Understanding Big O Notation: A Developer's Guide to Algorithm Efficiency
As a software developer, grasping Big O notation is essential, regardless of whether you're building web, mobile applications, or handling data processing. It's the key to evaluating algorithm efficiency, directly impacting application performance and scalability. The more you understand Big O, the better you'll be at code optimization.
This guide offers a thorough explanation of Big O notation, its significance, and how to analyze algorithms based on time and space complexity. We'll cover coding examples, real-world applications, and advanced concepts to provide a complete understanding.
Table of Contents
- What is Big O Notation?
- Why is Big O Notation Important?
- Key Big O Notations
- Advanced Big O Concepts
- Real-World Applications of Big O Notation
- Algorithm Optimization: Practical Solutions
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Big O Notation?
Big O notation is a mathematical tool for describing an algorithm's performance or complexity. Specifically, it shows how the algorithm's runtime or memory usage scales as the input size grows. Understanding Big O lets you predict how an algorithm will behave with large datasets.
Why is Big O Notation Important?
Consider a social media platform needing to handle millions of users and posts. Without optimized algorithms (analyzed using Big O), the platform could become slow or crash as user numbers increase. Big O helps you anticipate your code's performance with increasing input size (e.g., users or posts).
- Without Big O, you'd lack direction in code optimization.
- With Big O, you can design scalable, efficient algorithms even for massive datasets.
Key Big O Notations
-
Constant Time: O(1)
An O(1) algorithm performs a fixed number of operations regardless of input size. Its execution time remains constant as input grows.
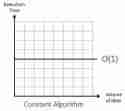
Example: A function retrieving the first array element:
function getFirstElement(arr) {
return arr[0];
}
The runtime is constant, regardless of array size – O(1).
Real-World Scenario: A vending machine dispensing a snack takes the same time regardless of the number of snacks available.
-
Logarithmic Time: O(log n)
Logarithmic time complexity arises when an algorithm halves the problem size with each iteration. This leads to O(log n) complexity, meaning runtime grows logarithmically with input size.

Example: Binary search is a classic example:
function getFirstElement(arr) {
return arr[0];
}
Each iteration halves the search space, resulting in O(log n).
Real-World Scenario: Finding a name in a sorted phone book.
-
Linear Time: O(n)
O(n) complexity means runtime grows directly proportional to input size. Adding one element increases runtime by a constant amount.
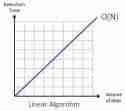
Example: Finding the maximum element in an array:
function binarySearch(arr, target) {
let low = 0;
let high = arr.length - 1;
while (low <= high) {
let mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2);
if (arr[mid] === target) {
return mid;
} else if (arr[mid] < target) {
low = mid + 1;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1; // Target not found
}
The algorithm iterates through each element once – O(n).
Real-World Scenario: Processing a queue of people one by one.
-
Linearithmic Time: O(n log n)
O(n log n) is common in efficient sorting algorithms like Merge Sort and Quick Sort. They divide the input into smaller parts and process them efficiently.
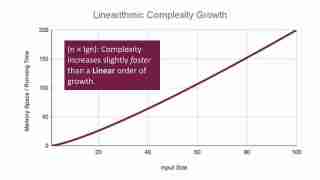
Example: Merge Sort (implementation omitted for brevity). It recursively divides the array (log n) and merges (O(n)), resulting in O(n log n).
Real-World Scenario: Sorting a large group of people by height.
-
Quadratic Time: O(n²)
O(n²) algorithms usually have nested loops where each element in one loop is compared to every element in another.
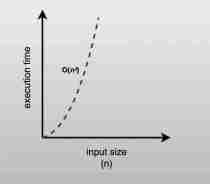
Example: Bubble Sort (implementation omitted for brevity). The nested loops lead to O(n²).
Real-World Scenario: Comparing everyone's height to everyone else's in a group.
-
Cubic Time: O(n³)
Algorithms with three nested loops often have O(n³) complexity. This is common in algorithms working with multidimensional data structures like matrices.

Example: Simple matrix multiplication (implementation omitted for brevity) with three nested loops results in O(n³).
Real-World Scenario: Processing a 3D object in a graphics program.
Advanced Big O Concepts
-
Amortized Time Complexity: An algorithm might have occasional expensive operations, but the average cost over many operations is lower (e.g., dynamic array resizing).
-
Best, Worst, and Average Case: Big O often represents the worst-case scenario. However, best-case (Ω), worst-case (O), and average-case (Θ) complexities provide a more complete picture.
-
Space Complexity: Big O also analyzes an algorithm's memory usage (space complexity). Understanding both time and space complexity is crucial for optimization.
Conclusion
This guide covered Big O notation from basic to advanced concepts. By understanding and applying Big O analysis, you can write more efficient and scalable code. Continuously practicing this will make you a more proficient developer.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is Big O notation? A mathematical description of algorithm performance (time and space) as input size grows.
- Why is Big O important? It helps optimize code for scalability and efficiency.
- Best, worst, average case differences? Best is the fastest, worst is the slowest, average is the expected performance.
- Time vs. space complexity? Time measures execution time; space measures memory usage.
- How to optimize using Big O? Analyze complexity and use techniques like caching or divide and conquer.
- Best sorting algorithm? Merge Sort and Quick Sort (O(n log n)) are efficient for large datasets.
- Can Big O be used for both time and space? Yes.
(Note: The images are assumed to be present and correctly linked as per the original input. The code examples are simplified for clarity. More robust implementations may exist.)
The above is the detailed content of Big-O Notation Simplified: Guide to Algorithm Efficiency | Mbloging. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Javascript Data Types : Is there any difference between Browser and NodeJs?May 14, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Javascript Data Types : Is there any difference between Browser and NodeJs?May 14, 2025 am 12:15 AMJavaScript core data types are consistent in browsers and Node.js, but are handled differently from the extra types. 1) The global object is window in the browser and global in Node.js. 2) Node.js' unique Buffer object, used to process binary data. 3) There are also differences in performance and time processing, and the code needs to be adjusted according to the environment.
 JavaScript Comments: A Guide to Using // and /* */May 13, 2025 pm 03:49 PM
JavaScript Comments: A Guide to Using // and /* */May 13, 2025 pm 03:49 PMJavaScriptusestwotypesofcomments:single-line(//)andmulti-line(//).1)Use//forquicknotesorsingle-lineexplanations.2)Use//forlongerexplanationsorcommentingoutblocksofcode.Commentsshouldexplainthe'why',notthe'what',andbeplacedabovetherelevantcodeforclari
 Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AMThe main difference between Python and JavaScript is the type system and application scenarios. 1. Python uses dynamic types, suitable for scientific computing and data analysis. 2. JavaScript adopts weak types and is widely used in front-end and full-stack development. The two have their own advantages in asynchronous programming and performance optimization, and should be decided according to project requirements when choosing.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AMWhether to choose Python or JavaScript depends on the project type: 1) Choose Python for data science and automation tasks; 2) Choose JavaScript for front-end and full-stack development. Python is favored for its powerful library in data processing and automation, while JavaScript is indispensable for its advantages in web interaction and full-stack development.
 Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMPython and JavaScript each have their own advantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1. Python is easy to learn, with concise syntax, suitable for data science and back-end development, but has a slow execution speed. 2. JavaScript is everywhere in front-end development and has strong asynchronous programming capabilities. Node.js makes it suitable for full-stack development, but the syntax may be complex and error-prone.
 JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AMJavaScriptisnotbuiltonCorC ;it'saninterpretedlanguagethatrunsonenginesoftenwritteninC .1)JavaScriptwasdesignedasalightweight,interpretedlanguageforwebbrowsers.2)EnginesevolvedfromsimpleinterpreterstoJITcompilers,typicallyinC ,improvingperformance.
 JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript can be used for front-end and back-end development. The front-end enhances the user experience through DOM operations, and the back-end handles server tasks through Node.js. 1. Front-end example: Change the content of the web page text. 2. Backend example: Create a Node.js server.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AMChoosing Python or JavaScript should be based on career development, learning curve and ecosystem: 1) Career development: Python is suitable for data science and back-end development, while JavaScript is suitable for front-end and full-stack development. 2) Learning curve: Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners; JavaScript syntax is flexible. 3) Ecosystem: Python has rich scientific computing libraries, and JavaScript has a powerful front-end framework.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools







