Home >Backend Development >Python Tutorial >python从入门到精通(DAY 1)
python从入门到精通(DAY 1)
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOriginal
- 2016-06-10 15:06:581237browse
1、要点
(1) 在C语言中没有字符串,只有字符,
在python中的字符串hello,在C语言中是以字符数组在内存存放['h','e','l','l','o'],如果对字符串修改,则是在内存中新开辟了一段空间进行存放。
字符串特性:一旦修改,需要重新创建。
例: "hello" + "ni" + "hao" 内存中:['h','e','l','l','o'] + ['n','i'] + ['h','a','o']
万恶的“+”,“+”号越多,在内存中多次重复创建,浪费空间。
C语言需要手动回收,而python,C#等高级语言自带虚拟机会进行GC垃圾回收没有被调用的内存访问空间。
(2) python字符串的格式化(占位符)可以节省内存空间,有如下二种方式,例:
说明:第二种format方式的效果会更好,性能更好,其实变量a的值没有变,在格式化赋值时会在内存中新开辟空间存放。在python2.7和python3.4中测试结果相同
>>> a = 'i am %s,age is %d'
>>> a % ('wangkai',33)
'i am wangkai,age is 33'
>>> print(a)
i am %s,age is %d
>>> a = 'i am {0},age is {1}'
>>> a.format('wangkai',33)
'i am wangkai,age is 33'
>>> print(a)
i am {0},age is {1}
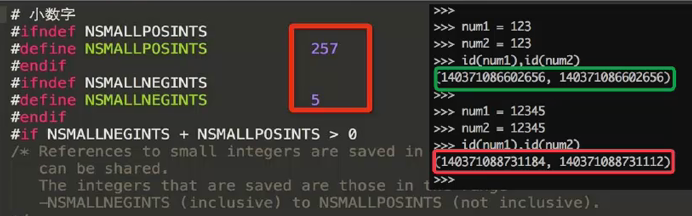
(3) 在python中会生成一个缓存池来节省内存空间,主要存放经常用到的字符串及数字,所以在一定范围内对变量赋同样的值,他们的id值是一样的,当超出这个池的时候,id值则会不同
分别在python2.7和python3.4版本中进行测试,测试结果如下:(经测试在python2.7和python3.4中效果一样)
针对字符串,无限制
>>> a = 'asdfsafsafasfsafasdfasfasfasf' >>> b = 'asdfsafsafasfsafasdfasfasfasf' >>> id(a),id(b) (140704388394128, 140704388394128) >>> a = 'ni' >>> b = 'ni' >>> id(a),id(b) (140704388417416, 140704388417416)
针对数字,范围:小于-5,大于256
>>> a = -5 >>> b = -5 >>> id(a),id(b) (8745920, 8745920) >>> a = -6 >>> b = -6 >>> id(a),id(b) (140718131946128, 140718131946320) >>> aa=256 >>> bb=256 >>> id(aa),id(bb) (8754272, 8754272) >>> aa = 257 >>> bb = 257 >>> id(aa),id(bb) (19083048, 18637656)
具体python源码对数字的定义如下:
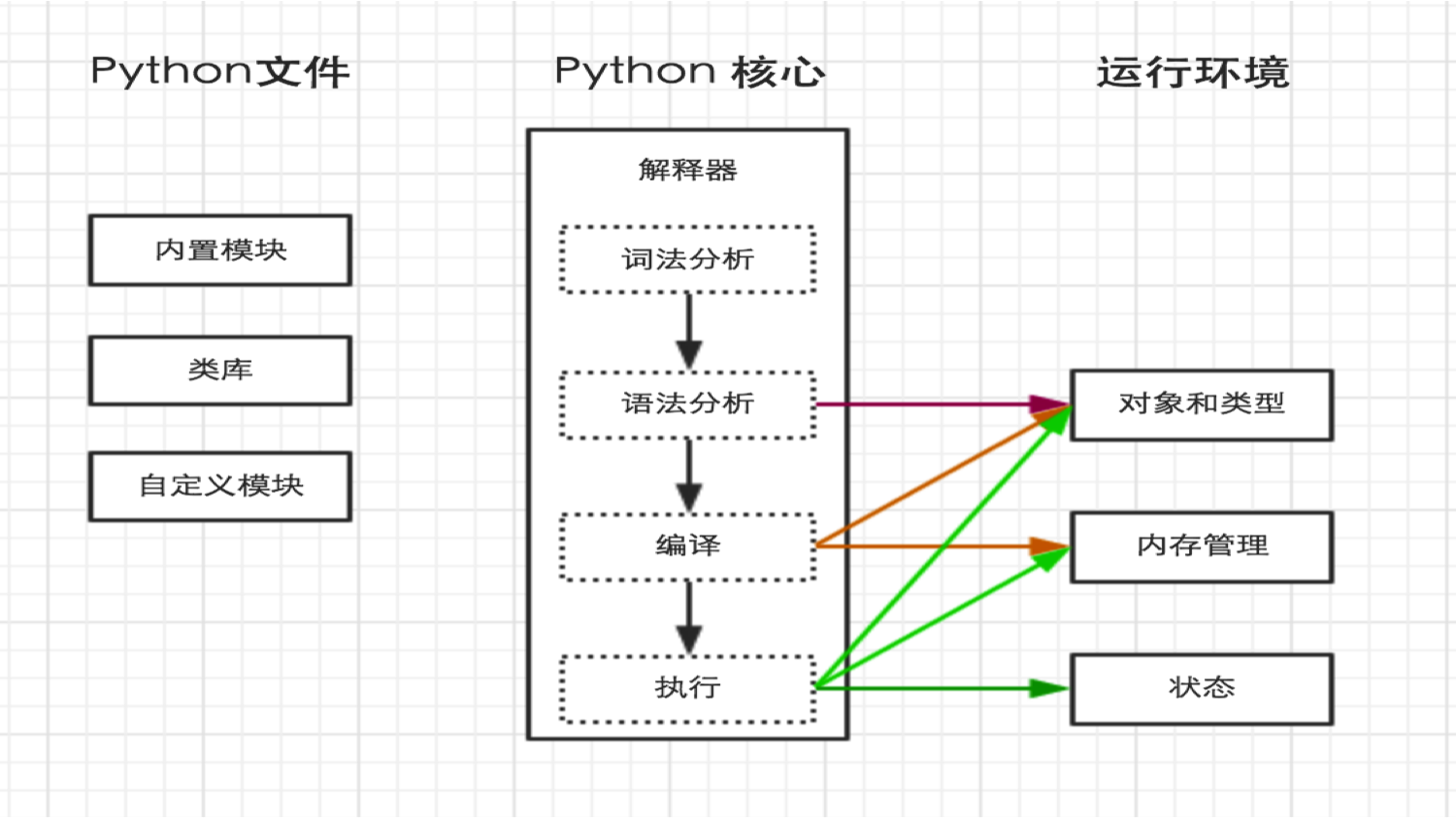
(4) python内部执行过程:
(5) print说明:
Python 2中的print语句被Python 3中的print()函数取代,这意味着在Python 3中必须用括号将需要输出的对象括起来。
特别说明:经测试在python2.6、python2.7,print作为语句,但已支持括号方式,例:a = 1 print a print(a)均可;
在python3.4版本中,print作为函数,只支持括号方式。
建议:为了代码在python2和3上的兼容性,请直接使用print函数括号方式。
2、编码转换
一般硬盘存储为utf-8,读入内存中为unicode,二者如何转换
a = '你好' '\xe4\xbd\xa0\xe5\xa5\xbd'
b = u'你好' u'\u4f60\u597d'
a.decode('utf-8') u'\u4f60\u597d' (utf-8格式解码为unicode)
b.encode('utf-8') '\xe4\xbd\xa0\xe5\xa5\xbd' (unicode格式加密为utf-8)
注:在python2.7版本中需要如上转换,在脚本中如要显示中文,
只要在文件开头加入 # _*_ coding: UTF-8 _*_ 或者 #coding=utf-8 就行了
在python3.4以后版本,无需转换
3、调用系统命令,并存入变量:
1.import os
a = os.system('df -Th')
b = os.popen('df -Th','r') 返回一个文件对象
2.import commands
c = commands.getoutput('df -Th') 返回一个字符串
4、sys调用
import sys
sys.exit
print sys.argv
sys.path
5、导入模板方法:
1.import sys [as newname]
多次重复使用import语句时,不会重新加载被指定的模块,只是把对该模块的内存地址给引用到本地变量环境。
2.from sys import argv或(*)
3.reload()
reload会重新加载已加载的模块,但原来已经使用的实例还是会使用旧的模块,而新生产的实例会使用新的模块;reload后还是用原来的内存地址;不能支持from。。import。。格式的模块进行重新加载。
建议使用第一种,第二种导入的对象或变量会与当前的变量会冲突。
6、用户交互:
在python2.7版本中
raw_input:交互输入内容转化为字符串;
input:交互输入内容不进行转化;
在python3.4版本中只有input,想要获取数字,需要进行int转变。
举例:
#_*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
info = 'This var will be printed out ...'
name = raw_input('Please input your name:')
age = int(raw_input('age:'))
#age = input('age:')
job = raw_input('Job:')
salary = input('Salary:')
print type(age)
print '''
Personal information of %s:
Name: %s
Age : %d
Job : %s
Salary: %d
--------------------------
''' % (name,name, age,job,salary)
7、用户输入内容隐藏:
输入密码时,如果想要不可见,需要利用getpass 模块中的 getpass方法,即:
>>> import getpass
>>> pwd = getpass.getpass("please input the passwd:")
please input the passwd:
>>> print(pwd)
asdfasdfa
8、文件操作:
python2.7版本中可以用file和open打开文件, python3.4版本中只有open
f = open('file_name','r')
g = file('file_name','r')
其中打开模式有'r','w,','a','b','+'
w:替换重写 a:追加
b:二进制文件,主要用于跨平台,来解决window和linux的回车换行区别
+:用于同时读写
* 一般会对文件读到的第一行去掉末尾的换行符 f.readline().strip('\n')
* xreadlines:针对大文件,一行一行读,默认是把全文件读入内存。
* r+ :读写,默认从文件尾写入,可以由seek跳到指定位置,然后替换文件内容。
初始文件aa.txt
kevin:123:1
wang:22:2
kai:311:3
对python2.7和python3.4测试结果一样。
# _*_ coding: UTF-8 _*_
import sys,os
file = sys.argv[1]
f = open(file,'r+')
line_list = f.readlines()
new_list = []
for line in line_list:
#去掉行尾的换行符
line = line.strip('\n')
#对行信息按分隔符进行分列
value_list = line.split(':')
#获取最后一字段并数字化
last_value = int(value_list[-1])
#对最后一字段进行数字计算
last_value *= 13
value_list[-1] = str(last_value)
#将列表转变为字符串
new_str = ':'.join(value_list)
#将循环的改变后的行追加到新的列表
new_list.append(new_str)
'''
######第一种方法按行追加到文件#####
#按修改后的行追加到文件中
#f.writelines(new_str + '\n')
'''
'''
#####第二种方法将所有行统一追加到文件#####
#将所有修改后的新列表转化为字符串
my_str = '\n'.join(new_list)
#将指标移到行首
f.seek(0)
#将写回到文件
f.write(my_str + '\n')
'''
f.close()
9、类型转变:
Python 有办法将任意值转为字符串:将它传入repr() 或str() 函数。
函数str() 用于将值转化为适于人阅读的形式,而repr() 转化为供解释器读取的形式(如果没有等价的
语法,则会发生SyntaxError 异常) 某对象没有适于人阅读的解释形式的话, str() 会返回与repr()等同的值。很多类型,诸如数值或链表、字典这样的结构,针对各函数都有着统一的解读方式。字符串和浮点数,有着独特的解读方式。
Some examples:
下面有些例子
>>> s = 'Hello, world.' >>> str(s) 'Hello, world.' >>> repr(s) "'Hello, world.'" >>> str(1.0/7.0) '0.142857142857' >>> repr(1.0/7.0) '0.14285714285714285'

