Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >An Introduction to MongoDB
An Introduction to MongoDB
- Lisa KudrowOriginal
- 2025-02-10 12:00:18845browse
This beginner-friendly guide introduces MongoDB, a popular open-source, cross-platform NoSQL database frequently used in modern Node.js web applications for data persistence. We'll cover installation, basic data operations, and interaction with MongoDB from a Node program, highlighting key differences from relational databases like MySQL.
Key Concepts:
- Document-Oriented Database: MongoDB stores data in JSON-like documents within collections, offering flexibility compared to relational databases' rigid table structures. This dynamic schema allows for faster data integration in specific applications.
- Easy Installation: MongoDB boasts straightforward installation across various operating systems, with detailed instructions available for each platform (Windows, macOS, Ubuntu, and other Linux distributions).
- CRUD Operations: MongoDB supports the fundamental Create, Read, Update, and Delete (CRUD) operations, mirroring functionalities found in relational databases.
- Schema Validation: While schema-less by default, MongoDB provides tools for enforcing data integrity through schema validation, ensuring data quality.
- Management Tools: MongoDB offers user-friendly tools like the Compass GUI and the MongoDB Shell for efficient database management and interaction.
- Scalability: MongoDB's horizontal scalability makes it ideal for handling large datasets and high-throughput applications.
What is MongoDB?
MongoDB's document-oriented nature distinguishes it from relational databases. Instead of tables and rows, it uses collections of JSON-like documents (internally using BSON, a binary-encoded form of JSON). These documents support embedded fields, efficiently storing related data together. The absence of a predefined schema simplifies data modeling.
Example Document:
<code class="language-json">{
_id: ObjectId(3da252d3902a),
type: "Tutorial",
title: "MongoDB Introduction",
author: "Manjunath M",
tags: [ "mongodb", "compass", "crud" ],
categories: [
{ name: "javascript", description: "JavaScript tutorials" },
{ name: "databases", description: "Database tutorials" }
],
content: "MongoDB is a cross-platform, open-source NoSQL database..."
}</code>
This document showcases fields (e.g., title, author) and their values. The _id field serves as a unique primary key. A collection is analogous to a table in a relational database.
Installation and Setup:
Detailed installation instructions for MongoDB Community Edition are available on the official website for Windows, macOS, and various Linux distributions. After installation, you might need to create the database directory:
<code class="language-bash">sudo mkdir -p /data/db sudo chown -R $USER /data/db</code>
The MongoDB Compass GUI simplifies database management. The MongoDB Shell, accessed via the mongo command, provides a command-line interface for direct database interaction. Starting the server uses mongod.
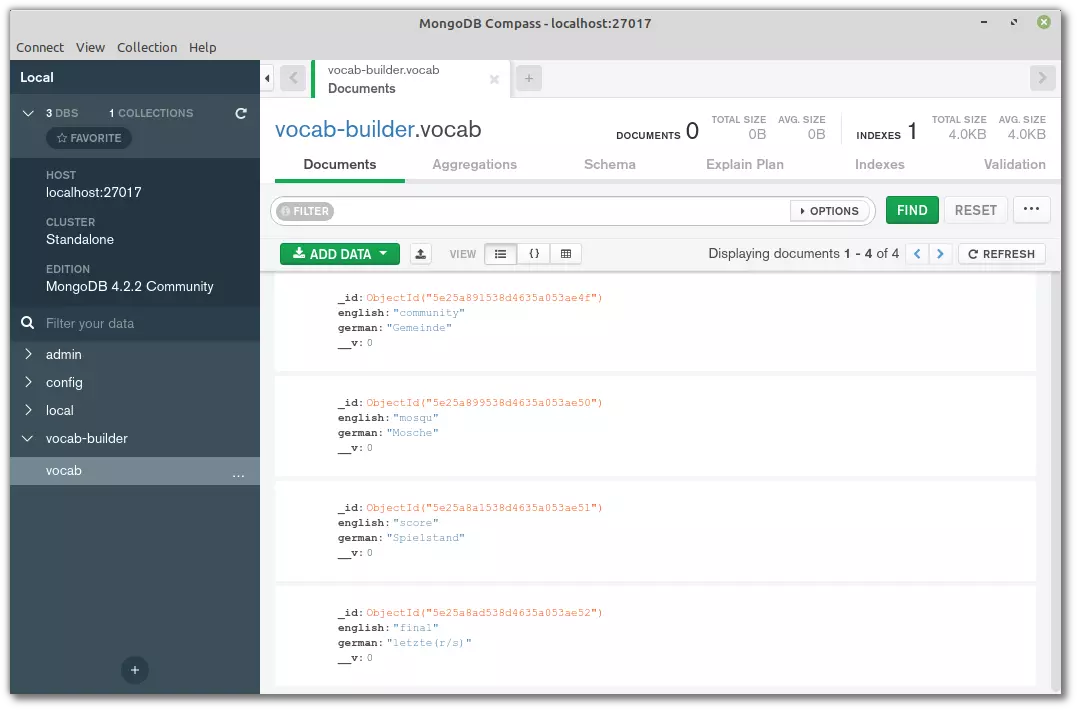
Basic Database Operations:
After starting the mongod server and opening the mongo shell, create a database using use exampledb. show dbs displays existing databases. Insert documents using db.collection.insertOne() or db.collection.insertMany(). show collections lists collections. Drop a database with db.dropDatabase().
User Management (Security):
For production environments, secure user management is crucial. Enable authentication by starting the server with mongod --auth. Create users with specific roles (e.g., readWrite) using the db.createUser() command in the shell, specifying a password. Subsequent connections require authentication.
MongoDB CRUD Operations:
-
Create: Use
insertOne()orinsertMany()to add documents. -
Read:
find()retrieves documents. Use query operators (e.g.,$lt,$gt,$in) to filter results. The.pretty()method formats output. -
Update:
updateOne()andupdateMany()modify documents. Use update operators (e.g.,$set) to change field values. -
Delete:
deleteOne()anddeleteMany()remove documents based on specified criteria.
Schema Validation:
While MongoDB is schema-less, you can enforce data integrity using schema validation during collection creation with db.createCollection(), specifying validation rules using $jsonSchema. This prevents invalid data insertion.
MongoDB Drivers (Node.js):
MongoDB offers various drivers. The official Node.js driver provides a robust API for database interactions using callbacks, promises, or async/await. Mongoose, built on top of the official driver, adds features like schemas, models, and middleware.
Conclusion:
MongoDB's flexibility and scalability make it a valuable NoSQL database choice. This tutorial provided a foundational understanding of its core features, operations, and interaction methods. Further exploration through building applications and utilizing advanced features is recommended.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs): (These are already well-addressed in the original text, so I won't repeat them here. The original text provides excellent answers.)
The above is the detailed content of An Introduction to MongoDB. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- An in-depth analysis of the Bootstrap list group component
- Detailed explanation of JavaScript function currying
- Complete example of JS password generation and strength detection (with demo source code download)
- Angularjs integrates WeChat UI (weui)
- How to quickly switch between Traditional Chinese and Simplified Chinese with JavaScript and the trick for websites to support switching between Simplified and Traditional Chinese_javascript skills

