Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >How SafeLine Shields Your Website with Advanced Dynamic Protection
How SafeLine Shields Your Website with Advanced Dynamic Protection
- PHPzOriginal
- 2024-08-22 18:40:331014browse
Developed over the past decade by Chaitin Tech, SafeLine is a state-of-the-art Web Application Firewall (WAF) that utilizes advanced semantic analysis algorithms to provide top-tier protection against online threats. Known and trusted in professional cybersecurity circles, SafeLine has established itself as a reliable choice for securing websites.
The SafeLine Community Edition is derived from the enterprise-grade Ray Shield product. By removing the complex features designed for large enterprises, it offers a more accessible WAF solution with lower hardware requirements and simplified usage, making it ideal for community use. Best of all, it’s available for free.
- Official Website: https://waf.chaitin.com
- GitHub Repository: https://github.com/chaitin/SafeLine
Dynamic Protection: Securing Your Website
SafeLine’s dynamic protection feature adds an extra layer of security to web pages by introducing dynamic characteristics while leaving the content unchanged from the user's perspective. This ensures that even static pages benefit from dynamic encryption, safeguarding them against a wide range of threats.
As a reverse proxy, SafeLine dynamically encrypts all web code that passes through it. This dynamic protection offers several critical benefits:
- Protecting front-end code privacy
- Blocking web crawlers
- Preventing vulnerability scanning
- Thwarting exploit attempts
Example: Dynamic Protection for HTML
Here's how a typical HTML page appears before dynamic protection is applied.
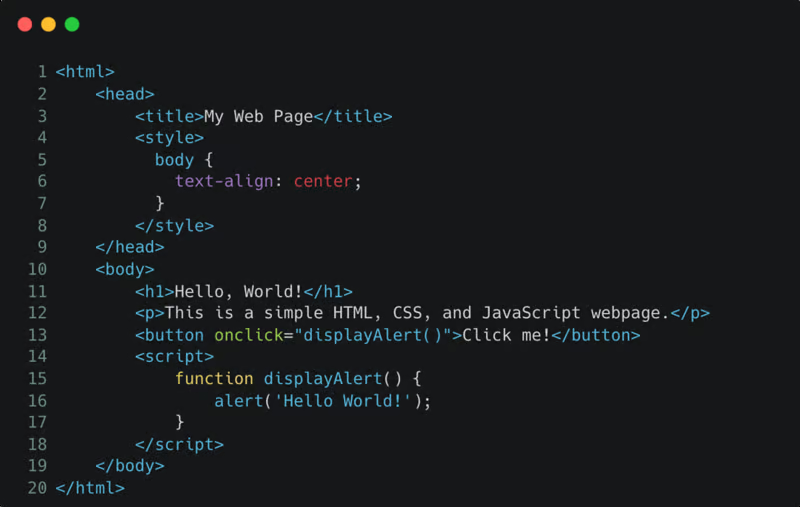
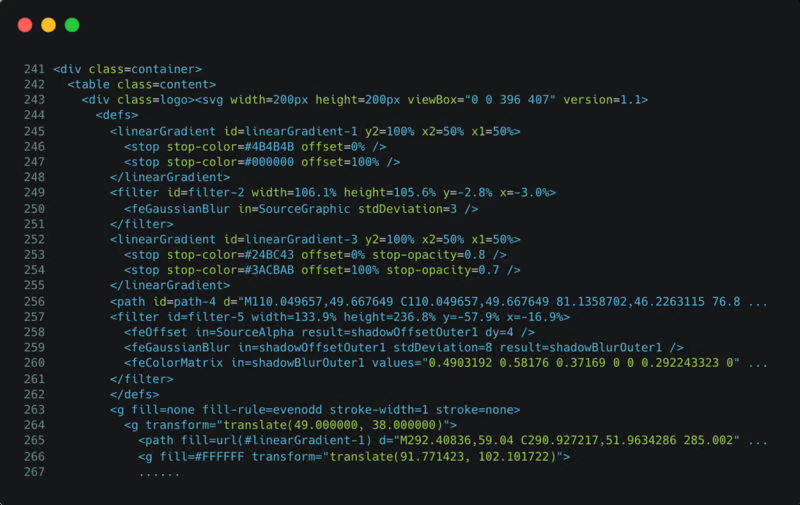
After SafeLine’s dynamic protection is enabled, the HTML code is encrypted and looks like this:
Example: Dynamic Protection for JavaScript
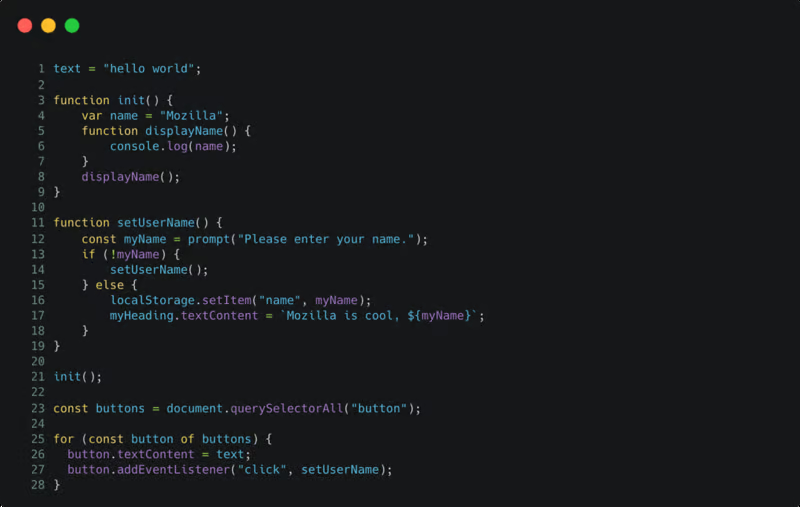
Similarly, this is how JavaScript code might look before applying dynamic protection.
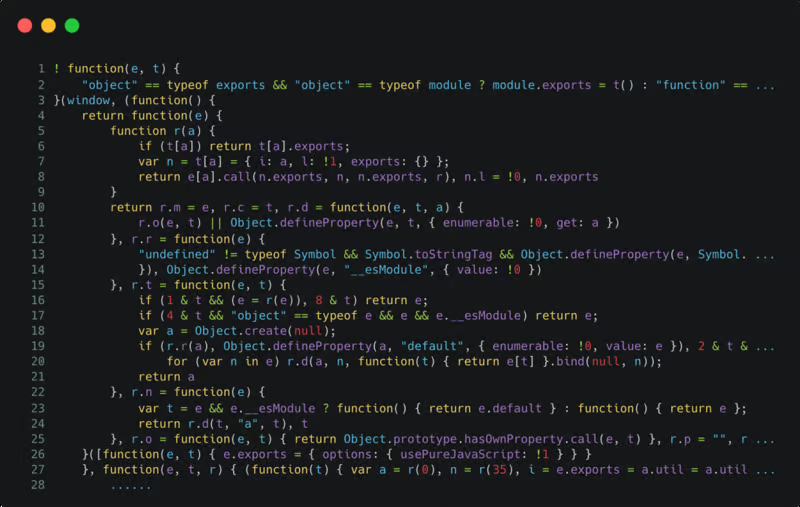
Once SafeLine’s dynamic protection is applied, the JavaScript code is encrypted, as shown below:
With dynamic protection enabled, the HTML and JavaScript code on your website will be dynamically encrypted, changing randomly with each visit. This makes it much harder for crawlers and automated attack tools to exploit your site.
Example: Blocking Crawlers
Consider a scenario where a crawler is designed to scrape critical information from your website. Typically, it would:
- Identify web pages with the target information (e.g., http://ct.cn/info?id=666)
- Send automated requests to retrieve the content
- Parse the HTML structure to extract key information
- Iterate through IDs to gather more data
With dynamic protection enabled, the structure of your web pages becomes randomized, preventing the crawler from functioning effectively.
Example: Defending Against Vulnerability Scanners
SafeLine also defends against web vulnerability scanners, which typically operate by:
- Checking for SQL injection by comparing responses to 1=1 and 1=2 conditions
- Detecting Remote Code Execution (RCE) by searching for specific characters in the web page's response
- Identifying information disclosure by scanning for error messages or sensitive data
- Brute-forcing logins by analyzing response consistency for successful and failed attempts
Dynamic protection ensures that the web page's response content is dynamically encrypted with each visit, disrupting the scanner’s logic and preventing it from accurately identifying vulnerabilities.
The above is the detailed content of How SafeLine Shields Your Website with Advanced Dynamic Protection. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- An in-depth analysis of the Bootstrap list group component
- Detailed explanation of JavaScript function currying
- Complete example of JS password generation and strength detection (with demo source code download)
- Angularjs integrates WeChat UI (weui)
- How to quickly switch between Traditional Chinese and Simplified Chinese with JavaScript and the trick for websites to support switching between Simplified and Traditional Chinese_javascript skills

