Simple form
Sort, display a certain column, read local data
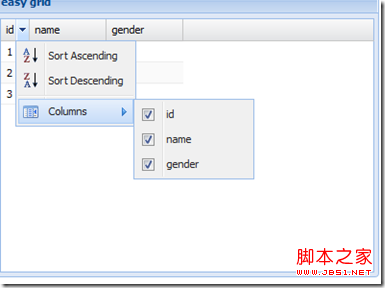
//Local data
var datas = [
['1', 'gao', 'man'], ['2', 'gao', 'man'], ['3', 'gao', 'man']
];
//Create panel
Ext.create('Ext.grid.Panel', {
title: 'easy grid',
width: 400,
height: 300,
renderTo: Ext.getBody(),
frame: true,
viewConfig: {
forceFit: true,
stripRows: true
},
store: {//Configuration data proxy
fields: ['id', 'name', 'gender'],
proxy: {
type: 'memory',
data: datas,
reader: 'array' //The data reader reads data
},
autoLoad: true
},
columns: [{ //Custom column information
header: 'id' ,
width: 30,
dataIndex: 'id', //Fields in bound fields
sortable: true
}, {
header: 'name',
width : 80,
dataIndex: 'name',
sortable: true
}, {
header: 'gender',
width: 80,
dataIndex: 'gender',
sortable: true
}
]
})
Table column:
row number, bool row conversion, date format formatted output (date, top day), number data type formatted output (change, volume), Action column (operation column)
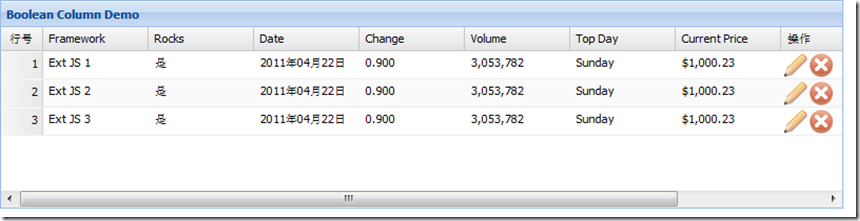
Code;
Ext.tip.QuickTipManager.init ();
Ext.create('Ext.data.Store', {
storeId: 'sampleStore',
fields: [{
name: 'framework',
type: ' string'
}, {
name: 'rocks',
type: 'boolean'
}, {
name: 'volume',
type: 'number'
}, {
name: 'topday',
type: 'date'
}, {
name: 'change',
type: 'number'
}, {
name: 'date',
type: 'date'
}, {
name: 'price',
type: 'number'
}
],
data: {
'items': [{
"framework": "Ext JS 1",
"rocks": true,
"symbol": "goog",
"date": '2011/04/22',
"change": 0.8997,
"volume": 3053782,
"topday": '04/11/2010',
"price": 1000.23
}, {
"framework": "Ext JS 2",
"rocks": true,
"symbol": "goog",
"date": '2011/04/22',
"change": 0.8997,
"volume": 3053782,
"topday": '04/11/2010',
" price": 1000.23
}, {
"framework": "Ext JS 3",
"rocks": true,
"symbol": "goog",
" date": '2011/04/22',
"change": 0.8997,
"volume": 3053782,
"topday": '04/11/2010',
"price" : 1000.23
}]
},
proxy: {
type: 'memory',
reader: {
type: 'json',
root: 'items'
}
}
});
Ext.create('Ext.grid.Panel', {
title: 'Boolean Column Demo',
store: Ext.data.StoreManager.lookup('sampleStore'),
columns: [
Ext.create('Ext.grid.RowNumberer', { text: 'Row Number', width: 40 }),
{
text: 'Framework',
dataIndex: 'framework',
width: 100
}, {
xtype: 'booleancolumn',
text: 'Rocks ',
trueText: 'Yes',
falseText: 'No',
dataIndex: 'rocks'
}, {
text: 'Date',
dataIndex: 'date ',
xtype: 'datecolumn',
format: 'Y year m month d day'
}, {
text: 'Change',
dataIndex: 'change',
xtype: 'numbercolumn',
format: '0.000'
}, {
text: 'Volume',
dataIndex: 'volume',
xtype: 'numbercolumn',
format: '0,000'
}, {
text: 'Top Day',
dataIndex: 'topday',
xtype: 'datecolumn',
format: 'l'
}, {
text: 'Current Price',
dataIndex: 'price',
renderer: Ext.util.Format.usMoney
}, {
header: 'Operation',
xtype: 'actioncolumn', //Action column
width: 100,
items: [{
icon: 'e.gif', //Edit image address
tooltip : 'Edit', //To use this function for text displayed by mouseover, Ext.tip.QuickTipManager.init();
handler: function (grid, rowIndex, colIndex) {
var rec = grid.getStore ().getAt(rowIndex);
alert("Edit " rec.get('framework'));
}
}, {
icon: 'd.gif',
tooltip: 'Delete',
handler: function (grid, rowIndex,
colIndex) {
var rec = grid.getStore().getAt(rowIndex);
alert("Terminate " rec. get('framework'));
}
}]
}, {
}
],
height: 200,
width: 800,
renderTo: Ext.getBody()
});
The picture below is the details of the callback function triggered by clicking the operation (edit, delete) button.
The following demonstrates the custom rendering function
Effect: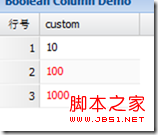
Ext.tip.QuickTipManager.init();
function customFunction(value, metadata) {
if (value > 10) {
metadata.style = 'color:red';
}
return value;
}
Ext.create('Ext.data.Store', {
storeId: 'sampleStore',
fields: [ {
name: 'custom',
type: 'number'
}
],
data: {
'items': [{
"custom": 10
} , {
"custom": 100
}, {
"custom": 1000
}]
},
proxy : {
type: 'memory',
reader: {
type: 'json',
root: 'items'
}
}
});
Ext.create('Ext.grid.Panel', {
title: 'Boolean Column Demo',
store: Ext.data.StoreManager.lookup('sampleStore'),
columns : [
Ext.create('Ext.grid.RowNumberer', { text: 'RowNumber', width: 40 }),
{
text: 'custom',
dataIndex: ' custom',
renderer: customFunction //Call custom function to render
}
],
height: 200,
width: 800,
renderTo: Ext.getBody()
});
Selection mode: Selection
Selection modes are divided into three categories:
1, row selection (default)
2. Cell selection
3. Checkbox selection (checkbox group)
Demo cell selection code:

Just add
tbar: [
{
text: 'Get the selected cell',
handler: function () {
var cell = grid.getSelectionModel().getCurrentPosition(); / /getSelectionModel() gets the current selection mode, getCurrentPosition() gets the currently selected cell
alert(Ext.JSON.encode(cell));
}
}
],
selType :'cellmodel' //Set the selection mode to cell selection
row selection:
Effect: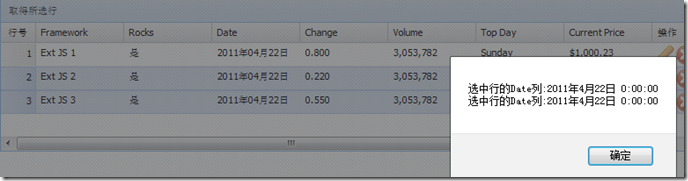
tbar: [
{
text: 'Get the selected rows',
handler: function () {
var rows = grid.getSelectionModel().getSelection(); //getSelection(); Get the currently selected record array
var msg = [];
for (var i = 0; i
var row = rows[i];
var myDate = new Date(row .get('date'));
msg.push('Date column of selected row:' myDate.toLocaleString()); //Convert time format
}
alert(msg. join('n'));
}
}
],
selType: 'rowmodel', //The selection mode is row selection
simpleSelect: true, //Simple Enable selection function
multiSelect: true, // Enable multi-line selection
enableKeyNav: true //Enable keyboard navigation
Check box selection:
Effect:
tbar: [
var rows = grid.getSelectionModel().getSelection(); //getSelection(); Get the currently selected record array
var msg = []; For (var i = 0; i
var row = rows[i];
var myDate = new Date(row.get('date'));
var s = grid.getstore (); // Get the data source of grid
var number = s.indexof (row) 1; // Get line number 1 because the line number starts from 0
msg.push('Select the Date column of row 'number':' myDate.toLocaleString());
simpleSelect: true, //Simple selection function is turned on
multiSelect: true, / / Enable multi-line selection enableKeyNav: true //Enable keyboard navigation
Table feature: Feature
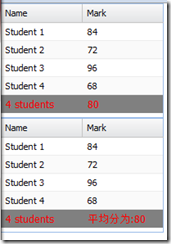
Table summary Ext.grid.feature.Summary
Summary value calculation is calculated based on each column of the table. The calculation method is determined by the specified summaryType. The default is
5 types in the picture above.
This example applies sum and average

Copy code
 The code is as follows:
The code is as follows:
Ext.define('TestResult', {
extend: 'Ext.data.Model',
fields: ['student', {
name: 'mark',
type: 'int'
}]
});
var grid = Ext.create('Ext.grid.Panel', {
width: 200,
height: 140,
renderTo: document.body,
features: [{
ftype: 'summary'
}],
store: {
model: 'TestResult',
data: [{
student: 'Student 1',
mark: 84
}, {
student: 'Student 2',
mark: 72
}, {
student: 'Student 3',
mark: 96
}, {
student: 'Student 4',
mark: 68
}]
},
columns: [{
dataIndex: 'student',
text: 'Name',
summaryType: 'count', //进行汇总的列名
summaryRenderer: function (value) {
grid.getStore()
return Ext.String.format('{0} student{1}', value, value !== 1 ? 's' : '');
}
}, {
dataIndex: 'mark',
text: 'Mark',
summaryType: 'average'
}]
})
var grid = Ext.create('Ext.grid.Panel', {
width: 200,
height: 140,
renderTo: document.body,
features: [{
ftype: 'summary'
}],
store: {
model: 'TestResult',
data: [{
student: 'Student 1',
mark: 84
}, {
student: 'Student 2',
mark: 72
}, {
student: 'Student 3',
mark: 96
}, {
student: 'Student 4',
mark: 68
}]
},
columns: [{
dataIndex: 'student',
text: 'Name',
summaryType: 'count', //进行汇总的列名
summaryRenderer: function (value) {
// grid.getStore()
return Ext.String.format('{0} student{1}', value, value !== 1 ? 's' : '');
}
}, {
dataIndex: 'mark',
text: 'Mark',
summaryType: 'average',
,
summaryRenderer: function (value) {
{0}', value);
Table grouping: Ext.grid.feature.Grouping
Code: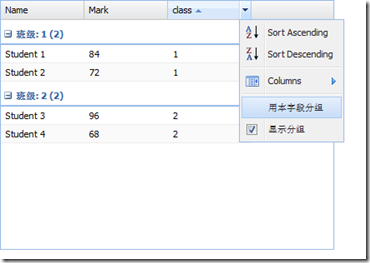
name: 'mark',
type: 'int'
}]
});
var grid = Ext.create('Ext.grid.Panel', {
width: 400,
height: 300,
renderTo: document .body,
features: [
Ext.create('Ext.grid.feature.Grouping',
{
groupByText: 'Group by this field',
showGroupsText: 'Display group',
groupHeaderTpl: 'Class: {name} ({rows.length})', //Template for group display
startCollapsed: true //Set whether the initial group is collapsed
} )
],
store: {
model: 'TestResult',
groupField: 'class',
data: [{
student: 'Student 1',
class: '1',
mark: 84
}, {
student: 'Student 2',
class: '1',
mark: 72
}, {
student: 'Student 3',
class: '2',
mark: 96
}, {
student: 'Student 4',
class: '2',
mark: 68
}]
},
columns: [{
dataIndex: 'student',
text: 'Name',
summaryType: 'count', / /Column name for summary
summaryRenderer: function (value) {
grid.getStore()
return Ext.String.format('{0} student{1}', value, value !== 1 ? 's' : '');
}
}, {
dataIndex: 'mark',
text: 'Mark',
summaryType: 'average'
} ,
{ dataIndex: 'class',
text: 'class'
}]
})
//Click "Group by this field" under different columns and the table will Change grouping rules immediately.
The code only needs to change the above  Grouping to GroupingSummary
Grouping to GroupingSummary
 Form plugin: plugin
Form plugin: plugin
Cell Editing Ext.grid.plugin.CellEditing

 Code:
Code: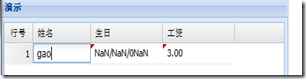
title: 'Demo',
frame: true,
renderTo: Ext.getBody(),
width: 400,
height: 300,
store: {
fields: ['name', 'birth', 'salary '],
data: datas,
proxy: {
type: 'memory',
data: datas,
reader: 'array'
},
autoLoad: true
},
plugins: [
Ext.create('Ext.grid.plugin.CellEditing', {
clicksToEdit: 1
})
],
selType: 'cellmodel',
columns: [Ext.create('Ext.grid.RowNumberer', { text: 'RowNumber', width: 40 }),
{
header: ' name',
width: 80,
dataIndex: 'name',
editor: {//Define field
xtype: 'textfield',
allowBlank: false,
}
}
,
{
header: 'birthday',
width: 100,
dataIndex: 'birth',
xtype: 'datecolumn',
editor: {//Definition fields
xtype: 'datefield',
format: 'Y-m-d',
allowBlank: false
}
}
,
{
header: 'salary',
width: 100,
dataIndex: 'salary', xtype: 'numbercolumn',
editor: {//Define fields
xtype: 'numberfield',
format: '$0,000',
allowBlank: false
}
}
]
})
Table row editor Ext.grid.plugin.RowEditing
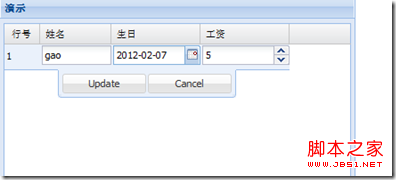
The code only needs: Change CellEditing to RowEditing
Change CellEditing to RowEditing
To obtain the modified data, ajax requests the server and responds.
grid.on('edit', onEdit, this); //Add edit event and get data
')); //get() parameter is the field name.
. 🎜>
The code is as follows:
})
}
}
 Javascript Data Types : Is there any difference between Browser and NodeJs?May 14, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Javascript Data Types : Is there any difference between Browser and NodeJs?May 14, 2025 am 12:15 AMJavaScript core data types are consistent in browsers and Node.js, but are handled differently from the extra types. 1) The global object is window in the browser and global in Node.js. 2) Node.js' unique Buffer object, used to process binary data. 3) There are also differences in performance and time processing, and the code needs to be adjusted according to the environment.
 JavaScript Comments: A Guide to Using // and /* */May 13, 2025 pm 03:49 PM
JavaScript Comments: A Guide to Using // and /* */May 13, 2025 pm 03:49 PMJavaScriptusestwotypesofcomments:single-line(//)andmulti-line(//).1)Use//forquicknotesorsingle-lineexplanations.2)Use//forlongerexplanationsorcommentingoutblocksofcode.Commentsshouldexplainthe'why',notthe'what',andbeplacedabovetherelevantcodeforclari
 Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AMThe main difference between Python and JavaScript is the type system and application scenarios. 1. Python uses dynamic types, suitable for scientific computing and data analysis. 2. JavaScript adopts weak types and is widely used in front-end and full-stack development. The two have their own advantages in asynchronous programming and performance optimization, and should be decided according to project requirements when choosing.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AMWhether to choose Python or JavaScript depends on the project type: 1) Choose Python for data science and automation tasks; 2) Choose JavaScript for front-end and full-stack development. Python is favored for its powerful library in data processing and automation, while JavaScript is indispensable for its advantages in web interaction and full-stack development.
 Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMPython and JavaScript each have their own advantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1. Python is easy to learn, with concise syntax, suitable for data science and back-end development, but has a slow execution speed. 2. JavaScript is everywhere in front-end development and has strong asynchronous programming capabilities. Node.js makes it suitable for full-stack development, but the syntax may be complex and error-prone.
 JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AMJavaScriptisnotbuiltonCorC ;it'saninterpretedlanguagethatrunsonenginesoftenwritteninC .1)JavaScriptwasdesignedasalightweight,interpretedlanguageforwebbrowsers.2)EnginesevolvedfromsimpleinterpreterstoJITcompilers,typicallyinC ,improvingperformance.
 JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript can be used for front-end and back-end development. The front-end enhances the user experience through DOM operations, and the back-end handles server tasks through Node.js. 1. Front-end example: Change the content of the web page text. 2. Backend example: Create a Node.js server.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AMChoosing Python or JavaScript should be based on career development, learning curve and ecosystem: 1) Career development: Python is suitable for data science and back-end development, while JavaScript is suitable for front-end and full-stack development. 2) Learning curve: Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners; JavaScript syntax is flexible. 3) Ecosystem: Python has rich scientific computing libraries, and JavaScript has a powerful front-end framework.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools






