大家好,前面入门已经说了那么多基础知识了,下面我们做几个实战项目来挑战一下吧。那么这次为大家带来,Python爬取糗事百科的小段子的例子。
首先,糗事百科大家都听说过吧?糗友们发的搞笑的段子一抓一大把,这次我们尝试一下用爬虫把他们抓取下来。
本篇目标
- 抓取糗事百科热门段子
- 过滤带有图片的段子
- 实现每按一次回车显示一个段子的发布时间,发布人,段子内容,点赞数。
糗事百科是不需要登录的,所以也没必要用到Cookie,另外糗事百科有的段子是附图的,我们把图抓下来图片不便于显示,那么我们就尝试过滤掉有图的段子吧。
好,现在我们尝试抓取一下糗事百科的热门段子吧,每按下一次回车我们显示一个段子。
1.确定URL并抓取页面代码
首先我们确定好页面的URL是 http://www.qiushibaike.com/hot/page/1,其中最后一个数字1代表页数,我们可以传入不同的值来获得某一页的段子内容。
我们初步构建如下的代码来打印页面代码内容试试看,先构造最基本的页面抓取方式,看看会不会成功
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import urllib
import urllib2
page = 1
url = 'http://www.qiushibaike.com/hot/page/' + str(page)
try:
request = urllib2.Request(url)
response = urllib2.urlopen(request)
print response.read()
except urllib2.URLError, e:
if hasattr(e,"code"):
print e.code
if hasattr(e,"reason"):
print e.reason
运行程序,哦不,它竟然报错了,真是时运不济,命途多舛啊
line 373, in _read_status raise BadStatusLine(line) httplib.BadStatusLine: ''
好吧,应该是headers验证的问题,我们加上一个headers验证试试看吧,将代码修改如下
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import urllib
import urllib2
page = 1
url = 'http://www.qiushibaike.com/hot/page/' + str(page)
user_agent = 'Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 5.5; Windows NT)'
headers = { 'User-Agent' : user_agent }
try:
request = urllib2.Request(url,headers = headers)
response = urllib2.urlopen(request)
print response.read()
except urllib2.URLError, e:
if hasattr(e,"code"):
print e.code
if hasattr(e,"reason"):
print e.reason
嘿嘿,这次运行终于正常了,打印出了第一页的HTML代码,大家可以运行下代码试试看。在这里运行结果太长就不贴了。
2.提取某一页的所有段子
好,获取了HTML代码之后,我们开始分析怎样获取某一页的所有段子。
首先我们审查元素看一下,按浏览器的F12,截图如下
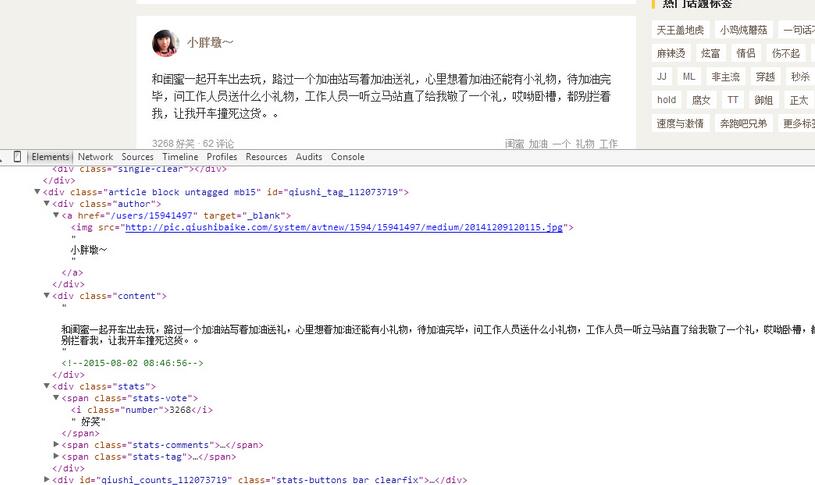
我们可以看到,每一个段子都是
现在我们想获取发布人,发布日期,段子内容,以及点赞的个数。不过另外注意的是,段子有些是带图片的,如果我们想在控制台显示图片是不现实的,所以我们直接把带有图片的段子给它剔除掉,只保存仅含文本的段子。
所以我们加入如下正则表达式来匹配一下,用到的方法是 re.findall 是找寻所有匹配的内容。方法的用法详情可以看前面说的正则表达式的介绍。
好,我们的正则表达式匹配语句书写如下,在原来的基础上追加如下代码
content = response.read().decode('utf-8')
pattern = re.compile('<div.*?author">.*?<a.*?<img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="http://pic.qiushibaike.com/system/pictures/11206/112061287/medium/app112061287.jpg" class="lazy" .*? alt="玩转python爬虫之爬取糗事百科段子" >(.*?)</a>.*?<div.*?'+
'content">(.*?)<!--(.*?)-->.*?</div>(.*?)<div class="stats.*?class="number">(.*?)</i>',re.S)
items = re.findall(pattern,content)
for item in items:
print item[0],item[1],item[2],item[3],item[4]
现在正则表达式在这里稍作说明
1).*? 是一个固定的搭配,.和*代表可以匹配任意无限多个字符,加上?表示使用非贪婪模式进行匹配,也就是我们会尽可能短地做匹配,以后我们还会大量用到 .*? 的搭配。
2)(.*?)代表一个分组,在这个正则表达式中我们匹配了五个分组,在后面的遍历item中,item[0]就代表第一个(.*?)所指代的内容,item[1]就代表第二个(.*?)所指代的内容,以此类推。
3)re.S 标志代表在匹配时为点任意匹配模式,点 . 也可以代表换行符。
这样我们就获取了发布人,发布时间,发布内容,附加图片以及点赞数。
在这里注意一下,我们要获取的内容如果是带有图片,直接输出出来比较繁琐,所以这里我们只获取不带图片的段子就好了。
所以,在这里我们就需要对带图片的段子进行过滤。
我们可以发现,带有图片的段子会带有类似下面的代码,而不带图片的则没有,所以,我们的正则表达式的item[3]就是获取了下面的内容,如果不带图片,item[3]获取的内容便是空。
<div class="thumb"> <a href="/article/112061287?list=hot&s=4794990" target="_blank"> <img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="http://pic.qiushibaike.com/system/pictures/11206/112061287/medium/app112061287.jpg" class="lazy" alt="但他们依然乐观"> </a> </div>
所以我们只需要判断item[3]中是否含有img标签就可以了。
好,我们再把上述代码中的for循环改为下面的样子
for item in items:
haveImg = re.search("img",item[3])
if not haveImg:
print item[0],item[1],item[2],item[4]
现在,整体的代码如下
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import urllib
import urllib2
import re
page = 1
url = 'http://www.qiushibaike.com/hot/page/' + str(page)
user_agent = 'Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 5.5; Windows NT)'
headers = { 'User-Agent' : user_agent }
try:
request = urllib2.Request(url,headers = headers)
response = urllib2.urlopen(request)
content = response.read().decode('utf-8')
pattern = re.compile('<div.*?author">.*?<a.*?<img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="http://files.jb51.net/file_images/article/201602/2016217155254841.jpg?201611715531" class="lazy" .*? alt="玩转python爬虫之爬取糗事百科段子" >(.*?)</a>.*?<div.*?'+
'content">(.*?)<!--(.*?)-->.*?</div>(.*?)<div class="stats.*?class="number">(.*?)</i>',re.S)
items = re.findall(pattern,content)
for item in items:
haveImg = re.search("img",item[3])
if not haveImg:
print item[0],item[1],item[2],item[4]
except urllib2.URLError, e:
if hasattr(e,"code"):
print e.code
if hasattr(e,"reason"):
print e.reason
运行一下看下效果

恩,带有图片的段子已经被剔除啦。是不是很开森?
3.完善交互,设计面向对象模式
好啦,现在最核心的部分我们已经完成啦,剩下的就是修一下边边角角的东西,我们想达到的目的是:
按下回车,读取一个段子,显示出段子的发布人,发布日期,内容以及点赞个数。
另外我们需要设计面向对象模式,引入类和方法,将代码做一下优化和封装,最后,我们的代码如下所示
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import urllib
import urllib2
import re
import thread
import time
#糗事百科爬虫类
class QSBK:
#初始化方法,定义一些变量
def __init__(self):
self.pageIndex = 1
self.user_agent = 'Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 5.5; Windows NT)'
#初始化headers
self.headers = { 'User-Agent' : self.user_agent }
#存放段子的变量,每一个元素是每一页的段子们
self.stories = []
#存放程序是否继续运行的变量
self.enable = False
#传入某一页的索引获得页面代码
def getPage(self,pageIndex):
try:
url = 'http://www.qiushibaike.com/hot/page/' + str(pageIndex)
#构建请求的request
request = urllib2.Request(url,headers = self.headers)
#利用urlopen获取页面代码
response = urllib2.urlopen(request)
#将页面转化为UTF-8编码
pageCode = response.read().decode('utf-8')
return pageCode
except urllib2.URLError, e:
if hasattr(e,"reason"):
print u"连接糗事百科失败,错误原因",e.reason
return None
#传入某一页代码,返回本页不带图片的段子列表
def getPageItems(self,pageIndex):
pageCode = self.getPage(pageIndex)
if not pageCode:
print "页面加载失败...."
return None
pattern = re.compile('<div.*?author">.*?<a.*?<img .*? alt="玩转python爬虫之爬取糗事百科段子" >(.*?)</a>.*?<div.*?'+
'content">(.*?)<!--(.*?)-->.*?</div>(.*?)<div class="stats.*?class="number">(.*?)</i>',re.S)
items = re.findall(pattern,pageCode)
#用来存储每页的段子们
pageStories = []
#遍历正则表达式匹配的信息
for item in items:
#是否含有图片
haveImg = re.search("img",item[3])
#如果不含有图片,把它加入list中
if not haveImg:
replaceBR = re.compile('<br/>')
text = re.sub(replaceBR,"\n",item[1])
#item[0]是一个段子的发布者,item[1]是内容,item[2]是发布时间,item[4]是点赞数
pageStories.append([item[0].strip(),text.strip(),item[2].strip(),item[4].strip()])
return pageStories
#加载并提取页面的内容,加入到列表中
def loadPage(self):
#如果当前未看的页数少于2页,则加载新一页
if self.enable == True:
if len(self.stories) < 2:
#获取新一页
pageStories = self.getPageItems(self.pageIndex)
#将该页的段子存放到全局list中
if pageStories:
self.stories.append(pageStories)
#获取完之后页码索引加一,表示下次读取下一页
self.pageIndex += 1
#调用该方法,每次敲回车打印输出一个段子
def getOneStory(self,pageStories,page):
#遍历一页的段子
for story in pageStories:
#等待用户输入
input = raw_input()
#每当输入回车一次,判断一下是否要加载新页面
self.loadPage()
#如果输入Q则程序结束
if input == "Q":
self.enable = False
return
print u"第%d页\t发布人:%s\t发布时间:%s\t赞:%s\n%s" %(page,story[0],story[2],story[3],story[1])
#开始方法
def start(self):
print u"正在读取糗事百科,按回车查看新段子,Q退出"
#使变量为True,程序可以正常运行
self.enable = True
#先加载一页内容
self.loadPage()
#局部变量,控制当前读到了第几页
nowPage = 0
while self.enable:
if len(self.stories)>0:
#从全局list中获取一页的段子
pageStories = self.stories[0]
#当前读到的页数加一
nowPage += 1
#将全局list中第一个元素删除,因为已经取出
del self.stories[0]
#输出该页的段子
self.getOneStory(pageStories,nowPage)
spider = QSBK()
spider.start()
好啦,大家来测试一下吧,点一下回车会输出一个段子,包括发布人,发布时间,段子内容以及点赞数,是不是感觉爽爆了!
我们第一个爬虫实战项目介绍到这里,希望大家喜欢。
 The Main Purpose of Python: Flexibility and Ease of UseApr 17, 2025 am 12:14 AM
The Main Purpose of Python: Flexibility and Ease of UseApr 17, 2025 am 12:14 AMPython's flexibility is reflected in multi-paradigm support and dynamic type systems, while ease of use comes from a simple syntax and rich standard library. 1. Flexibility: Supports object-oriented, functional and procedural programming, and dynamic type systems improve development efficiency. 2. Ease of use: The grammar is close to natural language, the standard library covers a wide range of functions, and simplifies the development process.
 Python: The Power of Versatile ProgrammingApr 17, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python: The Power of Versatile ProgrammingApr 17, 2025 am 12:09 AMPython is highly favored for its simplicity and power, suitable for all needs from beginners to advanced developers. Its versatility is reflected in: 1) Easy to learn and use, simple syntax; 2) Rich libraries and frameworks, such as NumPy, Pandas, etc.; 3) Cross-platform support, which can be run on a variety of operating systems; 4) Suitable for scripting and automation tasks to improve work efficiency.
 Learning Python in 2 Hours a Day: A Practical GuideApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Learning Python in 2 Hours a Day: A Practical GuideApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AMYes, learn Python in two hours a day. 1. Develop a reasonable study plan, 2. Select the right learning resources, 3. Consolidate the knowledge learned through practice. These steps can help you master Python in a short time.
 Python vs. C : Pros and Cons for DevelopersApr 17, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Python vs. C : Pros and Cons for DevelopersApr 17, 2025 am 12:04 AMPython is suitable for rapid development and data processing, while C is suitable for high performance and underlying control. 1) Python is easy to use, with concise syntax, and is suitable for data science and web development. 2) C has high performance and accurate control, and is often used in gaming and system programming.
 Python: Time Commitment and Learning PaceApr 17, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Python: Time Commitment and Learning PaceApr 17, 2025 am 12:03 AMThe time required to learn Python varies from person to person, mainly influenced by previous programming experience, learning motivation, learning resources and methods, and learning rhythm. Set realistic learning goals and learn best through practical projects.
 Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task ManagementApr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task ManagementApr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AMPython excels in automation, scripting, and task management. 1) Automation: File backup is realized through standard libraries such as os and shutil. 2) Script writing: Use the psutil library to monitor system resources. 3) Task management: Use the schedule library to schedule tasks. Python's ease of use and rich library support makes it the preferred tool in these areas.
 Python and Time: Making the Most of Your Study TimeApr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Python and Time: Making the Most of Your Study TimeApr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AMTo maximize the efficiency of learning Python in a limited time, you can use Python's datetime, time, and schedule modules. 1. The datetime module is used to record and plan learning time. 2. The time module helps to set study and rest time. 3. The schedule module automatically arranges weekly learning tasks.
 Python: Games, GUIs, and MoreApr 13, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Games, GUIs, and MoreApr 13, 2025 am 12:14 AMPython excels in gaming and GUI development. 1) Game development uses Pygame, providing drawing, audio and other functions, which are suitable for creating 2D games. 2) GUI development can choose Tkinter or PyQt. Tkinter is simple and easy to use, PyQt has rich functions and is suitable for professional development.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment





