Python 的内存管理架构(Objects/obmalloc.c):
_____ ______ ______ ________
[ int ] [ dict ] [ list ] ... [ string ] Python core |
+3 | | |
_______________________________ | |
[ Python's object allocator ] | |
+2 | ####### Object memory ####### | |
______________________________________________________________ |
[ Python's raw memory allocator (PyMem_ API) ] |
+1 | | |
__________________________________________________________________
[ Underlying general-purpose allocator (ex: C library malloc) ]
0 | |
0. C语言库函数提供的接口
1. PyMem_*家族,是对 C中的 malloc、realloc和free 简单的封装,提供底层的控制接口。
2. PyObject_* 家族,高级的内存控制接口。
3. 对象类型相关的管理接口
PyMem_*
PyMem_家族:低级的内存分配接口(low-level memory allocation interfaces)
Python 对C中的 malloc、realloc和free 提供了简单的封装:
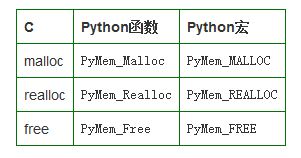
为什么要这么多次一举:
- 不同的C实现对于malloc(0)产生的结果有会所不同,而PyMem_MALLOC(0)会转成malloc(1).
- 不用的C实现的malloc与free混用会有潜在的问题。python提供封装可以避免这个问题。
- Python提供了宏和函数,但是宏无法避免这个问题,故编写扩展是应避免使用宏
源码:
Include/pymem.h
#define PyMem_MALLOC(n) ((size_t)(n) > (size_t)PY_SSIZE_T_MAX ? NULL \
: malloc((n) ? (n) : 1))
#define PyMem_REALLOC(p, n) ((size_t)(n) > (size_t)PY_SSIZE_T_MAX ? NULL \
: realloc((p), (n) ? (n) : 1))
#define PyMem_FREE free
Objects/object.c
/* Python's malloc wrappers (see pymem.h) */
void *
PyMem_Malloc(size_t nbytes)
{
return PyMem_MALLOC(nbytes);
}
...
PyMem_New 和 PyMem_NEW
PyMem_Resize和 PyMem_RESIZE
它们可以感知类型的大小
#define PyMem_New(type, n) \
( ((size_t)(n) > PY_SSIZE_T_MAX / sizeof(type)) ? NULL : \
( (type *) PyMem_Malloc((n) * sizeof(type)) ) )
#define PyMem_Resize(p, type, n) \
( (p) = ((size_t)(n) > PY_SSIZE_T_MAX / sizeof(type)) ? NULL : \
(type *) PyMem_Realloc((p), (n) * sizeof(type)) )
#define PyMem_Del PyMem_Free
#define PyMem_DEL PyMem_FREE
PyObject_*
PyObject_*家族,是高级的内存控制接口(high-level object memory interfaces)。
注意
- 不要和PyMem_*家族混用!!
- 除非有特殊的内粗管理要求,否则应该坚持使用PyObject_*
源码
Include/objimpl.h
#define PyObject_New(type, typeobj) \
( (type *) _PyObject_New(typeobj) )
#define PyObject_NewVar(type, typeobj, n) \
( (type *) _PyObject_NewVar((typeobj), (n)) )
Objects/object.c
PyObject *
_PyObject_New(PyTypeObject *tp)
{
PyObject *op;
op = (PyObject *) PyObject_MALLOC(_PyObject_SIZE(tp));
if (op == NULL)
return PyErr_NoMemory();
return PyObject_INIT(op, tp);
}
PyVarObject *
_PyObject_NewVar(PyTypeObject *tp, Py_ssize_t nitems)
{
PyVarObject *op;
const size_t size = _PyObject_VAR_SIZE(tp, nitems);
op = (PyVarObject *) PyObject_MALLOC(size);
if (op == NULL)
return (PyVarObject *)PyErr_NoMemory();
return PyObject_INIT_VAR(op, tp, nitems);
}
它们执行两项操作:
- 分配内存:PyObject_MALLOC
- 部分初始化对象:PyObject_INIT和PyObject_INIT_VAR
初始化没什么好看到,但是这个MALLOC就有点复杂无比了...
PyObject_{Malloc、Free}
这个和PyMem_*中的3个可是大不一样了,复杂的厉害!
void * PyObject_Malloc(size_t nbytes) void * PyObject_Realloc(void *p, size_t nbytes) void PyObject_Free(void *p)
Python程序运行时频繁地需要创建和销毁小对象,为了避免大量的malloc和free操作,Python使用了内存池的技术。
- 一系列的 arena(每个管理256KB) 构成一个内存区域的链表
- 每个 arena 有很多个 pool(每个4KB) 构成
- 每次内存的申请释放将在一个 pool 内进行
单次申请内存块
当申请大小在 1~256 字节之间的内存时,使用内存池(申请0或257字节以上时,将退而使用我们前面提到的PyMem_Malloc)。
每次申请时,实际分配的空间将按照某个字节数对齐,下表中为8字节(比如PyObject_Malloc(20)字节将分配24字节)。
Request in bytes Size of allocated block Size class idx
----------------------------------------------------------------
1-8 8 0
9-16 16 1
17-24 24 2
25-32 32 3
33-40 40 4
... ... ...
241-248 248 30
249-256 256 31
0, 257 and up: routed to the underlying allocator.
这些参数由一些宏进行控制:
#define ALIGNMENT 8 /* must be 2^N */ /* Return the number of bytes in size class I, as a uint. */ #define INDEX2SIZE(I) (((uint)(I) + 1) << ALIGNMENT_SHIFT) #define SMALL_REQUEST_THRESHOLD 256
pool
每次申请的内存块都是需要在 pool 中进行分配,一个pool的大小是 4k。由下列宏进行控制:
#define SYSTEM_PAGE_SIZE (4 * 1024)
#define POOL_SIZE SYSTEM_PAGE_SIZE /* must be 2^N */
每个pool的头部的定义如下:
struct pool_header {
union { block *_padding;
uint count; } ref; /* number of allocated blocks */
block *freeblock; /* pool's free list head */
struct pool_header *nextpool; /* next pool of this size class */
struct pool_header *prevpool; /* previous pool "" */
uint arenaindex; /* index into arenas of base adr */
uint szidx; /* block size class index */
uint nextoffset; /* bytes to virgin block */
uint maxnextoffset; /* largest valid nextoffset */
};
注意,其中有个成员 szidx,对应前面列表中最后一列的 Size class idx。这也说明一个问题:每个 pool 只能分配固定大小的内存块(比如,只分配16字节的块,或者只分配24字节的块...)。
要能分配前面列表中各种大小的内存块,必须有多个 pool。同一大小的pool分配完毕,也需要新的pool。多个pool依次构成一个链表
arena
多个pool对象使用被称为 arena 的东西进行管理。
struct arena_object {
uptr address;
block* pool_address;
uint nfreepools;
uint ntotalpools;
struct pool_header* freepools;
struct arena_object* nextarena;
struct arena_object* prevarena;
};
arean控制的内存的大小由下列宏控制:
#define ARENA_SIZE (256 << 10) /* 256KB */
一系列的 arena 构成一个链表。
引用计数与垃圾收集
Python中多数对象的生命周期是通过引用计数来控制的,从而实现了内存的动态管理。
但是引用计数有一个致命的问题:循环引用!
为了打破循环引用,Python引入了垃圾收集技术。
 Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of UseApr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of UseApr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AMPython is easier to learn and use, while C is more powerful but complex. 1. Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners. Dynamic typing and automatic memory management make it easy to use, but may cause runtime errors. 2.C provides low-level control and advanced features, suitable for high-performance applications, but has a high learning threshold and requires manual memory and type safety management.
 Python vs. C : Memory Management and ControlApr 19, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Python vs. C : Memory Management and ControlApr 19, 2025 am 12:17 AMPython and C have significant differences in memory management and control. 1. Python uses automatic memory management, based on reference counting and garbage collection, simplifying the work of programmers. 2.C requires manual management of memory, providing more control but increasing complexity and error risk. Which language to choose should be based on project requirements and team technology stack.
 Python for Scientific Computing: A Detailed LookApr 19, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python for Scientific Computing: A Detailed LookApr 19, 2025 am 12:15 AMPython's applications in scientific computing include data analysis, machine learning, numerical simulation and visualization. 1.Numpy provides efficient multi-dimensional arrays and mathematical functions. 2. SciPy extends Numpy functionality and provides optimization and linear algebra tools. 3. Pandas is used for data processing and analysis. 4.Matplotlib is used to generate various graphs and visual results.
 Python and C : Finding the Right ToolApr 19, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Python and C : Finding the Right ToolApr 19, 2025 am 12:04 AMWhether to choose Python or C depends on project requirements: 1) Python is suitable for rapid development, data science, and scripting because of its concise syntax and rich libraries; 2) C is suitable for scenarios that require high performance and underlying control, such as system programming and game development, because of its compilation and manual memory management.
 Python for Data Science and Machine LearningApr 19, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Python for Data Science and Machine LearningApr 19, 2025 am 12:02 AMPython is widely used in data science and machine learning, mainly relying on its simplicity and a powerful library ecosystem. 1) Pandas is used for data processing and analysis, 2) Numpy provides efficient numerical calculations, and 3) Scikit-learn is used for machine learning model construction and optimization, these libraries make Python an ideal tool for data science and machine learning.
 Learning Python: Is 2 Hours of Daily Study Sufficient?Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Learning Python: Is 2 Hours of Daily Study Sufficient?Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AMIs it enough to learn Python for two hours a day? It depends on your goals and learning methods. 1) Develop a clear learning plan, 2) Select appropriate learning resources and methods, 3) Practice and review and consolidate hands-on practice and review and consolidate, and you can gradually master the basic knowledge and advanced functions of Python during this period.
 Python for Web Development: Key ApplicationsApr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python for Web Development: Key ApplicationsApr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AMKey applications of Python in web development include the use of Django and Flask frameworks, API development, data analysis and visualization, machine learning and AI, and performance optimization. 1. Django and Flask framework: Django is suitable for rapid development of complex applications, and Flask is suitable for small or highly customized projects. 2. API development: Use Flask or DjangoRESTFramework to build RESTfulAPI. 3. Data analysis and visualization: Use Python to process data and display it through the web interface. 4. Machine Learning and AI: Python is used to build intelligent web applications. 5. Performance optimization: optimized through asynchronous programming, caching and code
 Python vs. C : Exploring Performance and EfficiencyApr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs. C : Exploring Performance and EfficiencyApr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AMPython is better than C in development efficiency, but C is higher in execution performance. 1. Python's concise syntax and rich libraries improve development efficiency. 2.C's compilation-type characteristics and hardware control improve execution performance. When making a choice, you need to weigh the development speed and execution efficiency based on project needs.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor





