 Backend Development
Backend Development Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial Using Google Cloud Functions for Three-Tier Data Processing with Google Composer and Automated Deployments via GitHub Actions
Using Google Cloud Functions for Three-Tier Data Processing with Google Composer and Automated Deployments via GitHub ActionsTable of Contents
- About
- Tools Used
- Solution Architecture Diagram
-
Deployment Process
- Prerequisites
- Secrets for GitHub Actions
- To create a new secret:
- Setting Up the DevOps Service Account
-
GitHub Actions Pipeline: Steps
- enable-services
- deploy-buckets
- deploy-cloud-function
- deploy-composer-service-account
- deploy-bigquery-dataset-bigquery-tables
- deploy-composer-environment
- deploy-composer-http-connection
- deploy-dags
- GitHub Actions Workflow Explanation
- Resources Created After Deployment
- Conclusion
- References
About
This post explores the use of Google Cloud Functions for processing data in a three-tier architecture. The solution is orchestrated with Google Composer and features automated deployments using GitHub Actions. We will walk through the tools used, deployment process, and pipeline steps, providing a clear guide for building an end-to-end cloud-based data pipeline.
Tools Used
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): The primary cloud environment.
- Cloud Storage: For storing input and processed data across different layers (Bronze, Silver, Gold).
- Cloud Functions: Serverless functions responsible for data processing in each tier.
- Google Composer: An orchestration tool based on Apache Airflow, used to schedule and manage workflows.
- GitHub Actions: Automation tool for deploying and managing the pipeline infrastructure.
Solution Architecture Diagram
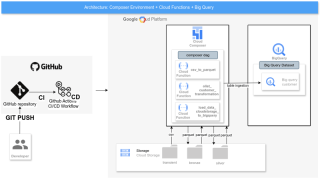
Deployment Process
Prerequisites
Before setting up the project, ensure you have the following:
- GCP Account: A Google Cloud account with billing enabled.
- Service Account for DevOps: A service account with the required permissions to deploy resources in GCP.
- Secrets in GitHub: Store the GCP service account credentials, project ID, and bucket name as secrets in GitHub for secure access.
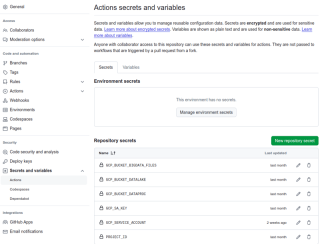
Secrets for GitHub Actions
To securely access your GCP project and resources, set the following secrets in GitHub Actions:
- BUCKET_DATALAKE: Your Cloud Storage bucket for the data lake.
- GCP_DEVOPS_SA_KEY: The service account key in JSON format.
- PROJECT_ID: Your GCP project ID.
- REGION_PROJECT_ID: The region where your GCP project is deployed.
To create a new secret:
1. In project repository, menu **Settings** 2. **Security**, 3. **Secrets and variables**,click in access **Action** 4. **New repository secret**, type a **name** and **value** for secret.
For more details , access :
https://docs.github.com/pt/actions/security-for-github-actions/security-guides/using-secrets-in-github-actions
Setting Up the DevOps Service Account
Create a service account in GCP with permissions for Cloud Functions, Composer, BigQuery, and Cloud Storage. Grant the necessary roles such as:
- Cloud Functions Admin
- Composer User
- BigQuery Data Editor
- Storage Object Admin
GitHub Actions Pipeline: Steps
The pipeline automates the entire deployment process, ensuring all components are set up correctly. Here's a breakdown of the key jobs from the GitHub Actions file, each responsible for a different aspect of the deployment.
