 System Tutorial
System Tutorial LINUX
LINUX The regular directory structure of the Linux system, no matter what version of directory you switch between
The regular directory structure of the Linux system, no matter what version of directory you switch betweenAfter we install the Linux system, the Linux system will also manually generate many files and directories like the Windows system. Such directories all contain different meanings. Next, let’s introduce what this kind of directory represents? And, in the command line interfaceWhat are the distribution versions of the Linux operating system, and how do we switch between different directories.
1. Linux system directory structure.
What we introduce here is the regular directory structure of the Linux system. No matter which version of the Linux system What are the distribution versions of the Linux operating system? Red Hat Linux usually includes the following directories.
bin: linux command directory (two's complement). sbin: Linux command directory (used by super administrators), s means SuperUser. boot: Linux startup directory, where the Linux kernel (boot, long/shirt) is stored. dev: Linux storage hardware directory, stored in a concrete file (device device). etc: Linux configuration file directory. lib: Linux system function library file directory, equivalent to the .dll file in window. mnt: Used for linux mounting. The initial version only has this mount. It is recommended to mount additional devices, such as U disks, mobile hard disks and partitions. medie: Used for linux mounting. The system recommends mounting media devices. misc: used for linux mounting. It is recommended to mount the shared directory of the NFS service. opt: Linux small software installation directory. sys: Linux virtual file system, which contains underlying hardware information and is stored in video memory. It mainly stores kernel-related information. tmp: Linux stores temporary files and will be manually deleted regularly. usr: Linux usually default installation directory of applications [unixsoftresource]. var: Linux dynamic data and process change storage location (such as logs, emails, cache, website). home: the home directory of the linux user, and the subdirectory is the folder name with the user name. root: Linux super administrator directory. proc: Linux virtual folder, which exists in the video memory and saves real-time information of the system, such as video memory, CPU and other hardware information.
In fact, different distribution versions may add more or less their own directories.
2. How to switch between directories?
The directory switching command in Linux is basically the same as the command under DOS in Windows system. If you have used DOS, it is not difficult to switch directories under the Linux system.
1. Switch to the current user’s home directory. We only need to enter the following command on the command line interface to switch to the current user's home directory:
cd
At this time, we can see in the command line interface that the current directory is the ~ location, and ~ represents the current user's home directory. As shown on the right:


2. Switch to the specified directory. The following command switches to the /home/ directory using an absolute path.
cd/home
If we are already in a directory, if we want to switch to the same level directory or the same level directory of the upper-level directory, we must use an absolute path. After the commands inside are switched, the current directory is changed to home. As shown on the right:


3. Switch to the previous directory. Switch to the previous directory, that is, switch to the directory before the current directory. The command is as follows:
cd-
Our current directory is home. After entering this command, we will switch back to the current user's home directory. As shown on the right:

4. Switch to the upper level directory. Switch with relative paths. The command is as follows:

cd..
One dot represents your own Linux video, and the two dots here represent the upper-level directory (parent directory). The copy results are as follows:

5. Switch to a subdirectory under the current directory. The following command switches to the gao directory in the current directory.
cdgao
If you want to switch to the home directory of another user, you must be an administrator. Ordinary users do not have this permission. The copy results of the commands inside are as shown on the right:

6. Switch to the root directory. Sometimes, we enter a directory that is quite deep and has several levels. At this time, we can directly return to the Linux root directory through the following command
cd/
The / here represents the root directory of the Linux system, which is also the largest directory of the Linux system. All the directories introduced earlier are stored in this root directory.
Okay, we have systematically introduced the overall directory structure of the Linux system and how to switch between such directories. The operation is very simple, I believe you can easily get started.
The above is the detailed content of The regular directory structure of the Linux system, no matter what version of directory you switch between. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Mastering Text Manipulation With the Sed CommandMar 16, 2025 am 09:48 AM
Mastering Text Manipulation With the Sed CommandMar 16, 2025 am 09:48 AMThe Linux command line interface provides a wealth of text processing tools, one of the most powerful tools is the sed command. sed is the abbreviation of Stream EDitor, a multi-functional tool that allows complex processing of text files and streams. What is Sed? sed is a non-interactive text editor that operates on pipeline inputs or text files. By providing directives, you can let it modify and process text in a file or stream. The most common use cases of sed include selecting text, replacing text, modifying original files, adding lines to text, or removing lines from text. It can be used from the command line in Bash and other command line shells. Sed command syntax sed
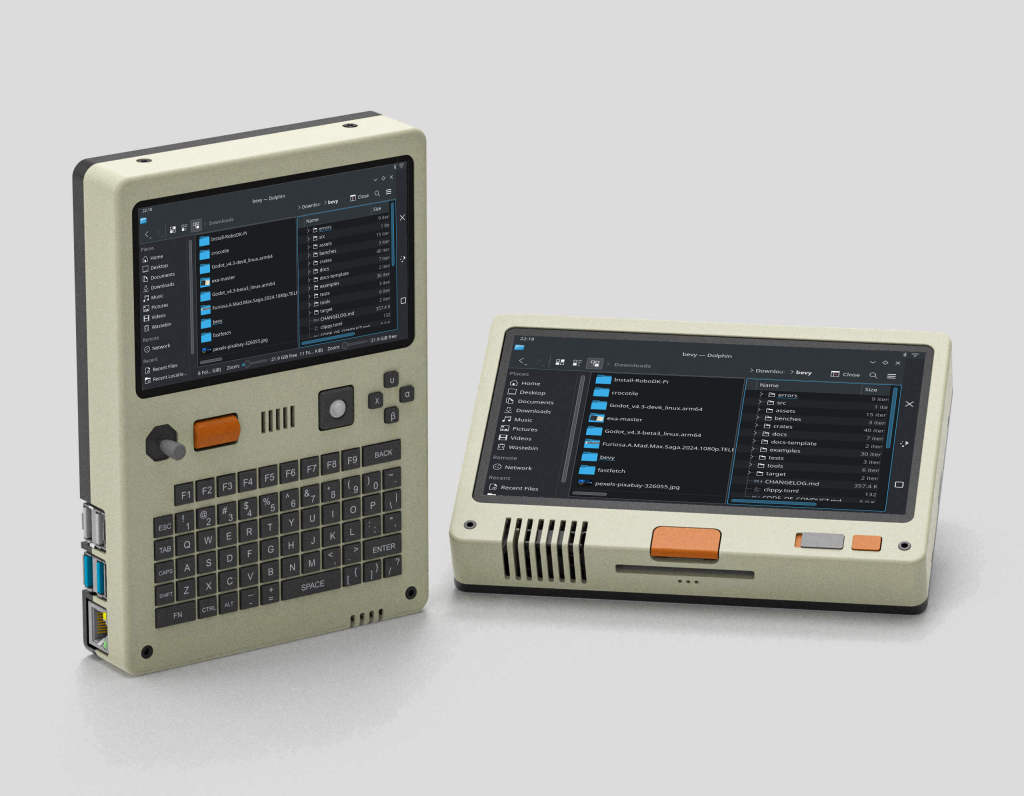 Pilet: A Modular, Portable Mini-Computer Powered by Raspberry PiMar 06, 2025 am 10:11 AM
Pilet: A Modular, Portable Mini-Computer Powered by Raspberry PiMar 06, 2025 am 10:11 AMDiscover Pilet: A Retro-Futuristic, Open-Source Mini-Computer Looking for a mini-computer that blends classic style with cutting-edge technology? Meet Pilet, a modular, open-source marvel powered by the Raspberry Pi 5. Boasting a 7-hour battery life
 How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's GuideMar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's GuideMar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AMEfficiently Counting Files and Folders in Linux: A Comprehensive Guide Knowing how to quickly count files and directories in Linux is crucial for system administrators and anyone managing large datasets. This guide demonstrates using simple command-l
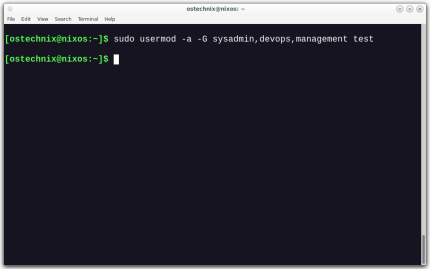 How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In LinuxMar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In LinuxMar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AMEfficiently managing user accounts and group memberships is crucial for Linux/Unix system administration. This ensures proper resource and data access control. This tutorial details how to add a user to multiple groups in Linux and Unix systems. We
 The Secret Weapon to Supercharge Your Linux System With Liquorix KernelMar 08, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
The Secret Weapon to Supercharge Your Linux System With Liquorix KernelMar 08, 2025 pm 12:12 PMLiquorix kernel: a powerful tool to improve Linux system performance Linux is known for its flexibility, security and high performance, becoming the operating system of choice for developers, system administrators, and advanced users. However, the universal Linux kernel is not always meeting the needs of users seeking maximum performance and responsiveness. This is where the Liquorix kernel comes into play—a performance-optimized alternative that promises to enhance your Linux system. This article will explore what the Liquorix kernel is, why you might want to use it, and how to install and configure it to get the most out of your system. Liquorix kernel detailed explanation Liquorix kernel is a precompiled Linux kernel designed for
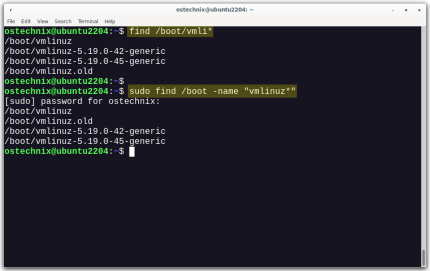 How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From CommandlineMar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From CommandlineMar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AMLinux Kernel is the core component of a GNU/Linux operating system. Developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991, it is a free, open-source, monolithic, modular, and multitasking Unix-like kernel. In Linux, it is possible to install multiple kernels on a sing
 How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu LinuxMar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu LinuxMar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AMThis brief guide explains how to type Indian Rupee symbol in Linux operating systems. The other day, I wanted to type "Indian Rupee Symbol (₹)" in a word document. My keyboard has a rupee symbol on it, but I don't know how to type it. After
 How To Keep Your Linux System Awake With Keep-AliveMar 06, 2025 am 11:13 AM
How To Keep Your Linux System Awake With Keep-AliveMar 06, 2025 am 11:13 AMKeep your computer awake effortlessly with Keep-Alive! This lightweight tool prevents your system from sleeping, ideal for long downloads, continuous processes, or simply maintaining system activity. Compatible with Linux, macOS, and Windows, Keep-


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.





