The max subarray problem and its history
In the late 1970s, Swedish mathematician Ulf Grenander had been discussing a problem: how can you analyze a 2D array of image data more efficiently than brute force? Computers then were slow and pictures were large relative to the RAM. To exacerbate things, in the worst case scenario brute force took O(n^6) time (sextic time complexity).
First, Grenandier simplified the question: Given just a one dimensional array of numbers, how would you most efficiently find the contiguous subarray with the largest sum?
Brute Force: A Naive Approach with Cubic Time Complexity
Brute force, it would be half as much time to analyze a 1D array as a 2D array, so O(n^3) to examine every possible combination (cubic time complexity).
def max_subarray_brute_force(arr):
max_sum = arr[0] # assumes arr has a length
# iterate over all possible subarrays
for i in range(len(arr)):
for j in range(i, len(arr)):
current_sum = 0
# sum the elements of the subarray arr[i:j+1]
for k in range(i, j + 1):
current_sum += arr[k]
# update max_sum if the current sum is greater
max_sum = max(max_sum, current_sum)
return max_sum
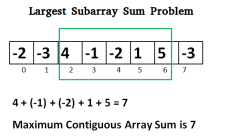
print(max_subarray_brute_force([-2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3]), "== 7")
Grenander’s O(n²) Optimization: A Step Forward
Grenander improved it to O(n^2) solution. I couldn't find his code in my research, but my guess is he simply got rid of the innermost loop that adds up all of the numbers between the two indices. Instead, we can keep a running sum while iterating over the subarray, thus reducing the number of loops from three to two.
def max_subarray_optimized(arr):
max_sum = arr[0] # assumes arr has a length
# iterate over all possible starting points of the subarray
for i in range(len(arr)):
current_sum = 0
# sum the elements of the subarray starting from arr[i]
for j in range(i, len(arr)):
current_sum += arr[j]
# update max_sum if the current sum is greater
max_sum = max(max_sum, current_sum)
return max_sum
Shamos's Divide and Conquer: Splitting the Problem for O(n log n)
Grenander showed the problem to computer scientist Michael Shamos. Shamos thought about it for one night and came up with a divide and conquer method which is O(n log n).
It's quite clever. The idea is to divide the array into two halves, then recursively find the maximum subarray sum for each half as well as the subarray crossing the midpoint.
def max_crossing_sum(arr, left, mid, right):
# left of mid
left_sum = float('-inf')
current_sum = 0
for i in range(mid, left - 1, -1):
current_sum += arr[i]
left_sum = max(left_sum, current_sum)
# right of mid
right_sum = float('inf')
current_sum = 0
for i in range(mid + 1, right + 1):
current_sum += arr[i]
right_sum = max(right_sum, current_sum)
# sum of elements on the left and right of mid, which is the maximum sum that crosses the midpoint
return left_sum + right_sum
def max_subarray_divide_and_conquer(arr, left, right):
# base case: only one element
if left == right:
return arr[left]
# find the midpoint
mid = (left + right) // 2
# recursively find the maximum subarray sum for the left and right halves
left_sum = max_subarray_divide_and_conquer(arr, left, mid)
right_sum = max_subarray_divide_and_conquer(arr, mid + 1, right)
cross_sum = max_crossing_sum(arr, left, mid, right)
# return the maximum of the three possible cases
return max(left_sum, right_sum, cross_sum)
def max_subarray(arr):
return max_subarray_divide_and_conquer(arr, 0, len(arr) - 1)
print(max_subarray([-2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3]), "== 7")
This reduces the time complexity to O(nlogn) time because first the array is divided into two halves (O(logn)) and then finding the max crossing subarray takes O(n)
Kadane’s Algorithm: The Elegant O(n) Solution
Stastician Jay Kadane looked at the code and immediately identified that Shamos's solution failed to use the contiguity restraint as part of the solution.
Here's what he realized
-If an array has only negative numbers, then the answer will always be the single largest number in the array, assuming we're not allowing empty subarrays.
-If an array only has positive numbers, the answer will always be to add up the entire array.
-If you have an array of both positive and negative numbers, then you can traverse the array step by step. If at any point the number you're looking at is bigger than the sum of all the numbers that came before it, the solution cannot include any of the previous numbers. Thus, you start a new sum from the current number, while keeping track of the maximum sum encountered so far.
maxSubArray(nums):
# avoiding type errors or index out of bounds errors
if nums is None or len(nums) == 0:
return 0
max_sum = nums[0] # max sum can't be smaller than any given element
curr_sum = 0
# Kadane's algorithm
for num in nums:
curr_sum = max(num, curr_sum + num)
max_sum = max(curr_sum, max_sum)
return max_sum
What I love about this algorithm is it can be applied to lots of other problems. Try adapting it to solve these LeetCode problems:
Ones and Zeroes
Maximum Sum Circular Subarray
Minimum Size Subarray Sum
Maximum Ascending Subarray Sum
Maximum Product Subarray
Continuous Subarray Sum
Maximum Alternating Sum Subarray (premium)
Max Sum of Rectangle No Larger Than K
The above is the detailed content of max subarray problem and kadane&#s algorithm. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Merging Lists in Python: Choosing the Right MethodMay 14, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Merging Lists in Python: Choosing the Right MethodMay 14, 2025 am 12:11 AMTomergelistsinPython,youcanusethe operator,extendmethod,listcomprehension,oritertools.chain,eachwithspecificadvantages:1)The operatorissimplebutlessefficientforlargelists;2)extendismemory-efficientbutmodifiestheoriginallist;3)listcomprehensionoffersf
 How to concatenate two lists in python 3?May 14, 2025 am 12:09 AM
How to concatenate two lists in python 3?May 14, 2025 am 12:09 AMIn Python 3, two lists can be connected through a variety of methods: 1) Use operator, which is suitable for small lists, but is inefficient for large lists; 2) Use extend method, which is suitable for large lists, with high memory efficiency, but will modify the original list; 3) Use * operator, which is suitable for merging multiple lists, without modifying the original list; 4) Use itertools.chain, which is suitable for large data sets, with high memory efficiency.
 Python concatenate list stringsMay 14, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Python concatenate list stringsMay 14, 2025 am 12:08 AMUsing the join() method is the most efficient way to connect strings from lists in Python. 1) Use the join() method to be efficient and easy to read. 2) The cycle uses operators inefficiently for large lists. 3) The combination of list comprehension and join() is suitable for scenarios that require conversion. 4) The reduce() method is suitable for other types of reductions, but is inefficient for string concatenation. The complete sentence ends.
 Python execution, what is that?May 14, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Python execution, what is that?May 14, 2025 am 12:06 AMPythonexecutionistheprocessoftransformingPythoncodeintoexecutableinstructions.1)Theinterpreterreadsthecode,convertingitintobytecode,whichthePythonVirtualMachine(PVM)executes.2)TheGlobalInterpreterLock(GIL)managesthreadexecution,potentiallylimitingmul
 Python: what are the key featuresMay 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Python: what are the key featuresMay 14, 2025 am 12:02 AMKey features of Python include: 1. The syntax is concise and easy to understand, suitable for beginners; 2. Dynamic type system, improving development speed; 3. Rich standard library, supporting multiple tasks; 4. Strong community and ecosystem, providing extensive support; 5. Interpretation, suitable for scripting and rapid prototyping; 6. Multi-paradigm support, suitable for various programming styles.
 Python: compiler or Interpreter?May 13, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python: compiler or Interpreter?May 13, 2025 am 12:10 AMPython is an interpreted language, but it also includes the compilation process. 1) Python code is first compiled into bytecode. 2) Bytecode is interpreted and executed by Python virtual machine. 3) This hybrid mechanism makes Python both flexible and efficient, but not as fast as a fully compiled language.
 Python For Loop vs While Loop: When to Use Which?May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Python For Loop vs While Loop: When to Use Which?May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMUseaforloopwheniteratingoverasequenceorforaspecificnumberoftimes;useawhileloopwhencontinuinguntilaconditionismet.Forloopsareidealforknownsequences,whilewhileloopssuitsituationswithundeterminediterations.
 Python loops: The most common errorsMay 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Python loops: The most common errorsMay 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMPythonloopscanleadtoerrorslikeinfiniteloops,modifyinglistsduringiteration,off-by-oneerrors,zero-indexingissues,andnestedloopinefficiencies.Toavoidthese:1)Use'i


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)






