1、Set基本数据类型
a、set集合,是一个无序且不重复的元素集合
class set(object):
"""
set() -> new empty set object
set(iterable) -> new set object
Build an unordered collection of unique elements.
"""
def add(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Add an element to a set,添加元素
This has no effect if the element is already present.
"""
pass
def clear(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Remove all elements from this set. 清楚内容"""
pass
def copy(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return a shallow copy of a set. 浅拷贝 """
pass
def difference(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Return the difference of two or more sets as a new set. A中存在,B中不存在
(i.e. all elements that are in this set but not the others.)
"""
pass
def difference_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Remove all elements of another set from this set. 从当前集合中删除和B中相同的元素"""
pass
def discard(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Remove an element from a set if it is a member.
If the element is not a member, do nothing. 移除指定元素,不存在不保错
"""
pass
def intersection(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Return the intersection of two sets as a new set. 交集
(i.e. all elements that are in both sets.)
"""
pass
def intersection_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Update a set with the intersection of itself and another. 取交集并更更新到A中 """
pass
def isdisjoint(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return True if two sets have a null intersection. 如果没有交集,返回True,否则返回False"""
pass
def issubset(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Report whether another set contains this set. 是否是子序列"""
pass
def issuperset(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Report whether this set contains another set. 是否是父序列"""
pass
def pop(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Remove and return an arbitrary set element.
Raises KeyError if the set is empty. 移除元素
"""
pass
def remove(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Remove an element from a set; it must be a member.
If the element is not a member, raise a KeyError. 移除指定元素,不存在保错
"""
pass
def symmetric_difference(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Return the symmetric difference of two sets as a new set. 对称交集
(i.e. all elements that are in exactly one of the sets.)
"""
pass
def symmetric_difference_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Update a set with the symmetric difference of itself and another. 对称交集,并更新到a中 """
pass
def union(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Return the union of sets as a new set. 并集
(i.e. all elements that are in either set.)
"""
pass
def update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Update a set with the union of itself and others. 更新 """
pass
b、数据类型模块举例
se = {11,22,33,44,55}
be = {44,55,66,77,88}
# se.add(66)
# print(se) #添加元素,不能直接打印!
#
#
#
# se.clear()
# print(se) #清除se集合里面所有的值,不能清除单个
#
#
#
# ce=be.difference(se) #se中存在,be中不存在的值,必须赋值给一个新的变量
# print(ce)
#
#
# se.difference_update(be)
# print(se) #在se中删除和be相同的值,不能赋值给一个新的变量,先输入转换,然后打印,也不能直接打印!
# se.discard(11)
# print(se) #移除指定元素,移除不存在的时候,不会报错
# se.remove(11)
# print(se) #移除指定的元素,移除不存在的会报错
# se.pop()
# print(se) #移除随机的元素
#
#
# ret=se.pop()
# print(ret) #移除元素,并且可以把移除的元素赋值给另一个变量
# ce = se.intersection(be)
# print(ce) #取出两个集合的交集(相同的元素)
# se.intersection_update(be)
# print(se) #取出两个集合的交集,并更新到se集合中
# ret = se.isdisjoint(be)
# print(ret) #判断两个集合之间又没有交集,如果有交集返回False,没有返回True
# ret=se.issubset(be)
# print(ret) #判断se是否是be集合的子序列,如果是返回True,不是返回Flase
# ret = se.issuperset(be)
# print(ret) #判断se是不是be集合的父序列,如果是返回True,不是返回Flase
# ret=se.symmetric_difference(be)
# print(ret) #对称交集,取出除了不相同的元素
# se.symmetric_difference_update(be)
# print(se) #对称交集,取出不相同的元素并更新到se集合中
# ret = se.union(be)
# print(ret) #并集,把两个元素集合并在一个新的变量中
2、深浅拷贝
a、数字和字符串
对于 数字 和 字符串 而言,赋值、浅拷贝和深拷贝无意义,因为其永远指向同一个内存地址。
import copy # ######### 数字、字符串 ######### n1 = 123 # n1 = "i am alex age 10" print(id(n1)) # ## 赋值 ## n2 = n1 print(id(n2)) # ## 浅拷贝 ## n2 = copy.copy(n1) print(id(n2)) # ## 深拷贝 ## n3 = copy.deepcopy(n1) print(id(n3))
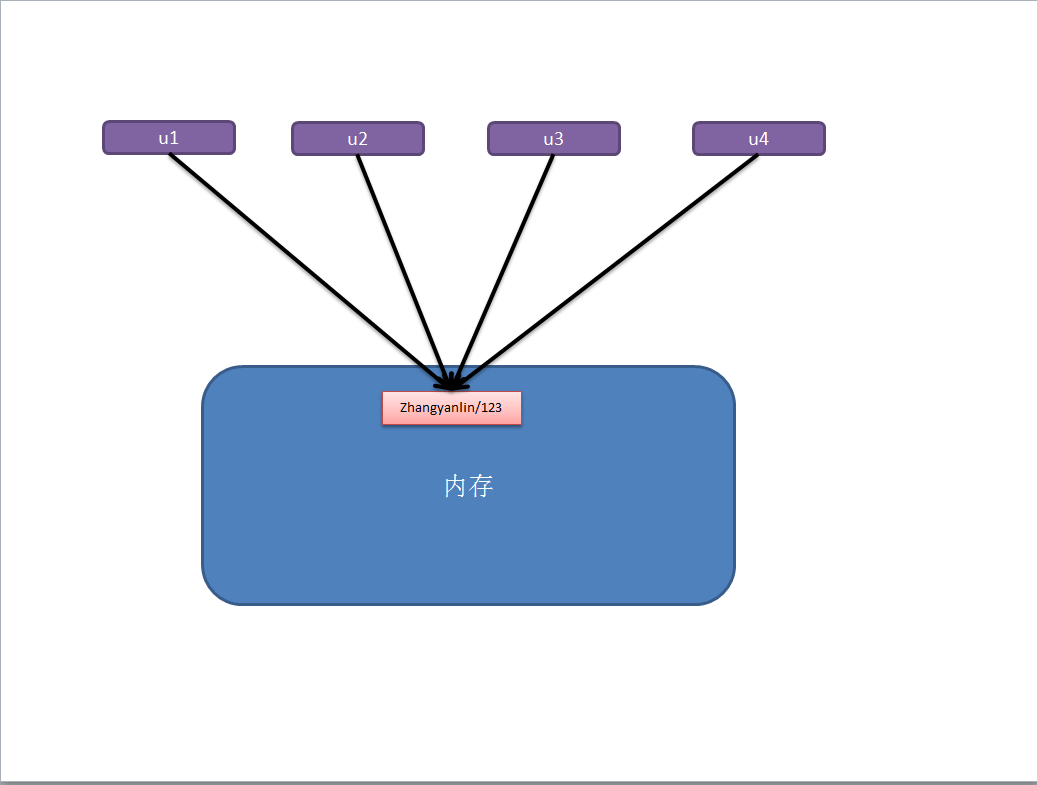
b、其他基本数据类型
对于字典、元祖、列表 而言,进行赋值、浅拷贝和深拷贝时,其内存地址的变化是不同的。
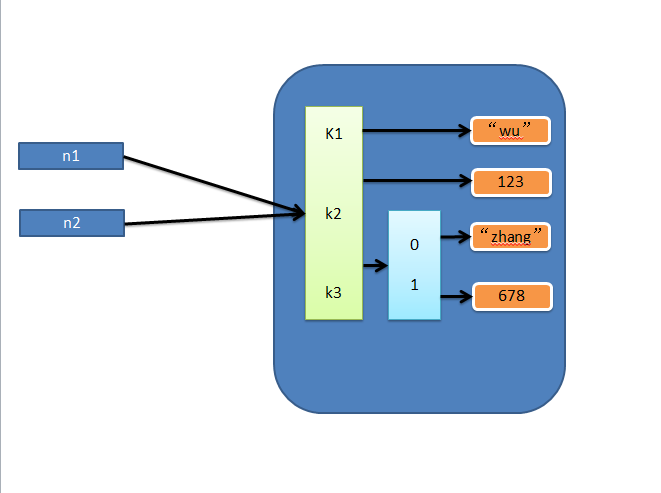
1、赋值
赋值,只是创建一个变量,该变量指向原来内存地址,如:
n1 = {"k1": "zhangyanlin", "k2": 123, "k3": ["Aylin", 456]}
n2 = n1
2、浅拷贝
浅拷贝,在内存中只额外创建第一层数据
import copy
n1 = {"k1": "zhangyanlin", "k2": 123, "k3": ["aylin", 456]}
n3 = copy.copy(n1)
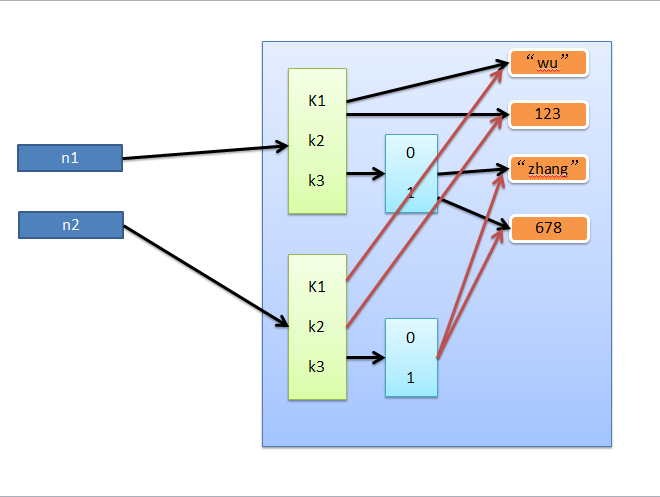
3、深拷贝
深拷贝,在内存中将所有的数据重新创建一份(排除最后一层,即:python内部对字符串和数字的优化)
3、函数
函数式:将某功能代码封装到函数中,日后便无需重复编写,仅调用函数即可
面向对象:对函数进行分类和封装,让开发“更快更好更强...
.函数的定义主要有如下要点:
def:表示函数的关键字
函数名:函数的名称,日后根据函数名调用函数
函数体:函数中进行一系列的逻辑计算,如:发送邮件、计算出 [11,22,38,888,2]中的最大数等...
参数:为函数体提供数据
返回值:当函数执行完毕后,可以给调用者返回数据。
1、返回值
函数是一个功能块,该功能到底执行成功与否,需要通过返回值来告知调用者。
以上要点中,比较重要有参数和返回值:
def 发送短信():
发送短信的代码...
if 发送成功:
return True
else:
return False
while True:
# 每次执行发送短信函数,都会将返回值自动赋值给result
# 之后,可以根据result来写日志,或重发等操作
result = 发送短信()
if result == False:
短信发送失败...
函数的有三中不同的参数:
普通参数
# ######### 定义函数 #########
# name 叫做函数func的形式参数,简称:形参
def func(name):
print name
# ######### 执行函数 #########
# 'zhangyanlin' 叫做函数func的实际参数,简称:实参
func('zhangyanlin')
默认参数
def func(name, age = 18):
print "%s:%s" %(name,age)
# 指定参数
func('zhangyanlin', 19)
# 使用默认参数
func('nick')
注:默认参数需要放在参数列表最后
动态参数
def func(*args): print args # 执行方式一 func(11,33,4,4454,5) # 执行方式二 li = [11,2,2,3,3,4,54] func(*li)
def func(**kwargs):
print args
# 执行方式一
func(name='wupeiqi',age=18)
# 执行方式二
li = {'name':'wupeiqi', age:18, 'gender':'male'}
func(**li)
def func(*args, **kwargs): print args print kwargs
邮件实例:
def email(p,j,k):
import smtplib
from email.mime.text import MIMEText
from email.utils import formataddr
set = True
try:
msg = MIMEText('j', 'plain', 'utf-8') #j 邮件内容
msg['From'] = formataddr(["武沛齐",'wptawy@126.com'])
msg['To'] = formataddr(["走人",'424662508@qq.com'])
msg['Subject'] = "k" #k主题
server = smtplib.SMTP("smtp.126.com", 25)
server.login("wptawy@126.com", "WW.3945.59")
server.sendmail('wptawy@126.com', [p], msg.as_string())
server.quit()
except:
set = False
return True
formmail = input("请你输入收件人邮箱:")
zhuti = input("请您输入邮件主题:")
neirong = input("请您输入邮件内容:")
aa=email(formmail,neirong,zhuti)
if aa:
print("邮件发送成功!")
else:
print("邮件发送失败!")
 Merging Lists in Python: Choosing the Right MethodMay 14, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Merging Lists in Python: Choosing the Right MethodMay 14, 2025 am 12:11 AMTomergelistsinPython,youcanusethe operator,extendmethod,listcomprehension,oritertools.chain,eachwithspecificadvantages:1)The operatorissimplebutlessefficientforlargelists;2)extendismemory-efficientbutmodifiestheoriginallist;3)listcomprehensionoffersf
 How to concatenate two lists in python 3?May 14, 2025 am 12:09 AM
How to concatenate two lists in python 3?May 14, 2025 am 12:09 AMIn Python 3, two lists can be connected through a variety of methods: 1) Use operator, which is suitable for small lists, but is inefficient for large lists; 2) Use extend method, which is suitable for large lists, with high memory efficiency, but will modify the original list; 3) Use * operator, which is suitable for merging multiple lists, without modifying the original list; 4) Use itertools.chain, which is suitable for large data sets, with high memory efficiency.
 Python concatenate list stringsMay 14, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Python concatenate list stringsMay 14, 2025 am 12:08 AMUsing the join() method is the most efficient way to connect strings from lists in Python. 1) Use the join() method to be efficient and easy to read. 2) The cycle uses operators inefficiently for large lists. 3) The combination of list comprehension and join() is suitable for scenarios that require conversion. 4) The reduce() method is suitable for other types of reductions, but is inefficient for string concatenation. The complete sentence ends.
 Python execution, what is that?May 14, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Python execution, what is that?May 14, 2025 am 12:06 AMPythonexecutionistheprocessoftransformingPythoncodeintoexecutableinstructions.1)Theinterpreterreadsthecode,convertingitintobytecode,whichthePythonVirtualMachine(PVM)executes.2)TheGlobalInterpreterLock(GIL)managesthreadexecution,potentiallylimitingmul
 Python: what are the key featuresMay 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Python: what are the key featuresMay 14, 2025 am 12:02 AMKey features of Python include: 1. The syntax is concise and easy to understand, suitable for beginners; 2. Dynamic type system, improving development speed; 3. Rich standard library, supporting multiple tasks; 4. Strong community and ecosystem, providing extensive support; 5. Interpretation, suitable for scripting and rapid prototyping; 6. Multi-paradigm support, suitable for various programming styles.
 Python: compiler or Interpreter?May 13, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python: compiler or Interpreter?May 13, 2025 am 12:10 AMPython is an interpreted language, but it also includes the compilation process. 1) Python code is first compiled into bytecode. 2) Bytecode is interpreted and executed by Python virtual machine. 3) This hybrid mechanism makes Python both flexible and efficient, but not as fast as a fully compiled language.
 Python For Loop vs While Loop: When to Use Which?May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Python For Loop vs While Loop: When to Use Which?May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMUseaforloopwheniteratingoverasequenceorforaspecificnumberoftimes;useawhileloopwhencontinuinguntilaconditionismet.Forloopsareidealforknownsequences,whilewhileloopssuitsituationswithundeterminediterations.
 Python loops: The most common errorsMay 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Python loops: The most common errorsMay 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMPythonloopscanleadtoerrorslikeinfiniteloops,modifyinglistsduringiteration,off-by-oneerrors,zero-indexingissues,andnestedloopinefficiencies.Toavoidthese:1)Use'i


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software






