本文实例讲述了Python聚类算法之凝聚层次聚类。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
凝聚层次聚类:所谓凝聚的,指的是该算法初始时,将每个点作为一个簇,每一步合并两个最接近的簇。另外即使到最后,对于噪音点或是离群点也往往还是各占一簇的,除非过度合并。对于这里的“最接近”,有下面三种定义。我在实现是使用了MIN,该方法在合并时,只要依次取当前最近的点对,如果这个点对当前不在一个簇中,将所在的两个簇合并就行:
单链(MIN):定义簇的邻近度为不同两个簇的两个最近的点之间的距离。
全链(MAX):定义簇的邻近度为不同两个簇的两个最远的点之间的距离。
组平均:定义簇的邻近度为取自两个不同簇的所有点对邻近度的平均值。
# scoding=utf-8
# Agglomerative Hierarchical Clustering(AHC)
import pylab as pl
from operator import itemgetter
from collections import OrderedDict,Counter
points = [[int(eachpoint.split('#')[0]), int(eachpoint.split('#')[1])] for eachpoint in open("points","r")]
# 初始时每个点指派为单独一簇
groups = [idx for idx in range(len(points))]
# 计算每个点对之间的距离
disP2P = {}
for idx1,point1 in enumerate(points):
for idx2,point2 in enumerate(points):
if (idx1 < idx2):
distance = pow(abs(point1[0]-point2[0]),2) + pow(abs(point1[1]-point2[1]),2)
disP2P[str(idx1)+"#"+str(idx2)] = distance
# 按距离降序将各个点对排序
disP2P = OrderedDict(sorted(disP2P.iteritems(), key=itemgetter(1), reverse=True))
# 当前有的簇个数
groupNum = len(groups)
# 过分合并会带入噪音点的影响,当簇数减为finalGroupNum时,停止合并
finalGroupNum = int(groupNum*0.1)
while groupNum > finalGroupNum:
# 选取下一个距离最近的点对
twopoins,distance = disP2P.popitem()
pointA = int(twopoins.split('#')[0])
pointB = int(twopoins.split('#')[1])
pointAGroup = groups[pointA]
pointBGroup = groups[pointB]
# 当前距离最近两点若不在同一簇中,将点B所在的簇中的所有点合并到点A所在的簇中,此时当前簇数减1
if(pointAGroup != pointBGroup):
for idx in range(len(groups)):
if groups[idx] == pointBGroup:
groups[idx] = pointAGroup
groupNum -= 1
# 选取规模最大的3个簇,其他簇归为噪音点
wantGroupNum = 3
finalGroup = Counter(groups).most_common(wantGroupNum)
finalGroup = [onecount[0] for onecount in finalGroup]
dropPoints = [points[idx] for idx in range(len(points)) if groups[idx] not in finalGroup]
# 打印规模最大的3个簇中的点
group1 = [points[idx] for idx in xrange(len(points)) if groups[idx]==finalGroup[0]]
group2 = [points[idx] for idx in xrange(len(points)) if groups[idx]==finalGroup[1]]
group3 = [points[idx] for idx in xrange(len(points)) if groups[idx]==finalGroup[2]]
pl.plot([eachpoint[0] for eachpoint in group1], [eachpoint[1] for eachpoint in group1], 'or')
pl.plot([eachpoint[0] for eachpoint in group2], [eachpoint[1] for eachpoint in group2], 'oy')
pl.plot([eachpoint[0] for eachpoint in group3], [eachpoint[1] for eachpoint in group3], 'og')
# 打印噪音点,黑色
pl.plot([eachpoint[0] for eachpoint in dropPoints], [eachpoint[1] for eachpoint in dropPoints], 'ok')
pl.show()
运行效果截图如下:
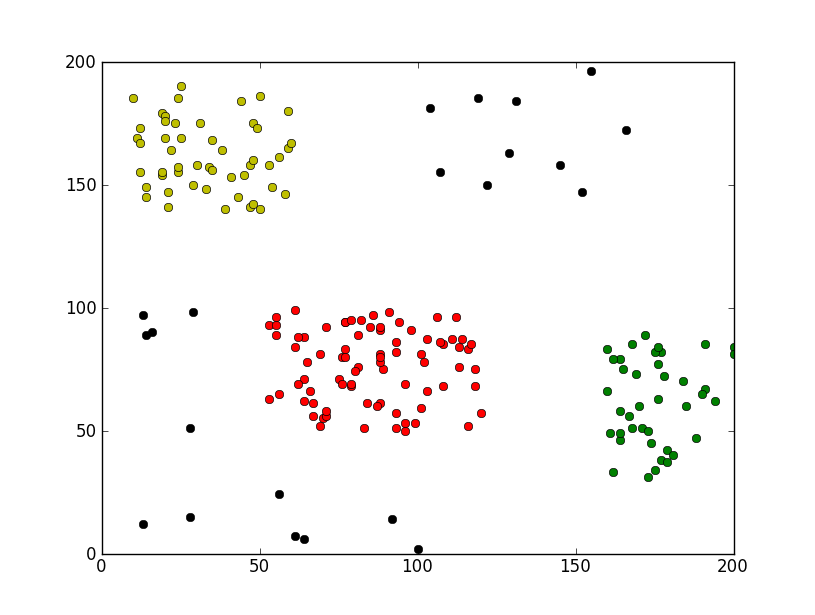
希望本文所述对大家Python程序设计有所帮助。
 Merging Lists in Python: Choosing the Right MethodMay 14, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Merging Lists in Python: Choosing the Right MethodMay 14, 2025 am 12:11 AMTomergelistsinPython,youcanusethe operator,extendmethod,listcomprehension,oritertools.chain,eachwithspecificadvantages:1)The operatorissimplebutlessefficientforlargelists;2)extendismemory-efficientbutmodifiestheoriginallist;3)listcomprehensionoffersf
 How to concatenate two lists in python 3?May 14, 2025 am 12:09 AM
How to concatenate two lists in python 3?May 14, 2025 am 12:09 AMIn Python 3, two lists can be connected through a variety of methods: 1) Use operator, which is suitable for small lists, but is inefficient for large lists; 2) Use extend method, which is suitable for large lists, with high memory efficiency, but will modify the original list; 3) Use * operator, which is suitable for merging multiple lists, without modifying the original list; 4) Use itertools.chain, which is suitable for large data sets, with high memory efficiency.
 Python concatenate list stringsMay 14, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Python concatenate list stringsMay 14, 2025 am 12:08 AMUsing the join() method is the most efficient way to connect strings from lists in Python. 1) Use the join() method to be efficient and easy to read. 2) The cycle uses operators inefficiently for large lists. 3) The combination of list comprehension and join() is suitable for scenarios that require conversion. 4) The reduce() method is suitable for other types of reductions, but is inefficient for string concatenation. The complete sentence ends.
 Python execution, what is that?May 14, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Python execution, what is that?May 14, 2025 am 12:06 AMPythonexecutionistheprocessoftransformingPythoncodeintoexecutableinstructions.1)Theinterpreterreadsthecode,convertingitintobytecode,whichthePythonVirtualMachine(PVM)executes.2)TheGlobalInterpreterLock(GIL)managesthreadexecution,potentiallylimitingmul
 Python: what are the key featuresMay 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Python: what are the key featuresMay 14, 2025 am 12:02 AMKey features of Python include: 1. The syntax is concise and easy to understand, suitable for beginners; 2. Dynamic type system, improving development speed; 3. Rich standard library, supporting multiple tasks; 4. Strong community and ecosystem, providing extensive support; 5. Interpretation, suitable for scripting and rapid prototyping; 6. Multi-paradigm support, suitable for various programming styles.
 Python: compiler or Interpreter?May 13, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python: compiler or Interpreter?May 13, 2025 am 12:10 AMPython is an interpreted language, but it also includes the compilation process. 1) Python code is first compiled into bytecode. 2) Bytecode is interpreted and executed by Python virtual machine. 3) This hybrid mechanism makes Python both flexible and efficient, but not as fast as a fully compiled language.
 Python For Loop vs While Loop: When to Use Which?May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Python For Loop vs While Loop: When to Use Which?May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMUseaforloopwheniteratingoverasequenceorforaspecificnumberoftimes;useawhileloopwhencontinuinguntilaconditionismet.Forloopsareidealforknownsequences,whilewhileloopssuitsituationswithundeterminediterations.
 Python loops: The most common errorsMay 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Python loops: The most common errorsMay 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMPythonloopscanleadtoerrorslikeinfiniteloops,modifyinglistsduringiteration,off-by-oneerrors,zero-indexingissues,andnestedloopinefficiencies.Toavoidthese:1)Use'i


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment






