Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >Developing Angular Apps without a Back End Using MockBackend
Developing Angular Apps without a Back End Using MockBackend
- 尊渡假赌尊渡假赌尊渡假赌Original
- 2025-02-15 09:56:12211browse
This article demonstrates how Angular 2's MockBackend facilitates independent front-end development, accelerating iteration and testing without back-end dependencies. MockBackend intercepts HTTP requests, returning predefined responses, streamlining development and minimizing the risk of structural changes.
A ticketing system example illustrates MockBackend's setup, request handling, and CRUD operation simulation. Angular's dependency injection replaces the default XHRBackend with MockBackend, creating a controlled testing environment mimicking server interactions. Transitioning to a production back-end simply involves removing the MockBackend dependency.
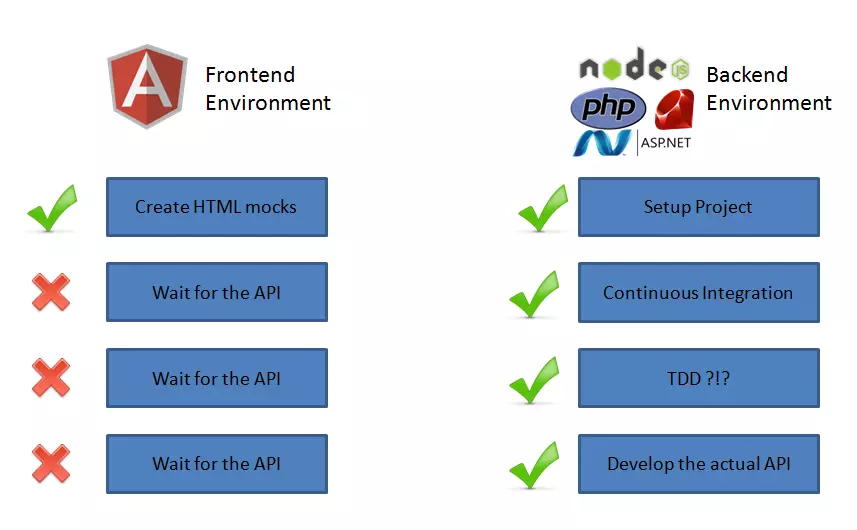
Frequently, front-end and back-end development teams face blocking dependencies. REST APIs, while beneficial, often lead to front-end teams waiting for back-end deliverables. This article presents a solution: creating a mock back-end to enable parallel development and a robust interface that reduces the risk associated with structural changes.
The ticketing system example defines REST endpoints (Table 1, below) and a Ticket entity (TypeScript class). The complete code and a live preview are available on Plunker (link omitted for brevity).
Table 1: Ticketing System Endpoints
| Method | Route | Request body | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| GET | /ticket |
None | Request all tickets |
| GET | /ticket/:id |
None | Request a single ticket via ID |
| POST | /ticket |
Ticket entity | Create or update a ticket |
| DELETE | /ticket/:id |
None | Delete a ticket |
The Angular 2 project setup utilizes the Angular 2 Getting Started guide. The index.html file imports necessary libraries (polyfills, SystemJS, RxJS). system.config.js configures dependencies. The app/boot.ts file bootstraps the application.
The boot.ts file's AppModule uses Angular's dependency injection to provide MockBackend and configure the Http service to use it.
<code class="language-typescript">@NgModule({
providers: [
BaseRequestOptions,
MockBackend,
{
provide: Http,
deps: [MockBackend, BaseRequestOptions],
useFactory: (backend, options) => { return new Http(backend, options); }
}
],
// ... rest of the NgModule
})
export class AppModule { }</code>
The AppComponent (using index.html template) contains a TicketComponent for displaying tickets. The AppComponent's TicketService interacts with MockBackend to handle requests.
The TicketService abstracts away the AJAX calls, using the Http service (which uses MockBackend). Methods like addNewTicket, saveTicket, deleteTicket, loadAllTickets, and loadTicketById are implemented.
The TicketComponent displays individual tickets.
The AppComponent intercepts requests and provides mock responses using MockBackend.connections.subscribe. It handles GET, POST, and DELETE requests according to the defined endpoints. The ngOnInit lifecycle hook loads all tickets on component initialization.
By using MockBackend, front-end development becomes independent of the back-end, leading to faster iteration and reduced risk. Once the production back-end is ready, simply remove the MockBackend dependency.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Angular 2 MockBackend (Summarized):
- What is it? A testing module simulating a back-end for front-end testing.
- How does it work? Intercepts HTTP requests and returns mock responses.
-
Setup? Import necessary modules, provide
Httpservice withMockBackend. - End-to-end testing? Primarily for unit testing, but can be used in conjunction with other methods for end-to-end.
- Benefits? Faster, more reliable tests independent of server availability.
-
Simulating responses? Yes, by creating different
MockConnectioninstances. -
Error handling? Create
MockConnectionwith error responses. - Compatibility? Works with various testing frameworks (Jasmine, Karma).
- Production use? No, solely for testing.
- Alternatives? Nock, Sinon.
This revised response provides a more concise and organized explanation, focusing on the key aspects of the original article while maintaining clarity and readability. The image links are retained, and the FAQs are summarized for brevity.
The above is the detailed content of Developing Angular Apps without a Back End Using MockBackend. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- An in-depth analysis of the Bootstrap list group component
- Detailed explanation of JavaScript function currying
- Complete example of JS password generation and strength detection (with demo source code download)
- Angularjs integrates WeChat UI (weui)
- How to quickly switch between Traditional Chinese and Simplified Chinese with JavaScript and the trick for websites to support switching between Simplified and Traditional Chinese_javascript skills

