对象
对象, 在C语言是如何实现的?
Python中对象分为两类: 定长(int等), 非定长(list/dict等)
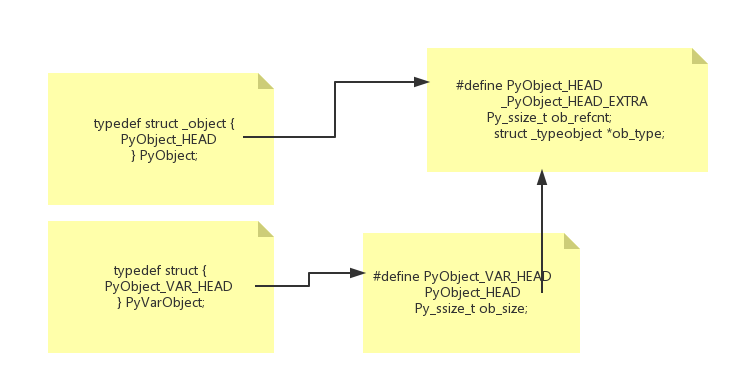
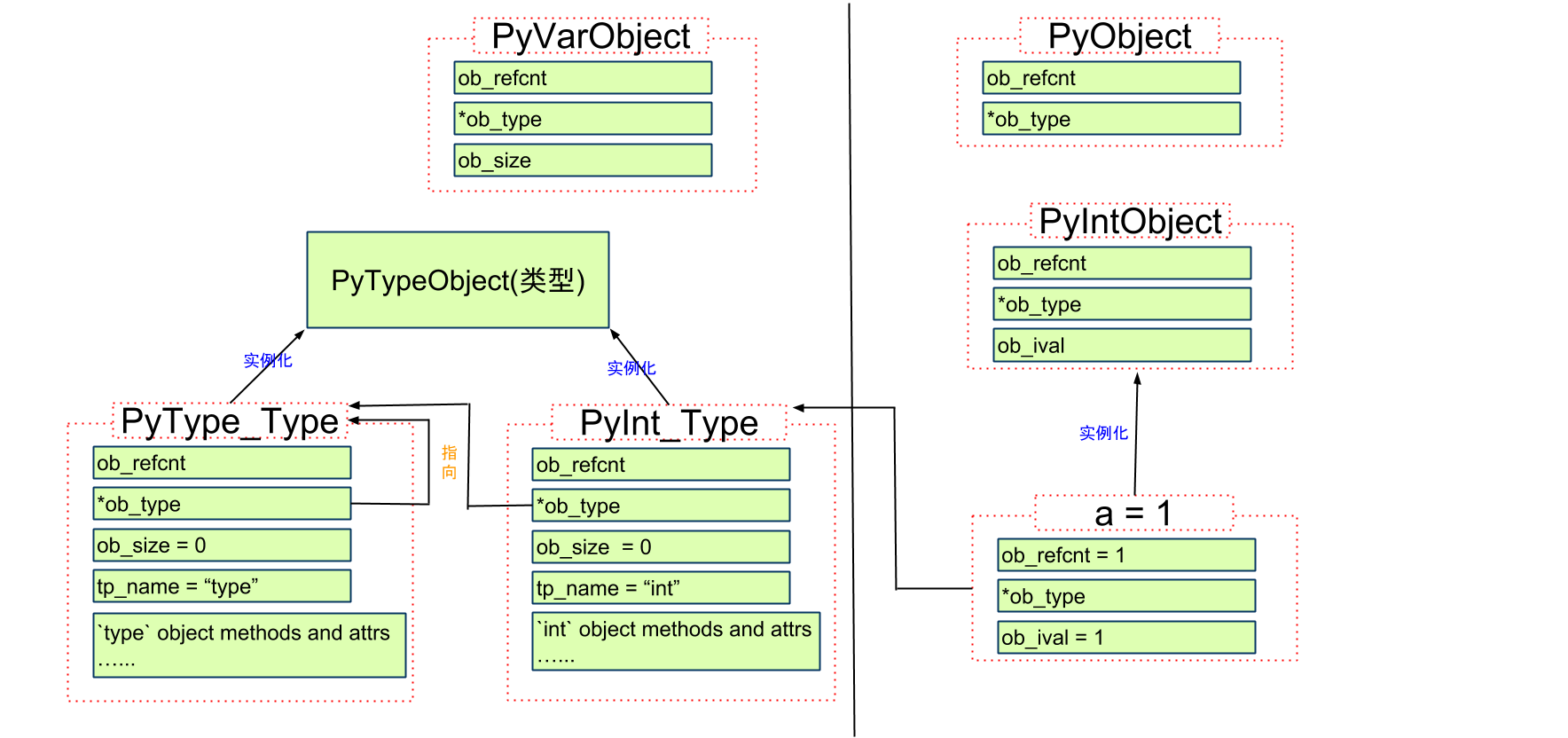
所有对象都有一些相同的东西, 源码中定义为PyObject和PyVarObject, 两个定义都有一个共同的头部定义PyObject_HEAD(其实PyVarObject有自己的头部定义PyObject_VAR_HEAD, 但其实际上用的也是PyObject_HEAD).
源码位置: Include/object.h
PyObject_HEAD
Python 内部, 每个对象拥有相同的头部.
定义
/* PyObject_HEAD defines the initial segment of every PyObject. */ #define PyObject_HEAD \ _PyObject_HEAD_EXTRA \ Py_ssize_t ob_refcnt; \ struct _typeobject *ob_type;
说明
1. _PyObject_HEAD_EXTRA
先忽略, 双向链表结构, 后面垃圾回收再说
2. Py_ssize_t ob_refcnt
Py_ssize_t在编译时确定, 整型
ob_refcnt, 引用计数, 跟Python的内存管理机制相关(基于引用计数的垃圾回收)
3. struct _typeobject *ob_type
*ob_type 指向类型对象的指针(指向_typeobject结构体)
决定了这个对象的类型!
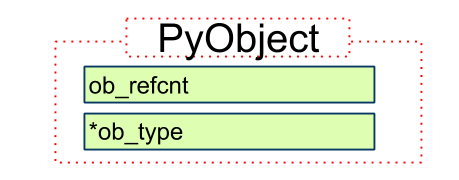
PyObject
定义
typedef struct _object {
PyObject_HEAD
} PyObject;
说明
1. 依赖关系
PyObject -> PyObject_HEAD
结构
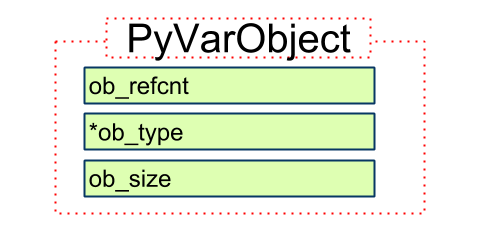
PyVarObject
定义
typedef struct {
PyObject_VAR_HEAD
} PyVarObject;
#define PyObject_VAR_HEAD \
PyObject_HEAD \
Py_ssize_t ob_size; /* Number of items in variable part */
说明
1. 依赖关系
PyVarObject -> PyObject_VAR_HEAD -> PyObject_HEAD
2.Py_ssize_t ob_size
ob_size, 变长对象容纳的元素个数
结构
代码关系
几个方法
跟对象相关的方法
#define Py_REFCNT(ob) (((PyObject*)(ob))->ob_refcnt)
读取引用计数
#define Py_TYPE(ob) (((PyObject*)(ob))->ob_type)
获取对象类型
#define Py_SIZE(ob) (((PyVarObject*)(ob))->ob_size)
读取元素个数(len)
跟引用计数相关的方法
Py_INCREF(op) 增加对象引用计数
Py_DECREF(op) 减少对象引用计数, 如果计数位0, 调用_Py_Dealloc
_Py_Dealloc(op) 调用对应类型的 tp_dealloc 方法(每种类型回收行为不一样的, 各种缓存池机制, 后面看)
其他
几个参数涉及
ob_refcnt 引用计数, 与内存管理/垃圾回收相关
ob_type 类型, 涉及Python的类型系统
类型
一个例子
>>> a = 1 >>> a 1 >>> type(a) <type 'int'> #等价的两个 >>> type(type(a)) <type 'type'> >>> type(int) <type 'type'> #还是等价的两个 >>> type(type(type(a))) <type 'type'> >>> type(type(int)) <type 'type'>
我们反向推导一个int对象是怎么生成的.
1. 首先, 定义一种类型叫PyTypeObject
代码位置 Include/object.h
定义
typedef struct _typeobject {
/* MARK: base, 注意, 是个变长对象*/
PyObject_VAR_HEAD
const char *tp_name; /* For printing, in format "<module>.<name>" */ //类型名
Py_ssize_t tp_basicsize, tp_itemsize; /* For allocation */ // 创建该类型对象时分配的内存空间大小
// 一堆方法定义, 函数和指针
/* Methods to implement standard operations */
printfunc tp_print;
hashfunc tp_hash;
/* Method suites for standard classes */
PyNumberMethods *tp_as_number; // 数值对象操作
PySequenceMethods *tp_as_sequence; // 序列对象操作
PyMappingMethods *tp_as_mapping; // 字典对象操作
// 一堆属性定义
....
} PyTypeObject;
说明
1. PyObject_VAR_HEAD
变长对象
2. const char *tp_name
tp_name, 类型名字符串数组
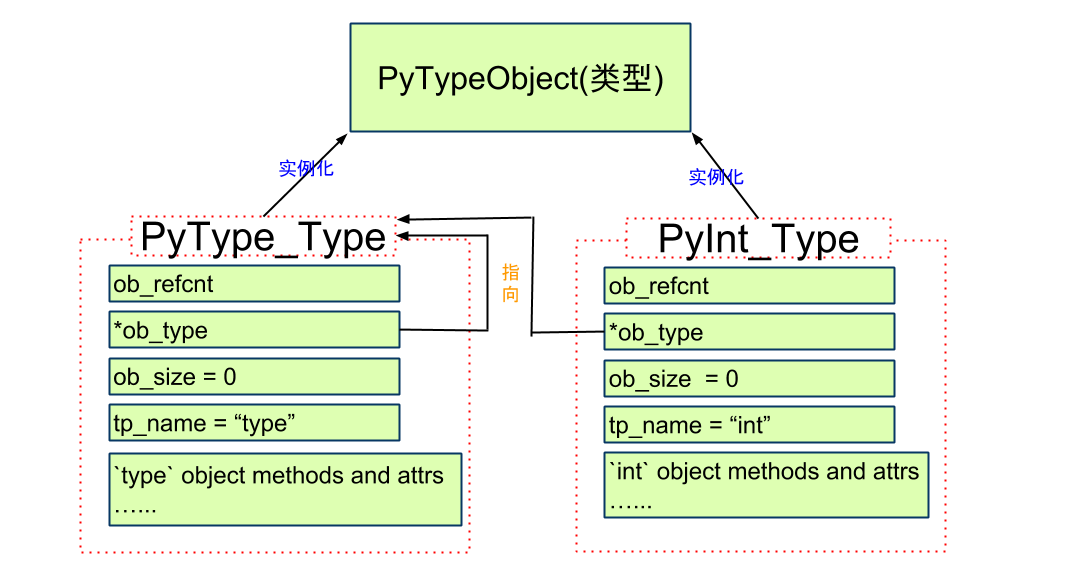
所有Type都是PyTypeObject的"实例": PyType_Type/PyInt_Type
2. 然后, 用PyTypeObject初始化得到一个对象PyType_Type
代码位置 Objects/typeobject.c
定义
PyTypeObject PyType_Type = {
PyVarObject_HEAD_INIT(&PyType_Type, 0)
"type", /* tp_name */
sizeof(PyHeapTypeObject), /* tp_basicsize */
sizeof(PyMemberDef), /* tp_itemsize */
(destructor)type_dealloc, /* tp_dealloc */
// type对象的方法和属性初始化值
.....
};
说明
1. tp_name
类型名, 这里是"type"
2. PyVarObject_HEAD_INIT(&PyType_Type, 0)
PyVarObject_HEAD_INIT, 这个方法在 Include/object.h中,
等价于
ob_refcnt = 1
*ob_type = &PyType_Type
ob_size = 0
即, PyType_Type的类型是其本身!
结构
第一张图, 箭头表示实例化(google doc用不是很熟找不到对应类型的箭头)
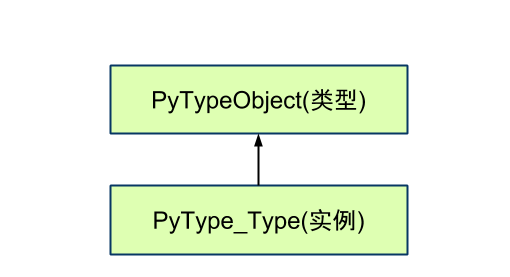
第二张图, 箭头表示指向
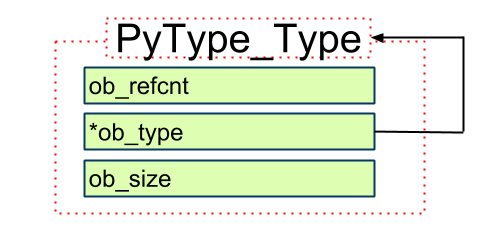
使用
# 1. int 的 类型 是`type` >>> type(int) <type 'type'> # 2. type 的类型 还是`type`, 对应上面说明第二点 >>> type(type(int)) <type 'type'>
注意: 无论任何时候, ob_type指向的是 PyTypeObject的实例: PyType_Type/PyInt_Type...
3. 再然后, 定义具体的类型, 这里以PyInt_Type为例子
代码位置 Objects/intobject.c
定义
PyTypeObject PyInt_Type = {
PyVarObject_HEAD_INIT(&PyType_Type, 0)
"int",
sizeof(PyIntObject),
0,
// int类型的相关方法和属性值
....
(hashfunc)int_hash, /* tp_hash */
};
说明
1. "int"
PyInt_Type的类型名是int
2.PyVarObject_HEAD_INIT(&PyType_Type, 0)
PyInt_Type的
*ob_type = &PyType_Type
结构
使用
>>> type(1) <type 'int'> >>> type(type(1)) <type 'type'>
4. 最后, 生成一个整数对象int
代码位置 Include/intobject.h
定义
typedef struct {
PyObject_HEAD
long ob_ival;
} PyIntObject;
结构
 Merging Lists in Python: Choosing the Right MethodMay 14, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Merging Lists in Python: Choosing the Right MethodMay 14, 2025 am 12:11 AMTomergelistsinPython,youcanusethe operator,extendmethod,listcomprehension,oritertools.chain,eachwithspecificadvantages:1)The operatorissimplebutlessefficientforlargelists;2)extendismemory-efficientbutmodifiestheoriginallist;3)listcomprehensionoffersf
 How to concatenate two lists in python 3?May 14, 2025 am 12:09 AM
How to concatenate two lists in python 3?May 14, 2025 am 12:09 AMIn Python 3, two lists can be connected through a variety of methods: 1) Use operator, which is suitable for small lists, but is inefficient for large lists; 2) Use extend method, which is suitable for large lists, with high memory efficiency, but will modify the original list; 3) Use * operator, which is suitable for merging multiple lists, without modifying the original list; 4) Use itertools.chain, which is suitable for large data sets, with high memory efficiency.
 Python concatenate list stringsMay 14, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Python concatenate list stringsMay 14, 2025 am 12:08 AMUsing the join() method is the most efficient way to connect strings from lists in Python. 1) Use the join() method to be efficient and easy to read. 2) The cycle uses operators inefficiently for large lists. 3) The combination of list comprehension and join() is suitable for scenarios that require conversion. 4) The reduce() method is suitable for other types of reductions, but is inefficient for string concatenation. The complete sentence ends.
 Python execution, what is that?May 14, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Python execution, what is that?May 14, 2025 am 12:06 AMPythonexecutionistheprocessoftransformingPythoncodeintoexecutableinstructions.1)Theinterpreterreadsthecode,convertingitintobytecode,whichthePythonVirtualMachine(PVM)executes.2)TheGlobalInterpreterLock(GIL)managesthreadexecution,potentiallylimitingmul
 Python: what are the key featuresMay 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Python: what are the key featuresMay 14, 2025 am 12:02 AMKey features of Python include: 1. The syntax is concise and easy to understand, suitable for beginners; 2. Dynamic type system, improving development speed; 3. Rich standard library, supporting multiple tasks; 4. Strong community and ecosystem, providing extensive support; 5. Interpretation, suitable for scripting and rapid prototyping; 6. Multi-paradigm support, suitable for various programming styles.
 Python: compiler or Interpreter?May 13, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python: compiler or Interpreter?May 13, 2025 am 12:10 AMPython is an interpreted language, but it also includes the compilation process. 1) Python code is first compiled into bytecode. 2) Bytecode is interpreted and executed by Python virtual machine. 3) This hybrid mechanism makes Python both flexible and efficient, but not as fast as a fully compiled language.
 Python For Loop vs While Loop: When to Use Which?May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Python For Loop vs While Loop: When to Use Which?May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMUseaforloopwheniteratingoverasequenceorforaspecificnumberoftimes;useawhileloopwhencontinuinguntilaconditionismet.Forloopsareidealforknownsequences,whilewhileloopssuitsituationswithundeterminediterations.
 Python loops: The most common errorsMay 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Python loops: The most common errorsMay 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMPythonloopscanleadtoerrorslikeinfiniteloops,modifyinglistsduringiteration,off-by-oneerrors,zero-indexingissues,andnestedloopinefficiencies.Toavoidthese:1)Use'i


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor






