This article has been updated. It was originally published on March 27, 2017.
Another day, another massive data breach—and another reminder to strengthen your online defenses. Our digital lives depend on passwords, the keys to everything from social media to bank accounts. Strong passwords and effective management are crucial for protecting your identity. While not the only security measure, they're undeniably vital.
Many of us fall short when it comes to password security. We favor easy-to-remember (and therefore easy-to-guess) passwords, often reusing them across multiple accounts. This article offers guidance on improving your password practices.
Essential Password Practices
Creating a secure password is like safeguarding a secret society: Members need to remember it, while intruders must find it impossible to crack.
Using "123456" or "password" is incredibly risky; millions use these common combinations. Hackers target these first, followed by predictable variations like "password1" and "passw0rd".
Avoid easily guessable combinations based on personal information readily available online. A quick Facebook scan might reveal your birthdate or address—incorporating this data weakens your password.
[Related: Twitter's Move Towards a Password-Free Future]
Aim for passwords at least 10 characters long. Longer passwords, diverse character sets (letters, numbers, symbols), and nonsensical sequences are stronger. Consider this: a four-digit numeric code has 10,000 possibilities; adding a single digit increases this to 100,000. The addition of letters and symbols, extending the length to 10 characters or more, exponentially strengthens the password.
Security expert Bruce Schneier suggests creating passwords from random sentences (not well-known quotes or phrases). For example, "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog" could become "Tqbfjotld" (first letter of each word). This generates a random sequence easily recalled by remembering the original sentence. Remember, this example is now compromised due to publication. Create your own unique sentence. You don't need to use only the first letter; you can be more creative.
Many websites assess password strength during creation, alerting you to weaknesses. They also help protect against "brute force" attacks (rapid attempts to guess passwords).

Reusing passwords across multiple accounts is a major vulnerability. It's like giving a hacker access to all your accounts simultaneously if one is compromised. Using unique passwords for each account minimizes the risk.
Effective Password Management
Remembering numerous strong passwords can be challenging. Fortunately, solutions exist. Web browsers offer basic password management, while dedicated password managers provide more robust features.
Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) whenever possible. This adds an extra layer of security, reducing reliance on the password alone. It's like needing both a password and a ticket for access. Most major services (Google, Facebook, etc.) support 2FA.

Most browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Edge) include built-in password managers. They often prompt you to save passwords, syncing them across devices. However, browser password managers are only as secure as your browser access. Ensure you have a strong, personal password for your operating system (Windows, macOS) to protect your password cache.
[Related: Why You Should Use a Password Manager]
For comprehensive password management, consider a dedicated password manager application. These programs securely store passwords across multiple devices, often assisting with strong password generation. They encrypt data, protected by a single master password.
Many password managers are free, with premium features available for a subscription. They often integrate with 2FA services. Some also store other sensitive information (Wi-Fi passwords, credit card details).

LastPass is a popular and reputable password manager, offering unlimited password storage across devices. 1Password is another strong contender, though not free (a trial is available). Dashlane and Keeper are also worth exploring. Research and choose the best option for your needs.
The above is the detailed content of How to choose safe passwords—and remember them, too. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Understanding Data Loss Risks of SSD Drives & How to PreventMay 15, 2025 pm 08:06 PM
Understanding Data Loss Risks of SSD Drives & How to PreventMay 15, 2025 pm 08:06 PMDespite their impressive speed and reliability, SSDs are not immune to failures. This article from MiniTool delves into the most common data loss risks associated with SSD drives and provides effective strategies to minimize the risk of file loss.Qui
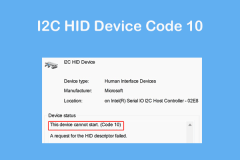 I2C HID Device Code 10 Happens on Win11/10? 8 Proven TipsMay 15, 2025 pm 08:05 PM
I2C HID Device Code 10 Happens on Win11/10? 8 Proven TipsMay 15, 2025 pm 08:05 PMHave you encountered problems with I2C HID device code 10 on your Windows 11/10 computer? Learn how to fix code 10 errors with some proven solutions. Here, MiniTool will provide you with detailed guidance to help you solve your problem. Quick navigation: - I2C HID device cannot start code 10 - Fix 1: Disable and enable I2C HID devices - Fix 2: Change the power management settings - Fix 3: Uninstalling I2C HID device drivers - Fix 4: Uninstall and reinstall HID-compliant mouse driver - Fix 5: Update I2C HID device driver - Fix 6: Change BIOS settings - Fixed
 Laptop Shuts Down Without Low Battery Notification? Fix ItMay 15, 2025 pm 08:04 PM
Laptop Shuts Down Without Low Battery Notification? Fix ItMay 15, 2025 pm 08:04 PMIf your laptop shuts down directly without warning when it is low, this may affect your work. To solve this problem, you can refer to the guide provided by MiniTool. Quick navigation: - No low battery notifications in Windows 11/10 - Method 1. Turn on Windows Notifications - Method 2. Run the power supply troubleshooting tool - Method 3. Change the battery power saving settings - Method 4. Check the power option settings - Method 5. Restore the default power plan - at last There is no low battery notification in Windows 11/10 When the battery is low, the desktop displays a warning message so that you can save your current work or plug in the charger. Usually, when the battery is low,
 A Complete Guide to Fix TeamViewer Protocol Negotiation FailedMay 15, 2025 pm 08:03 PM
A Complete Guide to Fix TeamViewer Protocol Negotiation FailedMay 15, 2025 pm 08:03 PMTeamViewer enables users to remotely control another computer, share files, and engage in real-time communication. However, issues like "TeamViewer protocol negotiation failed" can arise, disrupting the connection. This article from MiniToo
 Windows 11 KB5058411 Not Installing? Try These MethodsMay 15, 2025 pm 08:02 PM
Windows 11 KB5058411 Not Installing? Try These MethodsMay 15, 2025 pm 08:02 PMMicrosoft has rolled out the KB5058411 update for Windows 11 version 24H2 users. If you're curious about the new features, how to download and install it, or what to do if KB5058411 fails to install, this MiniTool article has you covered.Quick Naviga
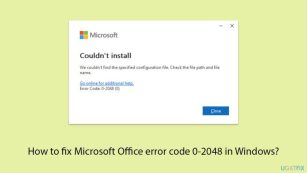 How to fix Microsoft Office error code 0-2048 in Windows?May 15, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
How to fix Microsoft Office error code 0-2048 in Windows?May 15, 2025 pm 08:00 PMMicrosoft Office is a cornerstone Windows productivity software that enables applications like Word, Excel, and Outlook to execute document creation all the way
 Revenge of the Savage Planet Crashing/Not Launching: FixedMay 15, 2025 pm 06:01 PM
Revenge of the Savage Planet Crashing/Not Launching: FixedMay 15, 2025 pm 06:01 PMNothing is more satisfying than having a problem with Survival: Revenge crashing or failing to start on PC. Don't worry, here are several fixes provided by MiniTool to solve these annoying problems. Quick navigation: - Fix 1. Run the game as administrator - Fix 2. Disable overlay - Fix 3. Update GPU drivers - Fix 4. Verify the integrity of the game file - in conclusion Survival of the Wild: Revenge is an exciting new adventure game where players travel between different planets, collecting resources and finding ways to return to Earth. Although the game isn't hardware-required, if you have problems with your download or your PC isn't fully updated, you may encounter Survival of the Wild: Revenge
 Top 5 Proven Fixes for VPN Not Working on ChromeMay 14, 2025 pm 08:02 PM
Top 5 Proven Fixes for VPN Not Working on ChromeMay 14, 2025 pm 08:02 PMAre you experiencing issues with websites not loading on Google Chrome while using a VPN, yet other browsers function normally? This guide from MiniTool will help you understand the causes and provide solutions to fix VPN issues on Chrome.Quick Navig


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment







