.3) → 6 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Custom Function | Rounds up to specified decimal places | round_up(3.14159, 2) → 3.15 |
||||||||||||||||||
NumPy's
|
Rounds up elements in an array | np.ceil([1.1, 2.5]) → [2., 3.] |
||||||||||||||||||
| Module | High-precision rounding | Decimal('2.675').quantize(...) → 2.68 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Built-in (workaround) | Approximation of upward rounding using built-in round() | round_up_builtin(4.2) → 5 |
Practical Applications
- Finance: Accurate budgeting and financial forecasting.
- Inventory Management: Preventing stockouts.
- Statistical Analysis: Ensuring sufficient sample sizes.
Conclusion
The upward rounding function is a crucial tool for precise calculations across various fields. Understanding its application improves numerical accuracy and decision-making.
Key Takeaways
- Upward rounding always rounds numbers upwards.
- It's applicable in various platforms (Excel, Python).
- Understanding its syntax is essential for correct usage.
- It has diverse applications in finance, inventory, and statistics.
- Mastering this function leads to better budgeting and forecasting.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: When to use upward rounding instead of regular rounding? Use upward rounding when underestimation is unacceptable (e.g., budgeting).
Q2: Can negative numbers be rounded up? Yes, they move closer to zero.
Q3: Upward rounding in Google Sheets? Use the ROUNDUP function.
Q4: num_digits as a negative value? Rounds to the left of the decimal point.
Q5: Upward rounding for currency? Yes, for accurate financial calculations.
The above is the detailed content of Python Round Up Function. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 The Hidden Dangers Of AI Internal Deployment: Governance Gaps And Catastrophic RisksApr 28, 2025 am 11:12 AM
The Hidden Dangers Of AI Internal Deployment: Governance Gaps And Catastrophic RisksApr 28, 2025 am 11:12 AMThe unchecked internal deployment of advanced AI systems poses significant risks, according to a new report from Apollo Research. This lack of oversight, prevalent among major AI firms, allows for potential catastrophic outcomes, ranging from uncont
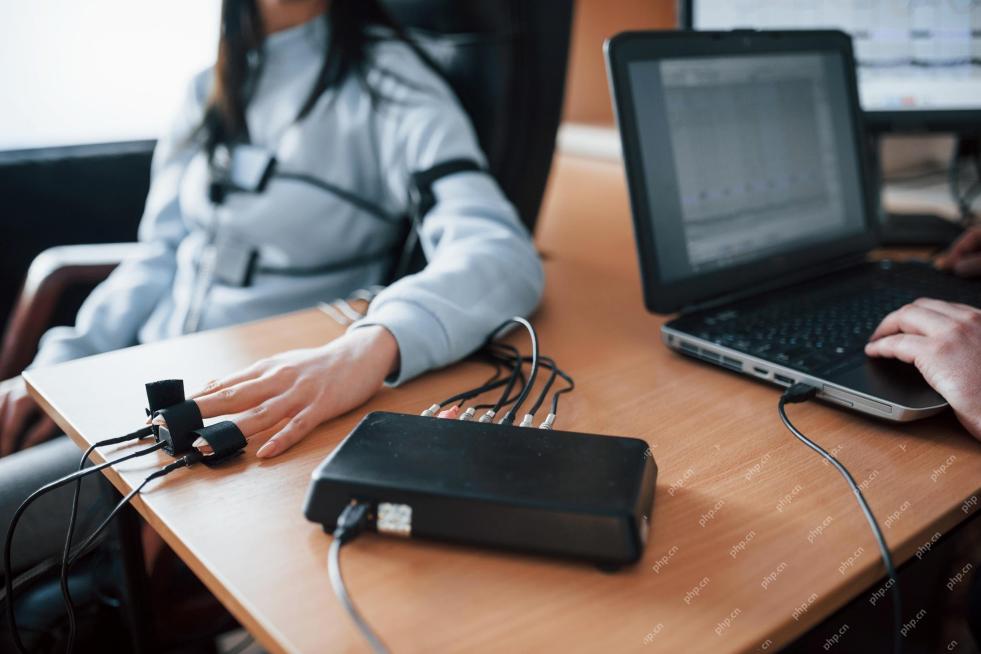 Building The AI PolygraphApr 28, 2025 am 11:11 AM
Building The AI PolygraphApr 28, 2025 am 11:11 AMTraditional lie detectors are outdated. Relying on the pointer connected by the wristband, a lie detector that prints out the subject's vital signs and physical reactions is not accurate in identifying lies. This is why lie detection results are not usually adopted by the court, although it has led to many innocent people being jailed. In contrast, artificial intelligence is a powerful data engine, and its working principle is to observe all aspects. This means that scientists can apply artificial intelligence to applications seeking truth through a variety of ways. One approach is to analyze the vital sign responses of the person being interrogated like a lie detector, but with a more detailed and precise comparative analysis. Another approach is to use linguistic markup to analyze what people actually say and use logic and reasoning. As the saying goes, one lie breeds another lie, and eventually
 Is AI Cleared For Takeoff In The Aerospace Industry?Apr 28, 2025 am 11:10 AM
Is AI Cleared For Takeoff In The Aerospace Industry?Apr 28, 2025 am 11:10 AMThe aerospace industry, a pioneer of innovation, is leveraging AI to tackle its most intricate challenges. Modern aviation's increasing complexity necessitates AI's automation and real-time intelligence capabilities for enhanced safety, reduced oper
 Watching Beijing's Spring Robot RaceApr 28, 2025 am 11:09 AM
Watching Beijing's Spring Robot RaceApr 28, 2025 am 11:09 AMThe rapid development of robotics has brought us a fascinating case study. The N2 robot from Noetix weighs over 40 pounds and is 3 feet tall and is said to be able to backflip. Unitree's G1 robot weighs about twice the size of the N2 and is about 4 feet tall. There are also many smaller humanoid robots participating in the competition, and there is even a robot that is driven forward by a fan. Data interpretation The half marathon attracted more than 12,000 spectators, but only 21 humanoid robots participated. Although the government pointed out that the participating robots conducted "intensive training" before the competition, not all robots completed the entire competition. Champion - Tiangong Ult developed by Beijing Humanoid Robot Innovation Center
 The Mirror Trap: AI Ethics And The Collapse Of Human ImaginationApr 28, 2025 am 11:08 AM
The Mirror Trap: AI Ethics And The Collapse Of Human ImaginationApr 28, 2025 am 11:08 AMArtificial intelligence, in its current form, isn't truly intelligent; it's adept at mimicking and refining existing data. We're not creating artificial intelligence, but rather artificial inference—machines that process information, while humans su
 New Google Leak Reveals Handy Google Photos Feature UpdateApr 28, 2025 am 11:07 AM
New Google Leak Reveals Handy Google Photos Feature UpdateApr 28, 2025 am 11:07 AMA report found that an updated interface was hidden in the code for Google Photos Android version 7.26, and each time you view a photo, a row of newly detected face thumbnails are displayed at the bottom of the screen. The new facial thumbnails are missing name tags, so I suspect you need to click on them individually to see more information about each detected person. For now, this feature provides no information other than those people that Google Photos has found in your images. This feature is not available yet, so we don't know how Google will use it accurately. Google can use thumbnails to speed up finding more photos of selected people, or may be used for other purposes, such as selecting the individual to edit. Let's wait and see. As for now
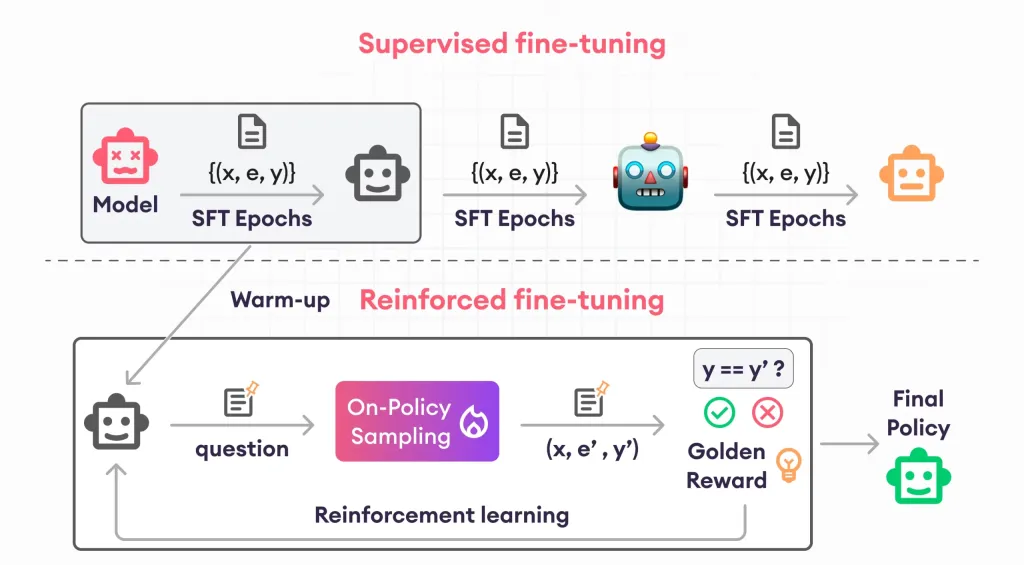 Guide to Reinforcement Finetuning - Analytics VidhyaApr 28, 2025 am 09:30 AM
Guide to Reinforcement Finetuning - Analytics VidhyaApr 28, 2025 am 09:30 AMReinforcement finetuning has shaken up AI development by teaching models to adjust based on human feedback. It blends supervised learning foundations with reward-based updates to make them safer, more accurate, and genuinely help
 Let's Dance: Structured Movement To Fine-Tune Our Human Neural NetsApr 27, 2025 am 11:09 AM
Let's Dance: Structured Movement To Fine-Tune Our Human Neural NetsApr 27, 2025 am 11:09 AMScientists have extensively studied human and simpler neural networks (like those in C. elegans) to understand their functionality. However, a crucial question arises: how do we adapt our own neural networks to work effectively alongside novel AI s


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor







