scraping or web scraping is a technique used to extract data from websites in an automated manner. It consists of using programs or scripts to navigate a web page, extract specific information (such as text, images, product prices, etc.), and save it.
In this post, I will teach the process I use to do scraping and what important points to keep in mind when doing it.
In my case, I will perform scraping in PcComponentes to collect information about laptops. This data will be used to create a dataset that will serve as the basis for a Machine Learning model, designed to predict the price of a laptop based on the components that are specified.
First, it is necessary to identify which URL the script should access to do the scraping:

In this case, if we look at the PcComponentes URL, we can see that it passes a parameter through the URL, which we can use to specify what we want to search for.
Once this is done, we will see the search result:
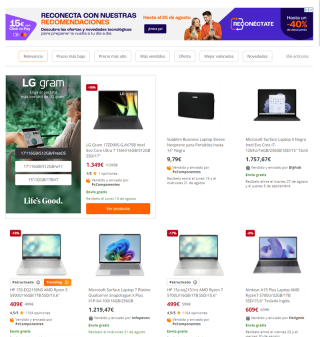
After this, we will use the developer tool that almost all browsers have integrated:
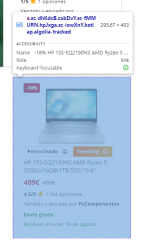
By right-clicking and then selecting the "Inspect" option, the developer tool will open, and we will see the following:

A tag of type anchor () that contains a lot of information regarding the product that we see in the search results.
If we look at the following area, we will see practically all the product data:

Done! We have the area from which to extract the data. Now it's time to create the script to extract them.
But we ran into a problem: if you access PcComponentes directly, it always asks us to accept the cookie policies. So, we can't make a GET request and scraping the result, since we wouldn't get anything.
Therefore, we will have to use Selenium to simulate the browser and be able to interact with it.
We start by doing the following:
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.firefox.options import Options
from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWait
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as EC
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
options = Options()
options.headless = True
#Abrimos el navegador
driver = webdriver.Firefox(options=options)
time.sleep(5)
#Vamos a la página indicada pccomponentes.com/laptops
driver.get(url+str(i))
#Esperamos 30 segundos hasta que aparezca el botón de cookies y al aparecer hace clic
accept_cookies = WebDriverWait(driver, 30).until(
EC.presence_of_element_located((By.ID, 'cookiesAcceptAll'))
)
accept_cookies.click()
#Descargamos el HTML
html = driver.page_source
Once this is done, in the html variable we will obtain the HTML code of the page to scrape.
However, we ran into another problem. When opening the browser with Selenium and making 2 or 3 requests, Cloudflare limits the requests and does not allow us to make more. Therefore, we could only scrape about 3 pages, which would be about 20 different computers. Not enough to make a dataset.
One solution I came up with was to download the page locally and work with the HTML locally. After having done the scraping, we could open another browser (waiting a reasonable amount of time) and download the following one.
So I added the above code to a function and wrapped it in a for as follows:
#Función que se conecta a pccomponentes y guarda el html en local
def guarda_datos_html(i=0):
try:
options = Options()
options.headless = True
#Abrimos el navegador
driver = webdriver.Firefox(options=options)
time.sleep(5)
#Vamos a la página indicada pccomponentes.com/laptops
driver.get(url+str(i))
#Esperamos 30 segundos hasta que aparezca el botón de cookies y al aparecer hace clic
accept_cookies = WebDriverWait(driver, 30).until(
EC.presence_of_element_located((By.ID, 'cookiesAcceptAll'))
)
accept_cookies.click()
#Descargamos el HTML
html = driver.page_source
#Lo guardamos en local
with open(f'html/laptops_{i}.html','w',encoding="utf-8") as document:
document.write(html)
driver.close()
except:
print(f'Error en página: {i}')
for i in range(0,58):
guarda_datos_html(i)
time.sleep(30)
Now we can recover the HTML and work with them. To do this, I installed BeautifulSoup, a package that is very often used in scraping.
We are going to develop the function to collect the information from the HTML that we have downloaded thanks to the previous function.
The function looked like this:
# Función que abre el HTML guardado con anterioridad y filtra los datos
# para guardarlos en un CSV ordenados
def get_datos_html(i=0):
try:
with open(f'laptop_data_actual.csv','a') as ldata:
field = ['Company','Inches','Cpu','Ram','Gpu','OpSys','SSD','Price']
writer = csv.DictWriter(ldata, fieldnames=field)
with open(f'html/laptops_{i}.html','r',encoding="utf-8") as document:
html = BeautifulSoup(document.read(), 'html.parser')
products = html.find_all('a')
for element in products:
pc = element.get('data-product-name')
if pc:
pc = pc.lower()
marca = element.get('data-product-brand')
price = element.get('data-product-price')
pc_data = pc.split('/')
cpu = pc_data[0].split(' ')
cpu = buscar_cpu(cpu)
gpu = buscar_gpu(pc_data)
inches = '.'.join([s for s in re.findall(r'\b\d+\b', pc_data[-1])])
OpSys = bucar_opsys(pc_data, marca)
row = {
'Company': marca,
'Inches': inches,
'Cpu': cpu,
'Ram': pc_data[1],
'Gpu': gpu,
'OpSys': OpSys,
'SSD': pc_data[2],
'Price': price
}
writer.writerow(row)
except:
print(f'Error en página: {i}')
Basically, we open the CSV file where we will save the information, then we tell the CSV what fields we want it to have, and then we read and work with the HTML. As you can see, I had to do some extra functions to be able to extract the necessary information from each field that we want to save in the CSV.
I leave you the complete script here in case you want to try it!
PccomponentsScrapper
The above is the detailed content of How to scrape. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Merging Lists in Python: Choosing the Right MethodMay 14, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Merging Lists in Python: Choosing the Right MethodMay 14, 2025 am 12:11 AMTomergelistsinPython,youcanusethe operator,extendmethod,listcomprehension,oritertools.chain,eachwithspecificadvantages:1)The operatorissimplebutlessefficientforlargelists;2)extendismemory-efficientbutmodifiestheoriginallist;3)listcomprehensionoffersf
 How to concatenate two lists in python 3?May 14, 2025 am 12:09 AM
How to concatenate two lists in python 3?May 14, 2025 am 12:09 AMIn Python 3, two lists can be connected through a variety of methods: 1) Use operator, which is suitable for small lists, but is inefficient for large lists; 2) Use extend method, which is suitable for large lists, with high memory efficiency, but will modify the original list; 3) Use * operator, which is suitable for merging multiple lists, without modifying the original list; 4) Use itertools.chain, which is suitable for large data sets, with high memory efficiency.
 Python concatenate list stringsMay 14, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Python concatenate list stringsMay 14, 2025 am 12:08 AMUsing the join() method is the most efficient way to connect strings from lists in Python. 1) Use the join() method to be efficient and easy to read. 2) The cycle uses operators inefficiently for large lists. 3) The combination of list comprehension and join() is suitable for scenarios that require conversion. 4) The reduce() method is suitable for other types of reductions, but is inefficient for string concatenation. The complete sentence ends.
 Python execution, what is that?May 14, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Python execution, what is that?May 14, 2025 am 12:06 AMPythonexecutionistheprocessoftransformingPythoncodeintoexecutableinstructions.1)Theinterpreterreadsthecode,convertingitintobytecode,whichthePythonVirtualMachine(PVM)executes.2)TheGlobalInterpreterLock(GIL)managesthreadexecution,potentiallylimitingmul
 Python: what are the key featuresMay 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Python: what are the key featuresMay 14, 2025 am 12:02 AMKey features of Python include: 1. The syntax is concise and easy to understand, suitable for beginners; 2. Dynamic type system, improving development speed; 3. Rich standard library, supporting multiple tasks; 4. Strong community and ecosystem, providing extensive support; 5. Interpretation, suitable for scripting and rapid prototyping; 6. Multi-paradigm support, suitable for various programming styles.
 Python: compiler or Interpreter?May 13, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python: compiler or Interpreter?May 13, 2025 am 12:10 AMPython is an interpreted language, but it also includes the compilation process. 1) Python code is first compiled into bytecode. 2) Bytecode is interpreted and executed by Python virtual machine. 3) This hybrid mechanism makes Python both flexible and efficient, but not as fast as a fully compiled language.
 Python For Loop vs While Loop: When to Use Which?May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Python For Loop vs While Loop: When to Use Which?May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMUseaforloopwheniteratingoverasequenceorforaspecificnumberoftimes;useawhileloopwhencontinuinguntilaconditionismet.Forloopsareidealforknownsequences,whilewhileloopssuitsituationswithundeterminediterations.
 Python loops: The most common errorsMay 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Python loops: The most common errorsMay 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMPythonloopscanleadtoerrorslikeinfiniteloops,modifyinglistsduringiteration,off-by-oneerrors,zero-indexingissues,andnestedloopinefficiencies.Toavoidthese:1)Use'i


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use