enable-services
enable-services:
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
# Step to Authenticate with GCP
- name: Authorize GCP
uses: 'google-github-actions/auth@v2'
with:
credentials_json: ${{ secrets.GCP_DEVOPS_SA_KEY }}
# Step to Configure Cloud SDK
- name: Set up Cloud SDK
uses: google-github-actions/setup-gcloud@v2
with:
version: '>= 363.0.0'
project_id: ${{ secrets.PROJECT_ID }}
# Step to Configure Docker to use the gcloud command-line tool as a credential helper
- name: Configure Docker
run: |-
gcloud auth configure-docker
- name: Set up python 3.8
uses: actions/setup-python@v2
with:
python-version: 3.8.16
# Step to Create GCP Bucket
- name: Enable gcp service api's
run: |-
gcloud services enable ${{ env.GCP_SERVICE_API_0 }}
gcloud services enable ${{ env.GCP_SERVICE_API_1 }}
gcloud services enable ${{ env.GCP_SERVICE_API_2 }}
gcloud services enable ${{ env.GCP_SERVICE_API_3 }}
gcloud services enable ${{ env.GCP_SERVICE_API_4 }}
deploy-buckets
deploy-buckets:
needs: [enable-services]
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
timeout-minutes: 10
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Authorize GCP
uses: 'google-github-actions/auth@v2'
with:
credentials_json: ${{ secrets.GCP_DEVOPS_SA_KEY }}
# Step to Authenticate with GCP
- name: Set up Cloud SDK
uses: google-github-actions/setup-gcloud@v2
with:
version: '>= 363.0.0'
project_id: ${{ secrets.PROJECT_ID }}
# Step to Configure Docker to use the gcloud command-line tool as a credential helper
- name: Configure Docker
run: |-
gcloud auth configure-docker
# Step to Create GCP Bucket
- name: Create Google Cloud Storage - datalake
run: |-
if ! gsutil ls -p ${{ secrets.PROJECT_ID }} gs://${{ secrets.BUCKET_DATALAKE }} &> /dev/null; \
then \
gcloud storage buckets create gs://${{ secrets.BUCKET_DATALAKE }} --default-storage-class=nearline --location=${{ env.REGION }}
else
echo "Cloud Storage : gs://${{ secrets.BUCKET_DATALAKE }} already exists" !
fi
# Step to Upload the file to GCP Bucket - transient files
- name: Upload transient files to Google Cloud Storage
run: |-
TARGET=${{ env.INPUT_FOLDER }}
BUCKET_PATH=${{ secrets.BUCKET_DATALAKE }}/${{ env.INPUT_FOLDER }}
gsutil cp -r $TARGET gs://${BUCKET_PATH}
deploy-cloud-function
deploy-cloud-function:
needs: [enable-services, deploy-buckets]
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
# Step to Authenticate with GCP
- name: Authorize GCP
uses: 'google-github-actions/auth@v2'
with:
credentials_json: ${{ secrets.GCP_DEVOPS_SA_KEY }}
# Step to Configure Cloud SDK
- name: Set up Cloud SDK
uses: google-github-actions/setup-gcloud@v2
with:
version: '>= 363.0.0'
project_id: ${{ secrets.PROJECT_ID }}
# Step to Configure Docker to use the gcloud command-line tool as a credential helper
- name: Configure Docker
run: |-
gcloud auth configure-docker
- name: Set up python 3.10
uses: actions/setup-python@v2
with:
python-version: 3.10.12
#cloud_function_scripts/csv_to_parquet
- name: Create cloud function - ${{ env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_1_NAME }}
run: |-
cd ${{ env.FUNCTION_SCRIPTS }}/${{ env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_1_NAME }}
gcloud functions deploy ${{ env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_1_NAME }} \
--gen2 \
--cpu=${{ env.FUNCTION_CPU }} \
--memory=${{ env.FUNCTION_MEMORY }} \
--runtime ${{ env.PYTHON_FUNCTION_RUNTIME }} \
--trigger-http \
--region ${{ env.REGION }} \
--entry-point ${{ env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_1_NAME }}
- name: Create cloud function - ${{ env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_2_NAME }}
run: |-
cd ${{ env.FUNCTION_SCRIPTS }}/${{ env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_2_NAME }}
gcloud functions deploy ${{ env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_2_NAME }} \
--gen2 \
--cpu=${{ env.FUNCTION_CPU }} \
--memory=${{ env.FUNCTION_MEMORY }} \
--runtime ${{ env.PYTHON_FUNCTION_RUNTIME }} \
--trigger-http \
--region ${{ env.REGION }} \
--entry-point ${{ env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_2_NAME }}
- name: Create cloud function - ${{ env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_3_NAME }}
run: |-
cd ${{ env.FUNCTION_SCRIPTS }}/${{ env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_3_NAME }}
gcloud functions deploy ${{ env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_3_NAME }} \
--gen2 \
--cpu=${{ env.FUNCTION_CPU }} \
--memory=${{ env.FUNCTION_MEMORY }} \
--runtime ${{ env.PYTHON_FUNCTION_RUNTIME }} \
--trigger-http \
--region ${{ env.REGION }} \
--entry-point ${{ env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_3_NAME }}
deploy-composer-service-account
deploy-composer-service-account:
needs: [enable-services, deploy-buckets, deploy-cloud-function ]
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
timeout-minutes: 10
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Authorize GCP
uses: 'google-github-actions/auth@v2'
with:
credentials_json: ${{ secrets.GCP_DEVOPS_SA_KEY }}
# Step to Authenticate with GCP
- name: Set up Cloud SDK
uses: google-github-actions/setup-gcloud@v2
with:
version: '>= 363.0.0'
project_id: ${{ secrets.PROJECT_ID }}
# Step to Configure Docker to use the gcloud command-line tool as a credential helper
- name: Configure Docker
run: |-
gcloud auth configure-docker
- name: Create service account
run: |-
if ! gcloud iam service-accounts list | grep -i ${{ env.SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}} &> /dev/null; \
then \
gcloud iam service-accounts create ${{ env.SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME }} \
--display-name=${{ env.SERVICE_ACCOUNT_DESCRIPTION }}
fi
- name: Add permissions to service account
run: |-
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding ${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}} \
--member="serviceAccount:${{env.SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}}@${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role="roles/composer.user"
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding ${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}} \
--member="serviceAccount:${{env.SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}}@${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role="roles/storage.objectAdmin"
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding ${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}} \
--member="serviceAccount:${{env.SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}}@${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role="roles/cloudfunctions.invoker"
# Permissão para criar e gerenciar ambientes Composer
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding ${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}} \
--member="serviceAccount:${{env.SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}}@${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role="roles/composer.admin"
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding ${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}} \
--member="serviceAccount:${{env.SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}}@${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role="roles/composer.worker"
# Permissão para criar e configurar instâncias e recursos na VPC
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding ${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}} \
--member="serviceAccount:${{env.SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}}@${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role="roles/compute.networkAdmin"
# Permissão para interagir com o Cloud Storage, necessário para buckets e logs
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding ${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}} \
--member="serviceAccount:${{env.SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}}@${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role="roles/storage.admin"
# Permissão para criar e gerenciar recursos no projeto, como buckets e instâncias
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding ${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}} \
--member="serviceAccount:${{env.SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}}@${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role="roles/editor"
# Permissão para acessar e usar recursos necessários para o IAM
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding ${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}} \
--member="serviceAccount:${{env.SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}}@${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role="roles/iam.serviceAccountUser"
gcloud functions add-iam-policy-binding ${{env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_1_NAME}} \
--region="${{env.REGION}}" \
--member="serviceAccount:${{env.SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}}@${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role="roles/cloudfunctions.invoker"
gcloud functions add-invoker-policy-binding ${{env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_1_NAME}} \
--region="${{env.REGION}}" \
--member="serviceAccount:${{env.SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}}@${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}}.iam.gserviceaccount.com"
gcloud functions add-iam-policy-binding ${{env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_2_NAME}} \
--region="${{env.REGION}}" \
--member="serviceAccount:${{env.SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}}@${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role="roles/cloudfunctions.invoker"
gcloud functions add-invoker-policy-binding ${{env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_2_NAME}} \
--region="${{env.REGION}}" \
--member="serviceAccount:${{env.SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}}@${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}}.iam.gserviceaccount.com"
gcloud functions add-iam-policy-binding ${{env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_3_NAME}} \
--region="${{env.REGION}}" \
--member="serviceAccount:${{env.SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}}@${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role="roles/cloudfunctions.invoker"
gcloud functions add-invoker-policy-binding ${{env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_3_NAME}} \
--region="${{env.REGION}}" \
--member="serviceAccount:${{env.SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}}@${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}}.iam.gserviceaccount.com"
SERVICE_NAME_1=$(gcloud functions describe ${{ env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_1_NAME }} --region=${{ env.REGION }} --format="value(serviceConfig.service)")
gcloud run services add-iam-policy-binding $SERVICE_NAME_1 \
--region="${{env.REGION}}" \
--member="serviceAccount:${{env.SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}}@${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role="roles/run.invoker"
SERVICE_NAME_2=$(gcloud functions describe ${{ env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_2_NAME }} --region=${{ env.REGION }} --format="value(serviceConfig.service)")
gcloud run services add-iam-policy-binding $SERVICE_NAME_2 \
--region="${{env.REGION}}" \
--member="serviceAccount:${{env.SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}}@${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role="roles/run.invoker"
SERVICE_NAME_3=$(gcloud functions describe ${{ env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_3_NAME }} --region=${{ env.REGION }} --format="value(serviceConfig.service)")
gcloud run services add-iam-policy-binding $SERVICE_NAME_3 \
--region="${{env.REGION}}" \
--member="serviceAccount:${{env.SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}}@${{secrets.PROJECT_ID}}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role="roles/run.invoker"
gcloud functions add-invoker-policy-binding ${{env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_1_NAME}} \
--region="${{env.REGION}}" \
--member="allUsers"
gcloud functions add-invoker-policy-binding ${{env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_2_NAME}} \
--region="${{env.REGION}}" \
--member="allUsers"
gcloud functions add-invoker-policy-binding ${{env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_3_NAME}} \
--region="${{env.REGION}}" \
--member="allUsers"
deploy-bigquery-dataset-bigquery-tables
deploy-bigquery-dataset-bigquery-tables:
needs: [enable-services, deploy-buckets, deploy-cloud-function, deploy-composer-service-account ]
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
timeout-minutes: 10
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Authorize GCP
uses: 'google-github-actions/auth@v2'
with:
credentials_json: ${{ secrets.GCP_DEVOPS_SA_KEY }}
# Step to Authenticate with GCP
- name: Set up Cloud SDK
uses: google-github-actions/setup-gcloud@v2
with:
version: '>= 363.0.0'
project_id: ${{ secrets.PROJECT_ID }}
# Step to Configure Docker to use the gcloud command-line tool as a credential helper
- name: Configure Docker
run: |-
gcloud auth configure-docker
- name: Create Big Query Dataset
run: |-
if ! bq ls --project_id ${{ secrets.PROJECT_ID}} -a | grep -w ${{ env.BIGQUERY_DATASET}} &> /dev/null; \
then
bq --location=${{ env.REGION }} mk \
--default_table_expiration 0 \
--dataset ${{ env.BIGQUERY_DATASET }}
else
echo "Big Query Dataset : ${{ env.BIGQUERY_DATASET }} already exists" !
fi
- name: Create Big Query table
run: |-
TABLE_NAME_CUSTOMER=${{ env.BIGQUERY_DATASET}}.${{ env.BIGQUERY_TABLE_CUSTOMER}}
c=0
for table in $(bq ls --max_results 1000 "${{ secrets.PROJECT_ID}}:${{ env.BIGQUERY_DATASET}}" | tail -n +3 | awk '{print }'); do
# Determine the table type and file extension
if bq show --format=prettyjson $BIGQUERY_TABLE_CUSTOMER | jq -r '.type' | grep -q -E "TABLE"; then
echo "Dataset ${{ env.BIGQUERY_DATASET}} already has table named : $table " !
if [ "$table" == "${{ env.BIGQUERY_TABLE_CUSTOMER}}" ]; then
echo "Dataset ${{ env.BIGQUERY_DATASET}} already has table named : $table " !
((c=c+1))
fi
else
echo "Ignoring $table"
continue
fi
done
echo " contador $c "
if [ $c == 0 ]; then
echo "Creating table named : $table for Dataset ${{ env.BIGQUERY_DATASET}} " !
bq mk --table \
$TABLE_NAME_CUSTOMER \
./big_query_schemas/customer_schema.json
fi
deploy-composer-environment
deploy-composer-environment:
needs: [enable-services, deploy-buckets, deploy-cloud-function, deploy-composer-service-account, deploy-bigquery-dataset-bigquery-tables ]
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
timeout-minutes: 40
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Authorize GCP
uses: 'google-github-actions/auth@v2'
with:
credentials_json: ${{ secrets.GCP_DEVOPS_SA_KEY }}
# Step to Authenticate with GCP
- name: Set up Cloud SDK
uses: google-github-actions/setup-gcloud@v2
with:
version: '>= 363.0.0'
project_id: ${{ secrets.PROJECT_ID }}
# Step to Configure Docker to use the gcloud command-line tool as a credential helper
- name: Configure Docker
run: |-
gcloud auth configure-docker
# Create composer environments
- name: Create composer environments
run: |-
if ! gcloud composer environments list --project=${{ secrets.PROJECT_ID }} --locations=${{ env.REGION }} | grep -i ${{ env.COMPOSER_ENV_NAME }} &> /dev/null; then
gcloud composer environments create ${{ env.COMPOSER_ENV_NAME }} \
--project ${{ secrets.PROJECT_ID }} \
--location ${{ env.REGION }} \
--environment-size ${{ env.COMPOSER_ENV_SIZE }} \
--image-version ${{ env.COMPOSER_IMAGE_VERSION }} \
--service-account ${{ env.SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME }}@${{ secrets.PROJECT_ID }}.iam.gserviceaccount.com
else
echo "Composer environment ${{ env.COMPOSER_ENV_NAME }} already exists!"
fi
# Create composer environments
- name: Create composer variable PROJECT_ID
run: |-
gcloud composer environments run ${{ env.COMPOSER_ENV_NAME }} \
--location ${{ env.REGION}} variables \
-- set PROJECT_ID ${{ secrets.PROJECT_ID }}
- name: Create composer variable REGION
run: |-
gcloud composer environments run ${{ env.COMPOSER_ENV_NAME }} \
--location ${{ env.REGION }} variables \
-- set REGION ${{ env.REGION }}
- name: Create composer variable CLOUD_FUNCTION_1_NAME
run: |-
gcloud composer environments run ${{ env.COMPOSER_ENV_NAME }}\
--location ${{ env.REGION }} variables \
-- set CLOUD_FUNCTION_1_NAME ${{ env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_1_NAME }}
- name: Create composer variable CLOUD_FUNCTION_2_NAME
run: |-
gcloud composer environments run ${{ env.COMPOSER_ENV_NAME }} \
--location ${{ env.REGION }} variables \
-- set CLOUD_FUNCTION_2_NAME ${{ env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_2_NAME }}
- name: Create composer variable CLOUD_FUNCTION_3_NAME
run: |-
gcloud composer environments run ${{ env.COMPOSER_ENV_NAME }} \
--location ${{ env.REGION }} variables \
-- set CLOUD_FUNCTION_3_NAME ${{ env.CLOUD_FUNCTION_3_NAME }}
- name: Create composer variable BUCKET_DATALAKE
run: |-
gcloud composer environments run ${{ env.COMPOSER_ENV_NAME }} \
--location ${{ env.REGION}} variables \
-- set BUCKET_NAME ${{ secrets.BUCKET_DATALAKE }}
- name: Create composer variable TRANSIENT_FILE_PATH
run: |-
gcloud composer environments run ${{ env.COMPOSER_ENV_NAME }} \
--location ${{ env.REGION }} variables \
-- set TRANSIENT_FILE_PATH ${{ env.TRANSIENT_FILE_PATH }}
- name: Create composer variable BRONZE_PATH
run: |-
gcloud composer environments run ${{ env.COMPOSER_ENV_NAME }} \
--location ${{ env.REGION }} variables \
-- set BRONZE_PATH ${{ env.BRONZE_PATH }}
- name: Create composer variable SILVER_PATH
run: |-
gcloud composer environments run ${{ env.COMPOSER_ENV_NAME }} \
--location ${{ env.REGION }} variables \
-- set SILVER_PATH ${{ env.SILVER_PATH }}
- name: Create composer variable REGION_PROJECT_ID
run: |-
gcloud composer environments run ${{ env.COMPOSER_ENV_NAME }} \
--location ${{ env.REGION }} variables \
-- set REGION_PROJECT_ID "${{ env.REGION }}-${{ secrets.PROJECT_ID }}"
- name: Create composer variable BIGQUERY_DATASET
run: |-
gcloud composer environments run ${{ env.COMPOSER_ENV_NAME }} \
--location ${{ env.REGION }} variables \
-- set BIGQUERY_DATASET "${{ env.BIGQUERY_DATASET }}"
- name: Create composer variable BIGQUERY_TABLE_CUSTOMER
run: |-
gcloud composer environments run ${{ env.COMPOSER_ENV_NAME }} \
--location ${{ env.REGION }} variables \
-- set BIGQUERY_TABLE_CUSTOMER "${{ env.BIGQUERY_TABLE_CUSTOMER }}"
deploy-composer-http-connection
deploy-composer-http-connection:
needs: [enable-services, deploy-buckets, deploy-cloud-function, deploy-composer-service-account, deploy-bigquery-dataset-bigquery-tables, deploy-composer-environment ]
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Authorize GCP
uses: 'google-github-actions/auth@v2'
with:
credentials_json: ${{ secrets.GCP_DEVOPS_SA_KEY }}
# Step to Authenticate with GCP
- name: Set up Cloud SDK
uses: google-github-actions/setup-gcloud@v2
with:
version: '>= 363.0.0'
project_id: ${{ secrets.PROJECT_ID }}
# Step to Configure Docker to use the gcloud command-line tool as a credential helper
- name: Configure Docker
run: |-
gcloud auth configure-docker
- name: Create composer http connection HTTP_CONNECTION
run: |-
HOST="https://${{ env.REGION }}-${{ secrets.PROJECT_ID }}.cloudfunctions.net"
gcloud composer environments run ${{ env.COMPOSER_ENV_NAME }} \
--location ${{ env.REGION }} connections \
-- add ${{ env.HTTP_CONNECTION }} \
--conn-type ${{ env.CONNECTION_TYPE }} \
--conn-host $HOST
deploy-dags
deploy-dags:
needs: [enable-services, deploy-buckets, deploy-cloud-function, deploy-composer-service-account, deploy-bigquery-dataset-bigquery-tables, deploy-composer-environment, deploy-composer-http-connection ]
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Authorize GCP
uses: 'google-github-actions/auth@v2'
with:
credentials_json: ${{ secrets.GCP_DEVOPS_SA_KEY }}
# Step to Authenticate with GCP
- name: Set up Cloud SDK
uses: google-github-actions/setup-gcloud@v2
with:
version: '>= 363.0.0'
project_id: ${{ secrets.PROJECT_ID }}
- name: Get Composer bucket name and Deploy DAG to Composer
run: |-
COMPOSER_BUCKET=$(gcloud composer environments describe ${{ env.COMPOSER_ENV_NAME }} \
--location ${{ env.REGION }} \
--format="value(config.dagGcsPrefix)")
gsutil -m cp -r ./dags/* $COMPOSER_BUCKET/dags/
Resources Created After Deployment
After the deployment process is complete, the following resources will be available:
- Cloud Storage Buckets: Organized into Bronze, Silver, and Gold layers.
- Cloud Functions:: Responsible for processing data across the three layers.
- Service Account for Composer:: With appropriate permissions for invoking Cloud Functions.
- BigQuery Dataset and Tables: A DataFrame created for storing processed data.
- Google Composer Environment: Orchestrates the Cloud Functions with daily executions.
- Composer DAG: The DAG manages the workflow that invokes Cloud Functions and processes data.
Conclusion
This solution demonstrates how to leverage Google Cloud Functions, Composer, and BigQuery to create a robust three-tier data processing pipeline. The automation using GitHub Actions ensures a smooth, reproducible deployment process, making it easier to manage cloud-based data pipelines at scale.
References
- Google Cloud Platform Documentation: https://cloud.google.com/docs
- GitHub Actions Documentation:: https://docs.github.com/en/actions
- Google Composer Documentation:: https://cloud.google.com/composer/docs
- Cloud Functions Documentation: https://cloud.google.com/functions/docs
- GitHub Repo: https://github.com/jader-lima/gcp-cloud-functions-to-bigquery
The above is the detailed content of Using Google Cloud Functions for Three-Tier Data Processing with Google Composer and Automated Deployments via GitHub Actions. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 How Do I Use Beautiful Soup to Parse HTML?Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:54 PM
How Do I Use Beautiful Soup to Parse HTML?Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:54 PMThis article explains how to use Beautiful Soup, a Python library, to parse HTML. It details common methods like find(), find_all(), select(), and get_text() for data extraction, handling of diverse HTML structures and errors, and alternatives (Sel
 How to solve the permissions problem encountered when viewing Python version in Linux terminal?Apr 01, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
How to solve the permissions problem encountered when viewing Python version in Linux terminal?Apr 01, 2025 pm 05:09 PMSolution to permission issues when viewing Python version in Linux terminal When you try to view Python version in Linux terminal, enter python...
 Serialization and Deserialization of Python Objects: Part 1Mar 08, 2025 am 09:39 AM
Serialization and Deserialization of Python Objects: Part 1Mar 08, 2025 am 09:39 AMSerialization and deserialization of Python objects are key aspects of any non-trivial program. If you save something to a Python file, you do object serialization and deserialization if you read the configuration file, or if you respond to an HTTP request. In a sense, serialization and deserialization are the most boring things in the world. Who cares about all these formats and protocols? You want to persist or stream some Python objects and retrieve them in full at a later time. This is a great way to see the world on a conceptual level. However, on a practical level, the serialization scheme, format or protocol you choose may determine the speed, security, freedom of maintenance status, and other aspects of the program
 Mathematical Modules in Python: StatisticsMar 09, 2025 am 11:40 AM
Mathematical Modules in Python: StatisticsMar 09, 2025 am 11:40 AMPython's statistics module provides powerful data statistical analysis capabilities to help us quickly understand the overall characteristics of data, such as biostatistics and business analysis. Instead of looking at data points one by one, just look at statistics such as mean or variance to discover trends and features in the original data that may be ignored, and compare large datasets more easily and effectively. This tutorial will explain how to calculate the mean and measure the degree of dispersion of the dataset. Unless otherwise stated, all functions in this module support the calculation of the mean() function instead of simply summing the average. Floating point numbers can also be used. import random import statistics from fracti
 How to Perform Deep Learning with TensorFlow or PyTorch?Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:52 PM
How to Perform Deep Learning with TensorFlow or PyTorch?Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:52 PMThis article compares TensorFlow and PyTorch for deep learning. It details the steps involved: data preparation, model building, training, evaluation, and deployment. Key differences between the frameworks, particularly regarding computational grap
 Scraping Webpages in Python With Beautiful Soup: Search and DOM ModificationMar 08, 2025 am 10:36 AM
Scraping Webpages in Python With Beautiful Soup: Search and DOM ModificationMar 08, 2025 am 10:36 AMThis tutorial builds upon the previous introduction to Beautiful Soup, focusing on DOM manipulation beyond simple tree navigation. We'll explore efficient search methods and techniques for modifying HTML structure. One common DOM search method is ex
 What are some popular Python libraries and their uses?Mar 21, 2025 pm 06:46 PM
What are some popular Python libraries and their uses?Mar 21, 2025 pm 06:46 PMThe article discusses popular Python libraries like NumPy, Pandas, Matplotlib, Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, Django, Flask, and Requests, detailing their uses in scientific computing, data analysis, visualization, machine learning, web development, and H
 How to Create Command-Line Interfaces (CLIs) with Python?Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
How to Create Command-Line Interfaces (CLIs) with Python?Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:48 PMThis article guides Python developers on building command-line interfaces (CLIs). It details using libraries like typer, click, and argparse, emphasizing input/output handling, and promoting user-friendly design patterns for improved CLI usability.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)




