 Computer Tutorials
Computer Tutorials Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Computer host case, is it better to have a large case or a small case?
Computer host case, is it better to have a large case or a small case?For computer hosts, choosing the appropriate chassis size is crucial. Large chassis and small chassis each have their own advantages and disadvantages, depending on the needs of the user. PHP editor Baicao will delve into the advantages and disadvantages of large chassis and small chassis to help everyone make a wise choice.

#Computer host chassis, is it better to have a large chassis or a small chassis?
Large chassis are better and have better heat dissipation. If the chassis is too small, there are restrictions on the choice, and the backline cannot be used
A chassis like the Patriot Dawn X chassis is also good.
Is it better to have a large computer host or a small chassis?
Computer host large chassis and small chassis have their own advantages and disadvantages, mainly depending on your needs.
The advantage of a large chassis is that it has a large capacity, can accommodate more hardware, can install more memory modules, larger graphics cards, and more cooling fans, and the internal space is larger, making it easier to dissipate heat. And maintenance.
The advantage of a small case is that it is more portable and can be placed on a desk without taking up too much space. Moreover, most small cases can be equipped with hardware that meets daily use, and the price will be more affordable than a large case. .
In short, if your needs are not high, such as playing games, browsing the web, etc., you can choose a small chassis, which can save space and the price is more affordable; if you need to install multiple hardware, then a large chassis is the best option A better choice because it has more internal space for more hardware and is easier to dissipate and maintain.
Recommended for installing in a small case?
Although desktop computers have many advantages over gaming laptops in terms of performance, scalability, heat dissipation, etc., the biggest problem is that they are one big, two thick, and bulky, making it even more difficult to move them around. This time, we specially selected five mini-ITX small cases, especially most of them support SFX specification small power supplies, which reduces the size of the case and makes the internal space more generous, making it easier to move. DIYing a mini-ITX platform desktop is much more fun than ATX platform.
Lian Li’s pure aluminum chassis has always been the benchmark for workmanship in the industry. Although this PC-TU100B is compact, it also inherits its consistent texture advantages. In addition, the PC-TU100 series has a handle on the top, which means that this chassis was originally designed for mobility. In addition to the PC-TU100 that supports SFX, there is also the PC-TU200 that supports ordinary power supply specifications.
JONSBO U1-PLUS ITX Chassis JONSBO U1-PLUS ITX Chassis 10L is a small ITX steel cannon chassis with small size, good workmanship and tempered side transparent side. It can accommodate Ryzen 7 1700 overclocked to 3.7G or 1700X default frequency. The graphics card can be installed with GTX 1070 AERO ITX configuration, plus two large-capacity 2.5-inch SSDs and M.2 SSDs. Except that it does not support water cooling, it can be said to be a pretty good ITX small steel cannon with a short graphics card. However, there is room for improvement due to the exhaust fan mounting holes and wiring originally designed by the manufacturer.
JONSBO JONSBO's chassis is more cost-effective than many major chassis brands. It has a price advantage while also ensuring good quality, which is quite commendable. U1-PLUS supports SFX small power supply, which also allows the chassis size to be well controlled. The measurements are only 220mm × 170mm × 302mm. However, please note that the graphics card only supports lengths within 190mm.
Is it better to host a computer with a large chassis or a small chassis?
The big chassis is good. Generally speaking, small cases are lightweight and easy to carry, while large cases are more expandable. Mini-ITX motherboards are often chosen for small cases. Not only are they expensive, but heat dissipation is also a problem. Large chassis can be adapted to various types of motherboards, and the matching RGB fans require a larger area to achieve good visual effects.
In terms of appearance, there are many small chassis that look good, and they are on par with many large chassis.
To summarize, if it needs to be portable, you can consider a small chassis. If you pursue ultimate performance and your budget is not very high, you can choose a large chassis.
Small chassis is better than small chassis, and big chassis is better. The small one can be placed on a table, and the more sophisticated one can be used as furniture. The large one has a lot of space and is easy to install. You don’t need to calculate and throw it into a corner. You don’t have to worry about its appearance. It has many hard disk slots and supports a large motherboard. It may have better scalability and upgradeability.
Change the computer host into a smaller case?
Computer motherboards mainly include ATX, MATX, MINI ATX, etc., with different sizes.
Whether it can be replaced depends on whether the original motherboard is a large board or a small board.
Large chassis can be equipped with large motherboards or small motherboards. Small cases can only accommodate small motherboards.
How to assemble a small main chassis?
The steps for assembling a small computer case can be briefly summarized as follows:
1. Preparation:
- Make sure you have all the parts you need, including motherboard, CPU, Memory, hard drive, power supply, graphics card, etc.
- Clear the work area and ensure the desktop is clear and spacious for assembly work.
- Read and accurately follow the operating manuals and instructions for the main chassis and other hardware devices.
2. Install the motherboard:
- Insert the motherboard into the main chassis and align it with the input/output connectors on the back panel of the main chassis.
- Use screws to secure the motherboard, usually low-profile screws to the corners of the motherboard. Make sure the screws are not too tight to avoid damaging the motherboard.
3. Install the CPU, memory and graphics card:
- Install the CPU into the CPU slot of the motherboard according to the instructions in the motherboard manual.
- Install the memory module into the memory slot of the motherboard.
- If necessary, install the graphics card into the PCIe slot on the motherboard.
4. Install the hard drive and other devices:
- Install the hard drive or SSD into the hard drive compartment of the main chassis and secure it with screws.
- Connect data and power cables to hard drives and other devices. Make sure the connection is correct and fastened reliably.
5. Connect the power supply:
- Install the power supply into the main chassis and secure it with screws.
- According to the needs of each hardware device, connect the appropriate power cord to the motherboard, graphics card, hard disk and other components.
6. Connect other accessories:
- Connect external devices such as monitors, keyboards, mice, and audio devices.
7. Verify and organize:
- Double-check all components and connections to make sure they are securely and correctly installed.
- Organize electrical and data cables so they are neat and orderly to provide better air flow and cooling.
8. Perform the first power-on test:
- Connect the power supply and start the computer, enter the BIOS interface for settings and verification.
- If everything is fine, you can proceed with installing the operating system and other required software.
Please note that the above is a brief overview and each host chassis and hardware device may have some specific details and differences. Therefore, before assembly, be sure to read and follow the operating manual and guidelines for each hardware device to ensure the assembly process is completed correctly and safely.
How to disassemble the computer main box?
The steps to disassemble the computer main case are as follows: 1. First, turn off the computer and disconnect the power cord to ensure that the computer is completely powered off. 2. Open the side panel on the main chassis. The side panels are usually fixed with screws, which can be removed using a screwdriver. 3. Once all the screws are removed, the side panel will usually have a handle or retaining buckle, use your hands to gently pull out the side panel. 4. After disassembling the main case, you will be able to see the motherboard, hard drive, fan, power supply and other computer components. Please note that when disassembling the computer case, be careful and avoid touching metal parts to prevent damage caused by static electricity. If you are not sure how to proceed, it is recommended to seek professional help.
How to place the computer main box?
First point: The computer host should avoid being placed in a dark and humid place, because in this case, the electronic components in the chassis will easily accelerate oxidation, which is very detrimental to the computer.
Second point: Don’t put it next to the stove in winter. I believe that few people use stoves. Most of them use ovens. Don’t put the computer host too close. It will still have an impact on the computer. .
The third point: Do not put it in the vent. The purpose of this is to ensure that dust does not enter the chassis.
The fourth point: It is best to buy a computer desk and put it on the shelf of the computer desk. This way it does not take up space, and it is convenient for dust to enter. It also solves the problem of dust. It can be said to kill two birds with one stone.
How to disassemble the computer main case?
First we need to power off the main chassis and unplug all the lines from the main chassis. It is very dangerous to disassemble the machine while the power is on. Then we unscrew the two large screws at the back so that we can take off the back cover of the main case.
3. Next we can remove the memory. We only need to unlock the memory module on both sides to take out the memory module.
4. Then we will dismantle the hard drive of the main chassis underground. We first unplug all the two wires of the hard drive, and then unscrew the screws that fix the hard drive.
5. After removing the hard drive, you can then remove the computer’s CPU. When removing the CPU, we must first remove its fan so that we can remove the CPU smoothly. If you need to install it, you must not forget to install the computer CPU fan.
6. Now there is basically only one optical drive left. We unscrew the screws at both ends of the optical drive and remove the optical drive. After the above steps, the disassembly of the main chassis is basically completed.
Is the main computer case better?
Currently there are several materials, iron plate (steel plate), acrylic, aluminum plate, and plastic. Low-end chassis are all made of iron plate (steel plate), and some high-end ones are also made of steel plate, but the workmanship is very different, and the accessories are also different.
Aluminum chassis is mid-to-high-end, generally has good workmanship, and the price is higher. Acrylic is mainly used for side transparency, and is used in both high-end and low-end products, but it is not the main material. Plastic is generally used as chassis parts and not as the main material. But the chassis is generally made of more than one material.
Generally speaking, aluminum chassis is better, but materials such as steel plate, plastic, and acrylic are also used. The material thickness, workmanship, design, and configuration are the comprehensive reflection of the value of the chassis.
The above is the detailed content of Computer host case, is it better to have a large case or a small case?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 What if KB5055683 Fails to Install? Here Are Some FixesApr 21, 2025 pm 08:03 PM
What if KB5055683 Fails to Install? Here Are Some FixesApr 21, 2025 pm 08:03 PMThe KB5055683 cumulative update is designed to improve the quality and reliability of .NET Framework 3.5, 4.8 and 4.8.1 in Windows 10 systems. If you encounter the failure of KB5055683 installation, how to solve it? This article will provide effective solutions. Windows 10 KB5055683 Update KB5055683 is a cumulative update for .NET Framework 3.5, 4.8 and 4.8.1 for Windows 10 22H2 versions, released on April 8, 2025. This update contains all security improvements from previous versions, but no new security improvements were added. It is recommended that you download and install KB50 as soon as possible
 Fresh Guide! Fix REMATCH A D3D12-compatible GPU ErrorApr 21, 2025 pm 08:01 PM
Fresh Guide! Fix REMATCH A D3D12-compatible GPU ErrorApr 21, 2025 pm 08:01 PMEncountering the REMATCH D3D12-compatible GPU error on Windows? This guide provides solutions to get you back in the game. REMATCH, a multiplayer online football game, requires a graphics card supporting DirectX 12 (Feature Level 12.0, Shader Model
 Clone a Hard Drive Without OS, Watch Pro Guide with Easy StepsApr 21, 2025 am 10:24 AM
Clone a Hard Drive Without OS, Watch Pro Guide with Easy StepsApr 21, 2025 am 10:24 AMThis guide shows you how to clone a hard drive even if your Windows system won't boot. MiniTool ShadowMaker simplifies this process. Windows boot failures are common, caused by issues like corrupted system files or MBR errors. Cloning your hard dri
 League of Legends Play Button Not Working on PC: ResolvedApr 21, 2025 am 10:09 AM
League of Legends Play Button Not Working on PC: ResolvedApr 21, 2025 am 10:09 AMThe League of Legends game buttons do not work properly, resulting in the inability to enter the game? don’t worry! This guide will guide you to solve this problem quickly and effectively, allowing you to easily resume the game. Just follow the steps below to quickly resolve the game button issue! Quick navigation: League of Legends game buttons don't work How to fix League of Legends game buttons not working on PC Summarize League of Legends game buttons don't work As a MOBA game, League of Legends continues to attract global players and has a huge and stable player group. To enhance the gaming experience, Riot Games regularly releases updates to introduce new content, but this doesn't always go smoothly. Sometimes, some accidental technical failures may occur after a new update, such as League of Legends games
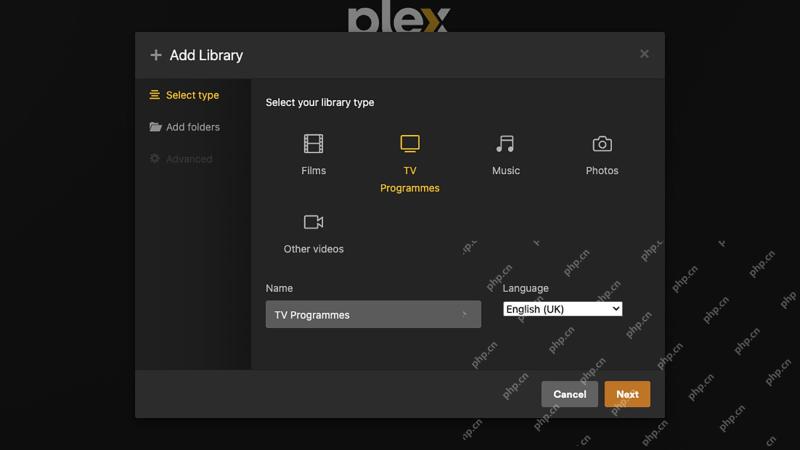 How to use Plex to create your own private Netflix or SpotifyApr 20, 2025 am 10:13 AM
How to use Plex to create your own private Netflix or SpotifyApr 20, 2025 am 10:13 AMBuild Your Own Streaming Service with Plex: A Step-by-Step Guide We're accustomed to on-demand content at our fingertips, thanks to services like Netflix and Spotify. However, building a personal media library offers unique advantages: ownership and
 Spotlight on How to Fix Taskbar Search Bar Blank Box on WindowsApr 19, 2025 pm 08:06 PM
Spotlight on How to Fix Taskbar Search Bar Blank Box on WindowsApr 19, 2025 pm 08:06 PMTroubleshooting a Blank Windows 11/10 Taskbar Search Box A blank search bar in Windows 10 or 11 severely impacts usability. This guide offers solutions to resolve this common issue, preventing you from easily searching for apps and files. The Proble
 How to Fix Forever Skies Crashing? Try the 6 Effortless WaysApr 19, 2025 pm 08:01 PM
How to Fix Forever Skies Crashing? Try the 6 Effortless WaysApr 19, 2025 pm 08:01 PMEncountering crashes in Forever Skies? This guide offers solutions to get your game running smoothly. We'll cover troubleshooting steps for crashes on startup and provide fixes for common causes. Forever Skies Crashes at Startup: Common Causes Fore
 Device Manager Is Blank or Not Showing Anything? Fix It NowApr 19, 2025 pm 06:02 PM
Device Manager Is Blank or Not Showing Anything? Fix It NowApr 19, 2025 pm 06:02 PMTroubleshooting a Blank Device Manager in Windows Device Manager, a crucial Windows utility for managing hardware, can sometimes fail to display any content. This issue, often caused by disabled services or registry permission problems, can lead to v


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor





