Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >Client-side Rendering & Server-side Rendering
Client-side Rendering & Server-side Rendering
- Linda HamiltonOriginal
- 2024-11-30 05:04:17758browse
Client-side rendering, also referred to as CSR, the browser renders the page itself with the use of JS. Instead of sending a ready-made page from the server, the server provides the JavaScript that will run in the browser and construct the content as the user interacts with the site. We have a lot of examples of client-side rendering websites, i.e facebook, and other social media, as they need continuous page load.
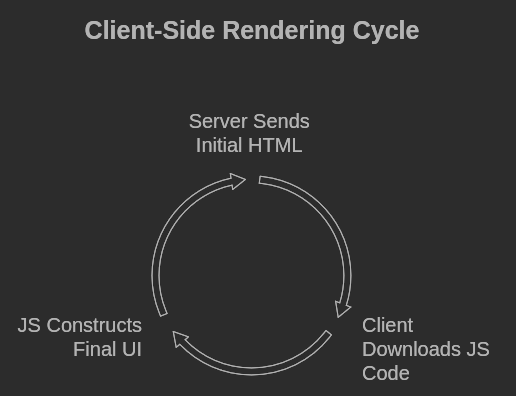
Process:
- Server sends an initial HTML file.
- Client-side download JS code from server.
- The JS code outputs the final UI.
Pros:
- More dynamic and interactive web applications.
- It provides a smoother experience for users and every load.
- It reduces the extra need for server-side-requests.
Cons:
- It has slower initial load times.
Server-side rendering, also abbreviated as SSR, is when the server composes and sends to client-side a fully-formed HTML page which includes all dynamic content. The browser, then, simply displays the page without any need to do extra work. As a result, users view content at a faster speed since all processing happens on the server side. For example, as I have read somewhere that wordpress & github are based on server-side rendering (correct me, if I am wrong)
Process:
- Server receives a request for the web page, retrieves the data required, populates into an HTML, and applies the necessary styles.
- Now, the fully rendered page is sent by the server to the browser to show.
- In the case of initial page loading, no type of JS is required.
- Subsequent user interactions and updates are managed by the client-side JS rendering.

Pros:
- It loads faster the first time.
- Better user experience even with a slower network.
Cons:
- More server load requires.
- It will be slow when it is requested multiple times.
In a nutshell:

At last, I will add my own opinion to it, for applications that consider interactivity and user engagement as the top aspects, like social media or web applications with lots of client-side logic, CSR stands the best. However, where content is heavy, such as websites with more of an interest in SEO and fast initial load speeds, SSR will be a better option. It depends on the nature of the application and target audience to be determined.
Thus, by careful analysis of the strength and weakness, the developer can take a decision to have the right rendering strategy balancing performance, usability, and searchability.
Happy Coding. Thanks.
The above is the detailed content of Client-side Rendering & Server-side Rendering. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- An in-depth analysis of the Bootstrap list group component
- Detailed explanation of JavaScript function currying
- Complete example of JS password generation and strength detection (with demo source code download)
- Angularjs integrates WeChat UI (weui)
- How to quickly switch between Traditional Chinese and Simplified Chinese with JavaScript and the trick for websites to support switching between Simplified and Traditional Chinese_javascript skills

