Just out of boredom, while waiting for my follow-up interview sessions, I built a state-machine library, powered by genruler. I built one in the past, to be exact, during my first job after graduation. This implementation is loosely based on the design my supervisor drafted back then. The project also aimed to showcase how the rule DSL can be utilized.
According to the helpful summary returned by a Google search on finite state machine (emphasis mine)
A “finite state machine” means a computational model where a system can only be in a limited number of distinct states at any given time, and transitions between these states are triggered by specific inputs, essentially allowing it to process information based on a set of defined conditions with no possibility of having an infinite number of states; “finite” here refers to the limited set of possible states the system can exist in.
The library receives a dictionary that represents the schema of the finite state machine. For example, we want to build an order tracking system
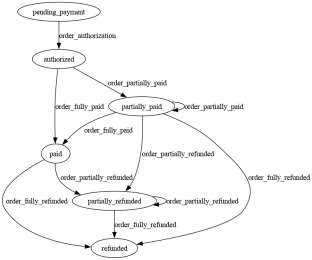
Finite state machine diagram generated by Graphviz
And the schema would look something like this (in truncated YAML form for clarity)
machine:
initial_state: pending_payment
states:
pending_payment:
name: pending payment
transitions:
order_authorization:
name: order is authorized
destination: authorized
rule: (condition.equal (basic.field "is_authorized") (boolean.tautology))
authorized:
name: authorized
action: authorize_order
transitions:
order_partially_paid:
name: order is partially paid
destination: partially_paid
rule: (boolean.tautology)
order_fully_paid:
name: order is fully paid
destination: paid
rule: (boolean.tautology)
...
Therefore, to set everything up, we call
import genstates
import yaml
import order_processor
with open("states.yaml") as schema:
machine = genstates.Machine(yaml.safe_load(schema), order_processor)
So in this fictional example, we will receive some payload whenever there is a change in the order. For example, when the seller acknowledges the order, we get
{
"is_authorized": true,
...
}
We can then check through the library
state = machine.initial # assume the order is created transition = machine.get_transition(state, "order_authorization") assert transition.check_condition(payload)
The check also runs an additional validation check if defined in the schema. This is helpful if you intend to return an error message to the caller.
try: assert transition.check_condition(payload) except ValidationFailedError as e: logger.exception(e)
Sometimes, we know that every time the payload arrives, it should trigger a transition, but we don’t always know which one. Therefore, we just pass it into Machine.progress
try: state = machine.progress(state, payload) except ValidationFailedError as e: logger.exception(e)
Once knowing what state the order should progress, we can start writing code to work on the logic
# fetch the order from database
order = Order.get(id=payload["order_id"])
current_state = machine.states[order.state]
# fetch next state
try:
new_state = machine.progress(current_state, payload)
except ValidationFailedError as e:
# validation failed, do something
logger.exception(e)
return
except MissingTransitionError as e:
# can't find a valid transition from given payload
logger.exception(e)
return
except DuplicateTransitionError as e:
# found more than one transition from given payload
logger.exception(e)
return
# do processing (example)
log = Log.create(order=order, **payload)
log.save()
order.state = new_state.key
order.save()
Ideally, I can also extract the processing logic away, which is the reason I imported order_processor in the beginning. In the authorization state definition, we also defined an action
authorized:
name: authorized
action: authorize_order
...
So in the module order_processor, we define a new function called authorized_order
def authorize_order(payload):
# do the processing here instead
pass
Such that the following is possible, where state management code is separated from the rest of processing logic
machine:
initial_state: pending_payment
states:
pending_payment:
name: pending payment
transitions:
order_authorization:
name: order is authorized
destination: authorized
rule: (condition.equal (basic.field "is_authorized") (boolean.tautology))
authorized:
name: authorized
action: authorize_order
transitions:
order_partially_paid:
name: order is partially paid
destination: partially_paid
rule: (boolean.tautology)
order_fully_paid:
name: order is fully paid
destination: paid
rule: (boolean.tautology)
...
However, I am still working on it now, and should make it in the next release. Meanwhile, it is also capable of doing something similar to map and reduce if every state has action defined. Feel free to check the project for development progress. And both genruler and genstates are now up on PyPI, yay!
Now, how about the AI thing?
I downloaded Codeium Windsurf after the library is somewhat usable. I eventually used it to strip hy dependency off from genruler, and added documentation and README to the project. For genstates, I used cascade to generate documentation, README, as well as tests. Overall, it feels like I have a mid to senior programmer around to help me out with tasks I would assign to my interns or even juniors.
Most of the core logic still comes from my end, as intelligent as the language model is at the moment, they still make mistakes here and there and hence, require supervision. I also experimented with qwen2.5-coder:7b model, and it works rather well, albeit rather slowly due to my crappy workstation. I find the price Codeium asks for is fair, if I am to build my own product and managed to make money out of it.
While the generation parts works fine, but writing actual code is not as great. I am not sure if Pylance is working properly there, considered it is proprietary, or whether it is due to the completion magic windsurf does, my editor is no longer able to do auto-import of libraries when I write code. For example, when I auto-completes reduce() function in my code, in vscode it would automagically insert from functools import reduce into my code. However, this is not the case in windsurf, which makes it a little bit irritating. However, considering this is new, the coding experience should be fixed over time.
On the other hand, I am still in search of a lighter editor, and zed does catch my attention. However, since my Surface Book 2 died recently, I am only left with a Samsung Galaxy Tab S7FE when I am away from my home office. Hence, vscode with a web frontend (and it is surprisingly usable) connected to my workstation is still my main editor (it even works with the neovim extension).
Generative AI powered by LLM is rapidly changing our lives, there’s no point in resisting it. However, IMHO, we should also have some self-restrain to not use it for everything. It really should be used as a complement to innovative or creative work, not a replacement to innovation and creativity.
We should also know what it is outputting, instead of blindly accept what it does. For example, in genruler, I made it improve my original README with more extensive examples. Instead of accepting it as-is, I made it to generate tests for all the examples it generates in the README, so the example code passes and works as I intended.
Overall, yea, I do think these Generative AI enhanced editors do worth the money they ask for. In the end, these are tools, they are meant to offer assistance to work, not replacing the person hitting the keyboard.
The above is the detailed content of Building state machine library with help from AI tools. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Merging Lists in Python: Choosing the Right MethodMay 14, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Merging Lists in Python: Choosing the Right MethodMay 14, 2025 am 12:11 AMTomergelistsinPython,youcanusethe operator,extendmethod,listcomprehension,oritertools.chain,eachwithspecificadvantages:1)The operatorissimplebutlessefficientforlargelists;2)extendismemory-efficientbutmodifiestheoriginallist;3)listcomprehensionoffersf
 How to concatenate two lists in python 3?May 14, 2025 am 12:09 AM
How to concatenate two lists in python 3?May 14, 2025 am 12:09 AMIn Python 3, two lists can be connected through a variety of methods: 1) Use operator, which is suitable for small lists, but is inefficient for large lists; 2) Use extend method, which is suitable for large lists, with high memory efficiency, but will modify the original list; 3) Use * operator, which is suitable for merging multiple lists, without modifying the original list; 4) Use itertools.chain, which is suitable for large data sets, with high memory efficiency.
 Python concatenate list stringsMay 14, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Python concatenate list stringsMay 14, 2025 am 12:08 AMUsing the join() method is the most efficient way to connect strings from lists in Python. 1) Use the join() method to be efficient and easy to read. 2) The cycle uses operators inefficiently for large lists. 3) The combination of list comprehension and join() is suitable for scenarios that require conversion. 4) The reduce() method is suitable for other types of reductions, but is inefficient for string concatenation. The complete sentence ends.
 Python execution, what is that?May 14, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Python execution, what is that?May 14, 2025 am 12:06 AMPythonexecutionistheprocessoftransformingPythoncodeintoexecutableinstructions.1)Theinterpreterreadsthecode,convertingitintobytecode,whichthePythonVirtualMachine(PVM)executes.2)TheGlobalInterpreterLock(GIL)managesthreadexecution,potentiallylimitingmul
 Python: what are the key featuresMay 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Python: what are the key featuresMay 14, 2025 am 12:02 AMKey features of Python include: 1. The syntax is concise and easy to understand, suitable for beginners; 2. Dynamic type system, improving development speed; 3. Rich standard library, supporting multiple tasks; 4. Strong community and ecosystem, providing extensive support; 5. Interpretation, suitable for scripting and rapid prototyping; 6. Multi-paradigm support, suitable for various programming styles.
 Python: compiler or Interpreter?May 13, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python: compiler or Interpreter?May 13, 2025 am 12:10 AMPython is an interpreted language, but it also includes the compilation process. 1) Python code is first compiled into bytecode. 2) Bytecode is interpreted and executed by Python virtual machine. 3) This hybrid mechanism makes Python both flexible and efficient, but not as fast as a fully compiled language.
 Python For Loop vs While Loop: When to Use Which?May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Python For Loop vs While Loop: When to Use Which?May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMUseaforloopwheniteratingoverasequenceorforaspecificnumberoftimes;useawhileloopwhencontinuinguntilaconditionismet.Forloopsareidealforknownsequences,whilewhileloopssuitsituationswithundeterminediterations.
 Python loops: The most common errorsMay 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Python loops: The most common errorsMay 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMPythonloopscanleadtoerrorslikeinfiniteloops,modifyinglistsduringiteration,off-by-oneerrors,zero-indexingissues,andnestedloopinefficiencies.Toavoidthese:1)Use'i


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools






