A detailed discussion of nodejs asynchronous programming_node.js
Current requirements involve a large number of asynchronous operations, and actual pages are increasingly leaning towards single-page applications. In the future, you may use backbone, angular, knockout and other frameworks, but the issue about asynchronous programming is the first issue that needs to be faced. With the rise of node, asynchronous programming has become a very hot topic. After a period of study and practice, some details of asynchronous programming are summarized.
1. Classification of asynchronous programming
Methods to solve asynchronous problems generally include: direct callback, pub/sub mode (event mode), asynchronous library control library (such as async, when), promise, Generator, etc.
1.1 Callback function
Callback function is a commonly used method to solve asynchronous problems. It is often contacted and used, easy to understand, and very easy to implement in libraries or functions. This is also a method often used by everyone when using asynchronous programming.
But the callback function method has the following problems:
1. It may form an evil nested pyramid, and the code is difficult to read;
2. Can only correspond to one callback function, which becomes a limitation in many scenarios.
1.2 pub/sub mode (event)
This mode is also called event mode, which is the eventization of callback functions. It is very common in libraries such as jQuery.
The event publishing subscriber model itself does not have the problem of synchronous and asynchronous calls, but in node, emit calls are mostly triggered asynchronously with the event loop. This mode is often used to decouple business logic. The event publisher does not need to pay attention to the registered callback functions, nor the number of callback functions. Data can be transferred flexibly through messages.
The advantages of this mode are: 1. Easy to understand; 2. No longer limited to one callback function.
Disadvantages: 1. Need to use class library; 2. The order of events and callback functions is very important
var img = document.querySelect(#id);
img.addEventListener('load', function() {
// Image loading completed
…
});
img.addEventListener('error', function() {
// Something went wrong
……
});
There are two problems with the above code:
a. The img has actually been loaded, and the load callback function is bound only at this time. As a result, the callback will not be executed, but we still hope to execute the corresponding callback function.
var img = document.querySelect(#id);
function load() {
...
}
if(img.complete) {
load();
} else {
img.addEventListener('load', load);
}
img.addEventListener('error', function() {
// Something went wrong
……
});
b. Unable to handle exceptions well
Conclusion: The event mechanism is most suitable for handling things that happen repeatedly on the same object. There is no need to consider the occurrence of events before the callback function is bound.
1.3 Asynchronous control library
The current asynchronous libraries mainly include Q, when.js, win.js, RSVP.js, etc.
The characteristic of these libraries is that the code is linear and can be written from top to bottom, which is in line with natural habits.
The disadvantage is that the styles are different, which makes it difficult to read and increases the cost of learning.
1.4 Promise
Promise is translated into Chinese as promise. My personal understanding is that after the asynchronous completion, it will give an external result (success or failure) and promise that the result will not change. In other words, Promise reflects the eventual return value of an operation (A promise represents the eventual value returned from the single completion of an operation). At present, Promise has been introduced into the ES6 specification, and advanced browsers such as Chrome and Firefox have implemented this native method internally, which is very convenient to use.
Let’s analyze the characteristics of Promise from the following aspects:
1.4.1 Status
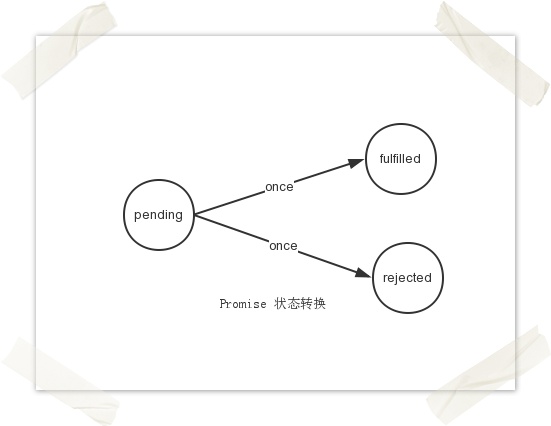
Contains three states: pending, fulfilled, and rejected. Only two transitions can occur among the three states (from pending--->fulfilled, pending-->rejected), and the state transition can only occur once.
1.4.2 then method
The then method is used to specify the callback function after the asynchronous event is completed.
This method can be said to be the soul method of Promise, which makes Promise full of magic. There are several specific manifestations as follows:
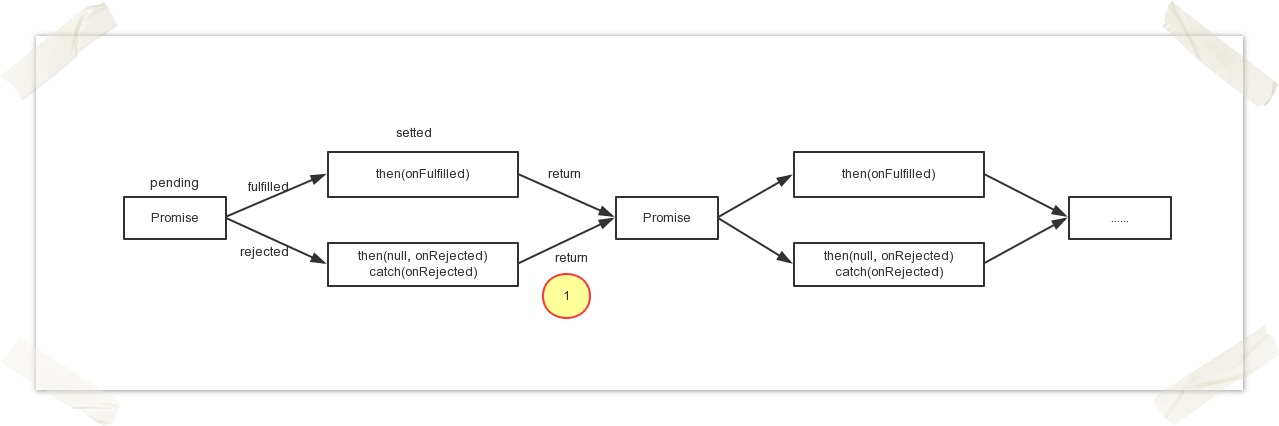
a) The then method returns Promise. This enables serial operations of multiple asynchronous operations.
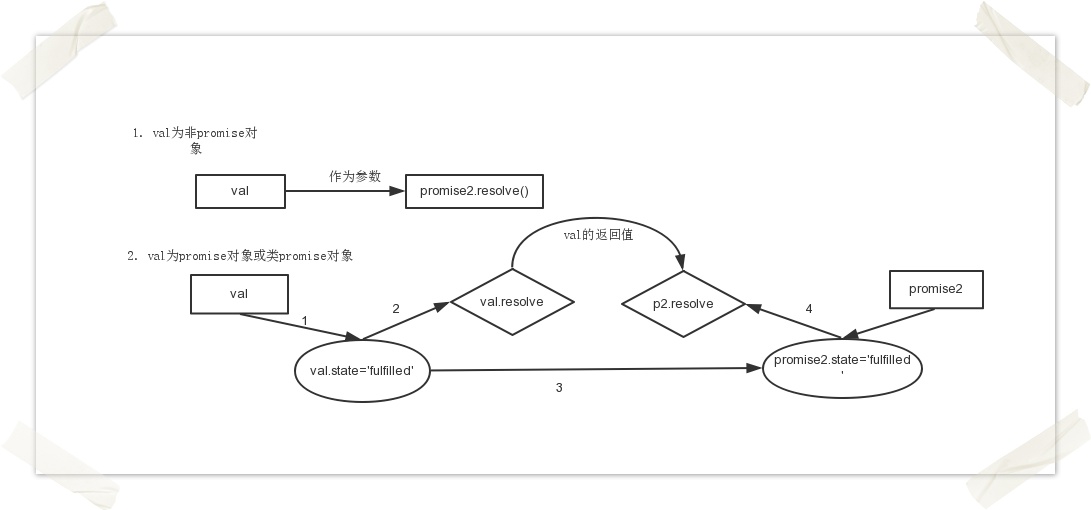
Regarding the processing of value in the yellow circle 1 in the above picture, it is a more complicated part of Promise. The processing of value is divided into two situations: Promise object and non-Promise object.
When value is not of Promise type, just use value as the parameter value of the resolve of the second Promise; when it is of Promise type, the status and parameters of promise2 are completely determined by value. It can be considered that promsie2 is completely a puppet of value. , promise2 is just a bridge connecting different asynchronous ones.
Promise.prototype.then = function(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) { //此处的Promise标注为promise2
handle({
onFulfilled: onFulfilled,
onRejected: onRejected,
resolve: resolve,
reject: reject
})
});
}
function handle(deferred) {
var handleFn;
if(state === 'fulfilled') {
handleFn = deferred.onFulfilled;
} else if(state === 'rejected') {
handleFn = deferred.onRejected;
}
var ret = handleFn(value);
deferred.resolve(ret); //注意,此时的resolve是promise2的resolve
}
function resolve(val) {
if(val && typeof val.then === 'function') {
val.then(resolve); // if val为promise对象或类promise对象时,promise2的状态完全由val决定
return;
}
if(callback) { // callback为指定的回调函数
callback(val);
}
}
b)实现了多个不同异步库之间的转换。
在异步中存在一个叫thenable的对象,就是指具有then方法的对象,只要一个对象对象具有then方法,就可以对其进行转换,例如:
var deferred = $('aa.ajax'); // !!deferred.then === true
var P = Promise.resolve(deferred);
p.then(......)
1.4.3 commonJS Promise/A规范
目前关于Promise的规范存在Promise/A和Promise/A 规范,这说明关于Promise的实现是挺复杂的。
then(fulfilledHandler, rejectedHandler, progressHandler)
1.4.4 注意事项
一个Promise里面的回调函数是共享value的,在结果处理中value作为参数传递给相应的回调函数,如果value是对象,那就要小心不要轻易修改value的值。
var p = Promise.resolve({x: 1});
p.then(function(val) {
console.log('first callback: ' val.x );
});
p.then(function(val) {
console.log('second callback: ' val.x)
})
// first callback: 1
// second callback: 2
1.5 Generator
All the above methods are based on callback functions to complete asynchronous operations. They are nothing more than encapsulation of callback functions. Generator is proposed in ES6, which adds a way to solve asynchronous operations and no longer relies on callback functions.
The biggest feature of Generator is that it can pause and restart functions. This feature is very helpful for solving asynchronous operations. Combining Generator's pause with promise's exception handling can solve asynchronous programming problems more elegantly. Specific implementation reference: Kyle Simpson
2. Problems with asynchronous programming
2.1 Exception handling
a) Asynchronous events include two links: issuing asynchronous requests and result processing. These two links are connected through event loop. Then when try catch is used to capture exceptions, it needs to be captured separately.
try {
asyncEvent(callback);
} catch(err) {
…
}
The above code cannot capture the exception in the callback, but can only get the exception in the request process. This creates a problem: If the issuance of the request and the processing of the request are completed by two people, will there be a problem when handling exceptions?
b) Promise implements exception delivery, which brings some benefits and ensures that the code is not blocked in actual projects. But if there are many asynchronous events, it is not easy to find out which asynchronous event caused the exception.
// Scenario description: Display price alarm information in CRM, including competition information. However, it takes a long time to obtain the competition information. In order to avoid slow queries, the backend split a record into two pieces and obtained them separately.
// Step one: Get price alarm information, in addition to competition information
function getPriceAlarmData() {
Return new Promise(function(resolve) {
Y.io(url, {
Method: 'get',
data: params,
on: function() {
Success: function(id, data) {
resolve(alarmData);
}
}
});
});
}
// After getting the alarm information, get the competition information
getPriceAlarmData().then(function(data) {
//Data rendering, except for competition information
render(data);
Return new Promise(function(resolve) {
Y.io(url, {
Method: 'get',
data: {alarmList: data},
on: function() {
Success: function(id, compData) {
resolve(compData);
}
}
});
});
}) // After obtaining all the data, render the competition information
.then(function(data) {
// Render competition information
render(data)
}, function(err) {
//Exception handling
console.log(err);
});
You can convert the above code into the following:
try{
// Get alarm information other than competition
var alarmData = alarmDataExceptCompare();
render(alarmData);
// Query competition information based on alarm information
var compareData = getCompareInfo(alarmData);
render(compareData);
} catche(err) {
console.log(err.message);
}
In the above example, exception handling is placed at the end, so that when an exception occurs in a certain link, we cannot accurately know which event caused it.
2.2 Problems with jQuery.Deferred
Asynchronous operations are also implemented in jQuery, but the implementation does not comply with the promise/A specification, mainly in the following aspects:
a. Number of parameters: Standard Promise can only accept one parameter, while jQuery can pass multiple parameters
function asyncInJQuery() {
var d = new $.Deferred();
setTimeout(function() {
d.resolve(1, 2);
}, 100);
Return d.promise()
}
asyncInJQuery().then(function(val1, val2) {
console.log('output: ', val1, val2);
});
// output: 1 2
b. Handling exceptions in result processing
function asyncInPromise() {
Return new Promise(function(resolve) {
setTimeout(function() {
var jsonStr = '{"name": "mt}';
resolve(jsonStr);
}, 100);
});
}
asyncInPromise().then(function(val) {
var d = JSON.parse(val);
console.log(d.name);
}).then(null, function(err) {
console.log('show error: ' err.message);
});
// show error: Unexpected end of input
function asyncInJQuery() {
var d = new $.Deferred();
setTimeout(function() {
var jsonStr = '{"name": "mt}';
d.resolve(jsonStr);
}, 100);
Return d.promise()
}
asyncInJQuery().then(function(val) {
var d = JSON.parse(val);
console.log(d.name);
}).then(function(v) {
console.log('success: ', v.name);
}, function(err){
console.log('show error: ' err.message);
});
//Uncaught SyntaxError: Unexpected end of input
It can be seen from this that Promise performs result processing on the callback function and can capture exceptions during the execution of the callback function, but jQuery.Deferred cannot.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AMWhether to choose Python or JavaScript depends on the project type: 1) Choose Python for data science and automation tasks; 2) Choose JavaScript for front-end and full-stack development. Python is favored for its powerful library in data processing and automation, while JavaScript is indispensable for its advantages in web interaction and full-stack development.
 Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMPython and JavaScript each have their own advantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1. Python is easy to learn, with concise syntax, suitable for data science and back-end development, but has a slow execution speed. 2. JavaScript is everywhere in front-end development and has strong asynchronous programming capabilities. Node.js makes it suitable for full-stack development, but the syntax may be complex and error-prone.
 JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AMJavaScriptisnotbuiltonCorC ;it'saninterpretedlanguagethatrunsonenginesoftenwritteninC .1)JavaScriptwasdesignedasalightweight,interpretedlanguageforwebbrowsers.2)EnginesevolvedfromsimpleinterpreterstoJITcompilers,typicallyinC ,improvingperformance.
 JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript can be used for front-end and back-end development. The front-end enhances the user experience through DOM operations, and the back-end handles server tasks through Node.js. 1. Front-end example: Change the content of the web page text. 2. Backend example: Create a Node.js server.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AMChoosing Python or JavaScript should be based on career development, learning curve and ecosystem: 1) Career development: Python is suitable for data science and back-end development, while JavaScript is suitable for front-end and full-stack development. 2) Learning curve: Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners; JavaScript syntax is flexible. 3) Ecosystem: Python has rich scientific computing libraries, and JavaScript has a powerful front-end framework.
 JavaScript Frameworks: Powering Modern Web DevelopmentMay 02, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JavaScript Frameworks: Powering Modern Web DevelopmentMay 02, 2025 am 12:04 AMThe power of the JavaScript framework lies in simplifying development, improving user experience and application performance. When choosing a framework, consider: 1. Project size and complexity, 2. Team experience, 3. Ecosystem and community support.
 The Relationship Between JavaScript, C , and BrowsersMay 01, 2025 am 12:06 AM
The Relationship Between JavaScript, C , and BrowsersMay 01, 2025 am 12:06 AMIntroduction I know you may find it strange, what exactly does JavaScript, C and browser have to do? They seem to be unrelated, but in fact, they play a very important role in modern web development. Today we will discuss the close connection between these three. Through this article, you will learn how JavaScript runs in the browser, the role of C in the browser engine, and how they work together to drive rendering and interaction of web pages. We all know the relationship between JavaScript and browser. JavaScript is the core language of front-end development. It runs directly in the browser, making web pages vivid and interesting. Have you ever wondered why JavaScr
 Node.js Streams with TypeScriptApr 30, 2025 am 08:22 AM
Node.js Streams with TypeScriptApr 30, 2025 am 08:22 AMNode.js excels at efficient I/O, largely thanks to streams. Streams process data incrementally, avoiding memory overload—ideal for large files, network tasks, and real-time applications. Combining streams with TypeScript's type safety creates a powe


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.






